Commerce Exam > Commerce Questions > what do you mean by circular flow of income R...
Start Learning for Free
what do you mean by circular flow of income
?Most Upvoted Answer
what do you mean by circular flow of income Related: Important Questi...
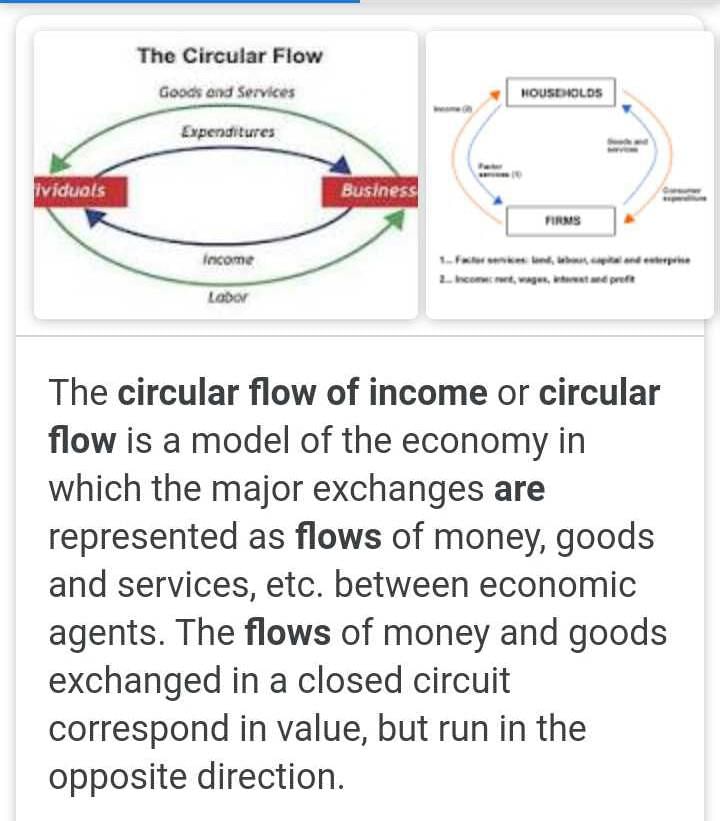
Community Answer
what do you mean by circular flow of income Related: Important Questi...
The circular flow of income refers to the continuous flow of money and goods and services between different sectors of the economy. It illustrates how income is generated, distributed, and spent within an economy. The concept is an important part of macroeconomics, as it helps us understand the overall functioning of an economy.
Components of the Circular Flow of Income:
The circular flow of income consists of four major components:
1. Households: Households are the primary consumers in an economy. They own factors of production, such as labor, land, and capital, and provide these factors to businesses in exchange for income.
2. Businesses: Businesses are the producers of goods and services. They hire factors of production from households, such as labor, and use them to produce goods and services. In return, they pay wages, rent, interest, and profits to households.
3. Government: The government collects taxes from households and businesses and provides public goods and services, such as infrastructure, education, and healthcare. It also redistributes income through various welfare programs.
4. Foreign Sector: The foreign sector includes foreign households, businesses, and governments. It represents the flow of imports and exports between countries, as well as international financial transactions.
The Flow of Income:
The circular flow of income can be explained through the following steps:
1. Households receive income: Households receive income through wages, salaries, rent, interest, and profits. This income is either spent on goods and services or saved.
2. Consumption and saving: Households spend their income on consumption goods and services, such as food, clothing, and entertainment. Some portion of income is also saved for future purposes.
3. Business revenue: Businesses receive revenue from the sale of goods and services produced. This revenue is used to pay for factors of production, such as wages, rent, and interest.
4. Government revenue and expenditure: The government collects taxes from households and businesses. It uses this revenue to provide public goods and services and redistribute income through welfare programs.
5. Imports and exports: The foreign sector engages in trade with the domestic sector. Imports represent goods and services purchased from foreign countries, while exports represent goods and services sold to foreign countries.
Significance of the Circular Flow of Income:
The circular flow of income is significant for several reasons:
1. Economic stability: Understanding the circular flow helps policymakers identify potential imbalances in the economy, such as a lack of demand or excess inflationary pressure. It allows them to implement appropriate measures to maintain economic stability.
2. Income distribution: The circular flow shows how income is distributed among different sectors of the economy. It helps policymakers assess the level of inequality and devise policies to promote more equitable income distribution.
3. Interdependence: The circular flow highlights the interdependence between different sectors of the economy. Changes in one sector can have ripple effects on other sectors, emphasizing the need for coordination and cooperation.
4. National income accounting: The circular flow serves as the basis for national income accounting, which measures the overall economic performance of a country. It helps calculate important macroeconomic indicators, such as GDP (Gross Domestic Product), national income, and savings.
In conclusion, the circular flow of income is a fundamental concept in macroeconomics that depicts the continuous flow of money and goods and services between households, businesses, government, and the foreign sector. It helps us understand how income is generated, distributed, and spent within an economy,
Components of the Circular Flow of Income:
The circular flow of income consists of four major components:
1. Households: Households are the primary consumers in an economy. They own factors of production, such as labor, land, and capital, and provide these factors to businesses in exchange for income.
2. Businesses: Businesses are the producers of goods and services. They hire factors of production from households, such as labor, and use them to produce goods and services. In return, they pay wages, rent, interest, and profits to households.
3. Government: The government collects taxes from households and businesses and provides public goods and services, such as infrastructure, education, and healthcare. It also redistributes income through various welfare programs.
4. Foreign Sector: The foreign sector includes foreign households, businesses, and governments. It represents the flow of imports and exports between countries, as well as international financial transactions.
The Flow of Income:
The circular flow of income can be explained through the following steps:
1. Households receive income: Households receive income through wages, salaries, rent, interest, and profits. This income is either spent on goods and services or saved.
2. Consumption and saving: Households spend their income on consumption goods and services, such as food, clothing, and entertainment. Some portion of income is also saved for future purposes.
3. Business revenue: Businesses receive revenue from the sale of goods and services produced. This revenue is used to pay for factors of production, such as wages, rent, and interest.
4. Government revenue and expenditure: The government collects taxes from households and businesses. It uses this revenue to provide public goods and services and redistribute income through welfare programs.
5. Imports and exports: The foreign sector engages in trade with the domestic sector. Imports represent goods and services purchased from foreign countries, while exports represent goods and services sold to foreign countries.
Significance of the Circular Flow of Income:
The circular flow of income is significant for several reasons:
1. Economic stability: Understanding the circular flow helps policymakers identify potential imbalances in the economy, such as a lack of demand or excess inflationary pressure. It allows them to implement appropriate measures to maintain economic stability.
2. Income distribution: The circular flow shows how income is distributed among different sectors of the economy. It helps policymakers assess the level of inequality and devise policies to promote more equitable income distribution.
3. Interdependence: The circular flow highlights the interdependence between different sectors of the economy. Changes in one sector can have ripple effects on other sectors, emphasizing the need for coordination and cooperation.
4. National income accounting: The circular flow serves as the basis for national income accounting, which measures the overall economic performance of a country. It helps calculate important macroeconomic indicators, such as GDP (Gross Domestic Product), national income, and savings.
In conclusion, the circular flow of income is a fundamental concept in macroeconomics that depicts the continuous flow of money and goods and services between households, businesses, government, and the foreign sector. It helps us understand how income is generated, distributed, and spent within an economy,
Attention Commerce Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Commerce study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Commerce.

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|
Similar Commerce Doubts
what do you mean by circular flow of income Related: Important Questions Bank, Macro Economics, class 12?
Question Description
what do you mean by circular flow of income Related: Important Questions Bank, Macro Economics, class 12? for Commerce 2024 is part of Commerce preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. Information about what do you mean by circular flow of income Related: Important Questions Bank, Macro Economics, class 12? covers all topics & solutions for Commerce 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what do you mean by circular flow of income Related: Important Questions Bank, Macro Economics, class 12?.
what do you mean by circular flow of income Related: Important Questions Bank, Macro Economics, class 12? for Commerce 2024 is part of Commerce preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Commerce exam syllabus. Information about what do you mean by circular flow of income Related: Important Questions Bank, Macro Economics, class 12? covers all topics & solutions for Commerce 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what do you mean by circular flow of income Related: Important Questions Bank, Macro Economics, class 12?.
Solutions for what do you mean by circular flow of income Related: Important Questions Bank, Macro Economics, class 12? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Commerce.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Commerce Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of what do you mean by circular flow of income Related: Important Questions Bank, Macro Economics, class 12? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
what do you mean by circular flow of income Related: Important Questions Bank, Macro Economics, class 12?, a detailed solution for what do you mean by circular flow of income Related: Important Questions Bank, Macro Economics, class 12? has been provided alongside types of what do you mean by circular flow of income Related: Important Questions Bank, Macro Economics, class 12? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice what do you mean by circular flow of income Related: Important Questions Bank, Macro Economics, class 12? tests, examples and also practice Commerce tests.

|
Explore Courses for Commerce exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























