Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > who gave photoelectric effect Related: Photo...
Start Learning for Free
who gave photoelectric effect
?Most Upvoted Answer
who gave photoelectric effect Related: Photoelectric Effect and Wave ...
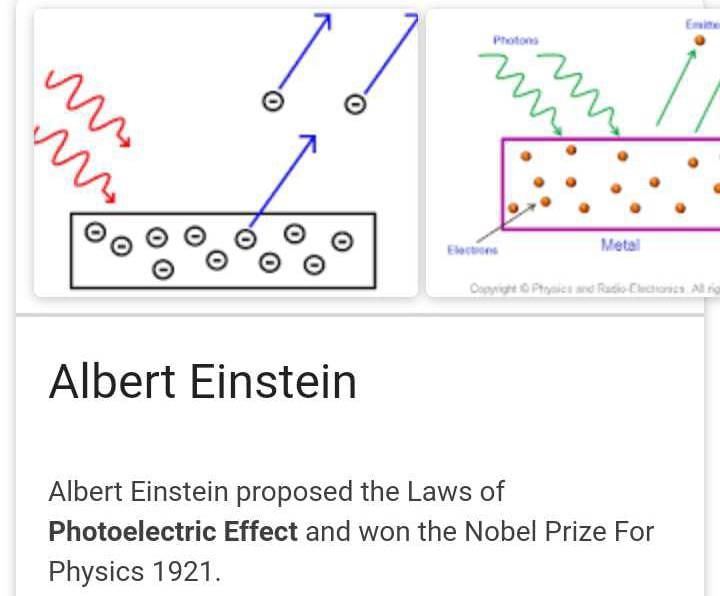
Community Answer
who gave photoelectric effect Related: Photoelectric Effect and Wave ...
The Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light:
The photoelectric effect is a phenomenon in which electrons are emitted from a material when it is exposed to light or electromagnetic radiation. It was first explained by Albert Einstein in 1905, and his explanation challenged the prevailing wave theory of light proposed by James Clerk Maxwell. In order to understand the relationship between the photoelectric effect and the wave theory of light, it is important to examine the key aspects of both theories.
Wave Theory of Light:
The wave theory of light, proposed by James Clerk Maxwell, states that light is an electromagnetic wave that propagates through space. According to this theory, light waves have a continuous range of wavelengths and frequencies. The intensity of light is determined by the amplitude of the wave, and the energy carried by the wave is spread out over the entire wavefront.
The Photoelectric Effect:
The photoelectric effect, on the other hand, is a phenomenon in which electrons are emitted from a material when it is exposed to light or electromagnetic radiation. This effect was observed and studied by various scientists before Einstein provided a theoretical explanation for it. The key observations of the photoelectric effect are as follows:
1. The emission of electrons occurs instantaneously when the material is exposed to light of a certain frequency, called the threshold frequency.
2. The number of electrons emitted is proportional to the intensity of the light.
3. The kinetic energy of the emitted electrons depends on the frequency of the light, not its intensity.
Einstein's Explanation:
Albert Einstein's explanation of the photoelectric effect was based on the quantum theory of light. He proposed that light consists of discrete packets of energy called photons. According to Einstein, when a photon of sufficient energy strikes a material, it can transfer its energy to an electron in the material, causing the electron to be emitted. The energy of a photon is given by the equation E = hf, where E is the energy, h is Planck's constant, and f is the frequency of the light.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the photoelectric effect and the wave theory of light are related in that they both pertain to the behavior of light. The photoelectric effect, however, cannot be explained solely by the wave theory of light, as it requires the concept of photons and the quantization of energy. Einstein's explanation of the photoelectric effect provided a crucial insight into the nature of light and laid the groundwork for the development of quantum mechanics.
The photoelectric effect is a phenomenon in which electrons are emitted from a material when it is exposed to light or electromagnetic radiation. It was first explained by Albert Einstein in 1905, and his explanation challenged the prevailing wave theory of light proposed by James Clerk Maxwell. In order to understand the relationship between the photoelectric effect and the wave theory of light, it is important to examine the key aspects of both theories.
Wave Theory of Light:
The wave theory of light, proposed by James Clerk Maxwell, states that light is an electromagnetic wave that propagates through space. According to this theory, light waves have a continuous range of wavelengths and frequencies. The intensity of light is determined by the amplitude of the wave, and the energy carried by the wave is spread out over the entire wavefront.
The Photoelectric Effect:
The photoelectric effect, on the other hand, is a phenomenon in which electrons are emitted from a material when it is exposed to light or electromagnetic radiation. This effect was observed and studied by various scientists before Einstein provided a theoretical explanation for it. The key observations of the photoelectric effect are as follows:
1. The emission of electrons occurs instantaneously when the material is exposed to light of a certain frequency, called the threshold frequency.
2. The number of electrons emitted is proportional to the intensity of the light.
3. The kinetic energy of the emitted electrons depends on the frequency of the light, not its intensity.
Einstein's Explanation:
Albert Einstein's explanation of the photoelectric effect was based on the quantum theory of light. He proposed that light consists of discrete packets of energy called photons. According to Einstein, when a photon of sufficient energy strikes a material, it can transfer its energy to an electron in the material, causing the electron to be emitted. The energy of a photon is given by the equation E = hf, where E is the energy, h is Planck's constant, and f is the frequency of the light.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, the photoelectric effect and the wave theory of light are related in that they both pertain to the behavior of light. The photoelectric effect, however, cannot be explained solely by the wave theory of light, as it requires the concept of photons and the quantization of energy. Einstein's explanation of the photoelectric effect provided a crucial insight into the nature of light and laid the groundwork for the development of quantum mechanics.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
who gave photoelectric effect Related: Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light?
Question Description
who gave photoelectric effect Related: Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about who gave photoelectric effect Related: Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for who gave photoelectric effect Related: Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light?.
who gave photoelectric effect Related: Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about who gave photoelectric effect Related: Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for who gave photoelectric effect Related: Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light?.
Solutions for who gave photoelectric effect Related: Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of who gave photoelectric effect Related: Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
who gave photoelectric effect Related: Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light?, a detailed solution for who gave photoelectric effect Related: Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light? has been provided alongside types of who gave photoelectric effect Related: Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice who gave photoelectric effect Related: Photoelectric Effect and Wave Theory of Light? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















