Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > The minimum energy necessary to permit a reac...
Start Learning for Free
The minimum energy necessary to permit a reaction?
Most Upvoted Answer
The minimum energy necessary to permit a reaction?
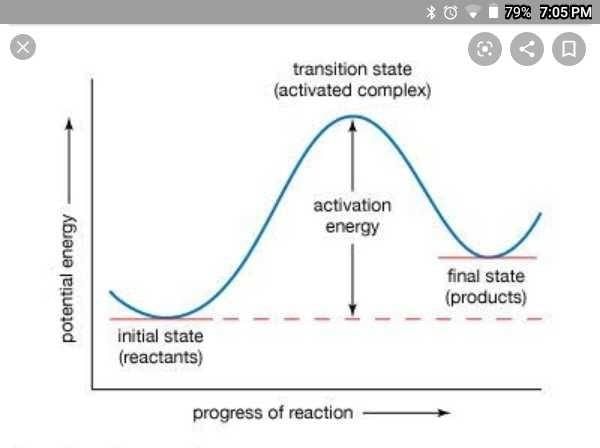
Community Answer
The minimum energy necessary to permit a reaction?
Activation Energy:
Activation energy is the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction. It is often denoted as Ea. In order for a reaction to occur, molecules must collide with enough energy to break the existing bonds and form new ones. The activation energy barrier prevents reactions from happening spontaneously and ensures that only reactions with enough energy input will proceed.
Factors affecting Activation Energy:
- Nature of reactants: Different reactants have different activation energy requirements based on their chemical properties. For example, reactions involving large, complex molecules often have higher activation energies compared to reactions with smaller, simpler molecules.
- Temperature: Increasing the temperature generally increases the kinetic energy of molecules, leading to more frequent and energetic collisions. This can lower the activation energy barrier and speed up the reaction.
- Catalysts: Catalysts are substances that lower the activation energy of a reaction by providing an alternative reaction pathway. This allows the reaction to occur more easily and quickly.
Importance of Activation Energy:
Understanding activation energy is crucial in designing and optimizing chemical reactions. By knowing the activation energy of a reaction, scientists can control the rate of the reaction, select appropriate reaction conditions, and develop efficient catalysts. This knowledge is essential in various fields such as drug development, materials science, and environmental chemistry.
In conclusion, activation energy plays a vital role in determining whether a reaction will occur and how quickly it will proceed. By studying and manipulating activation energy, scientists can enhance the efficiency and selectivity of chemical reactions for various applications.
Activation energy is the minimum amount of energy required to start a chemical reaction. It is often denoted as Ea. In order for a reaction to occur, molecules must collide with enough energy to break the existing bonds and form new ones. The activation energy barrier prevents reactions from happening spontaneously and ensures that only reactions with enough energy input will proceed.
Factors affecting Activation Energy:
- Nature of reactants: Different reactants have different activation energy requirements based on their chemical properties. For example, reactions involving large, complex molecules often have higher activation energies compared to reactions with smaller, simpler molecules.
- Temperature: Increasing the temperature generally increases the kinetic energy of molecules, leading to more frequent and energetic collisions. This can lower the activation energy barrier and speed up the reaction.
- Catalysts: Catalysts are substances that lower the activation energy of a reaction by providing an alternative reaction pathway. This allows the reaction to occur more easily and quickly.
Importance of Activation Energy:
Understanding activation energy is crucial in designing and optimizing chemical reactions. By knowing the activation energy of a reaction, scientists can control the rate of the reaction, select appropriate reaction conditions, and develop efficient catalysts. This knowledge is essential in various fields such as drug development, materials science, and environmental chemistry.
In conclusion, activation energy plays a vital role in determining whether a reaction will occur and how quickly it will proceed. By studying and manipulating activation energy, scientists can enhance the efficiency and selectivity of chemical reactions for various applications.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
The minimum energy necessary to permit a reaction?
Question Description
The minimum energy necessary to permit a reaction? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about The minimum energy necessary to permit a reaction? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The minimum energy necessary to permit a reaction?.
The minimum energy necessary to permit a reaction? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about The minimum energy necessary to permit a reaction? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The minimum energy necessary to permit a reaction?.
Solutions for The minimum energy necessary to permit a reaction? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The minimum energy necessary to permit a reaction? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The minimum energy necessary to permit a reaction?, a detailed solution for The minimum energy necessary to permit a reaction? has been provided alongside types of The minimum energy necessary to permit a reaction? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The minimum energy necessary to permit a reaction? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















