IIT JAM Exam > IIT JAM Questions > (a) Draw the unit cell structure of NaCl. Cal...
Start Learning for Free
(a) Draw the unit cell structure of NaCl. Calculate the limiting radius ratio of any ionic solid having NaCl like structure.
(b) Give molecular formula and structure of the compound formed by reaction of Be(OH)2 with acetic acid.
(b) Give molecular formula and structure of the compound formed by reaction of Be(OH)2 with acetic acid.
Correct answer is '(a) Unit cell of NaCl Cl– = F.C.C arrangement Na+ = All octahedral voids.'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
(a) Draw the unit cell structure of NaCl. Calculate the limiting radiu...
(a) Unit cell of NaCl Cl– = F.C.C arrangement Na+ = All octahedral voids.
Limiting Radius Ratio:
Let a = Edge length
Let a = Edge length
= 1.414 -1 = 0.414
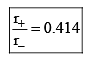
Most Upvoted Answer
(a) Draw the unit cell structure of NaCl. Calculate the limiting radiu...
Unit Cell Structure of NaCl:
The unit cell structure of NaCl is based on a face-centered cubic (FCC) arrangement. In this arrangement, the Cl- ions occupy the corner positions of the cube, while the Na+ ions are located at the center of each face of the cube. This arrangement is also known as the rock salt structure.
Calculating the Limiting Radius Ratio:
The limiting radius ratio is a measure of the relative sizes of the cation and anion in an ionic solid. It is given by the ratio of the radius of the cation (r+) to the radius of the anion (r-).
In the case of the NaCl structure, the Na+ ion is smaller than the Cl- ion. Let's assume the radius of the Na+ ion is "r" and the radius of the Cl- ion is "R".
Since the Na+ ions occupy the octahedral voids in the FCC arrangement, the distance between two Na+ ions along the body diagonal of the unit cell is equal to 4r (twice the length of the face diagonal). Similarly, the distance between two Cl- ions along the edge of the unit cell is equal to 2R.
Using the Pythagorean theorem, we can calculate the length of the body diagonal of the unit cell:
(diagonal)^2 = (edge)^2 + (face diagonal)^2
(4r)^2 = (2R)^2 + (edge)^2
16r^2 = 4R^2 + (2R)^2
16r^2 = 4R^2 + 4R^2
16r^2 = 8R^2
r^2 = 0.5R^2
Taking the square root of both sides, we get:
r = 0.707R
Therefore, the limiting radius ratio for NaCl-like structures is approximately 0.707.
Molecular Formula and Structure of Compound Formed:
When Be(OH)2 reacts with acetic acid (CH3COOH), it forms the compound Be(CH3COO)2, also known as beryllium acetate.
The molecular formula of beryllium acetate is Be(CH3COO)2. It consists of one beryllium ion (Be2+) and two acetate ions (CH3COO-). The acetate ion is a polyatomic ion formed by the combination of a methyl group (CH3-) and a carboxylate group (COO-).
The structure of beryllium acetate can be represented as follows:
O
//
Be - C - O
\\
O
In this structure, the beryllium ion is bonded to two acetate ions through ionic bonds. The beryllium ion has a linear geometry, while the acetate ions have a trigonal planar geometry.
It is important to note that beryllium compounds are highly toxic, and proper safety precautions should be taken when handling them.
The unit cell structure of NaCl is based on a face-centered cubic (FCC) arrangement. In this arrangement, the Cl- ions occupy the corner positions of the cube, while the Na+ ions are located at the center of each face of the cube. This arrangement is also known as the rock salt structure.
Calculating the Limiting Radius Ratio:
The limiting radius ratio is a measure of the relative sizes of the cation and anion in an ionic solid. It is given by the ratio of the radius of the cation (r+) to the radius of the anion (r-).
In the case of the NaCl structure, the Na+ ion is smaller than the Cl- ion. Let's assume the radius of the Na+ ion is "r" and the radius of the Cl- ion is "R".
Since the Na+ ions occupy the octahedral voids in the FCC arrangement, the distance between two Na+ ions along the body diagonal of the unit cell is equal to 4r (twice the length of the face diagonal). Similarly, the distance between two Cl- ions along the edge of the unit cell is equal to 2R.
Using the Pythagorean theorem, we can calculate the length of the body diagonal of the unit cell:
(diagonal)^2 = (edge)^2 + (face diagonal)^2
(4r)^2 = (2R)^2 + (edge)^2
16r^2 = 4R^2 + (2R)^2
16r^2 = 4R^2 + 4R^2
16r^2 = 8R^2
r^2 = 0.5R^2
Taking the square root of both sides, we get:
r = 0.707R
Therefore, the limiting radius ratio for NaCl-like structures is approximately 0.707.
Molecular Formula and Structure of Compound Formed:
When Be(OH)2 reacts with acetic acid (CH3COOH), it forms the compound Be(CH3COO)2, also known as beryllium acetate.
The molecular formula of beryllium acetate is Be(CH3COO)2. It consists of one beryllium ion (Be2+) and two acetate ions (CH3COO-). The acetate ion is a polyatomic ion formed by the combination of a methyl group (CH3-) and a carboxylate group (COO-).
The structure of beryllium acetate can be represented as follows:
O
//
Be - C - O
\\
O
In this structure, the beryllium ion is bonded to two acetate ions through ionic bonds. The beryllium ion has a linear geometry, while the acetate ions have a trigonal planar geometry.
It is important to note that beryllium compounds are highly toxic, and proper safety precautions should be taken when handling them.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Similar IIT JAM Doubts
(a) Draw the unit cell structure of NaCl. Calculate the limiting radius ratio of any ionic solid having NaCl like structure.(b) Give molecular formula and structure of the compound formed by reaction of Be(OH)2 with acetic acid.Correct answer is '(a) Unit cell of NaCl Cl– = F.C.C arrangement Na+ = All octahedral voids.'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
(a) Draw the unit cell structure of NaCl. Calculate the limiting radius ratio of any ionic solid having NaCl like structure.(b) Give molecular formula and structure of the compound formed by reaction of Be(OH)2 with acetic acid.Correct answer is '(a) Unit cell of NaCl Cl– = F.C.C arrangement Na+ = All octahedral voids.'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about (a) Draw the unit cell structure of NaCl. Calculate the limiting radius ratio of any ionic solid having NaCl like structure.(b) Give molecular formula and structure of the compound formed by reaction of Be(OH)2 with acetic acid.Correct answer is '(a) Unit cell of NaCl Cl– = F.C.C arrangement Na+ = All octahedral voids.'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for (a) Draw the unit cell structure of NaCl. Calculate the limiting radius ratio of any ionic solid having NaCl like structure.(b) Give molecular formula and structure of the compound formed by reaction of Be(OH)2 with acetic acid.Correct answer is '(a) Unit cell of NaCl Cl– = F.C.C arrangement Na+ = All octahedral voids.'. Can you explain this answer?.
(a) Draw the unit cell structure of NaCl. Calculate the limiting radius ratio of any ionic solid having NaCl like structure.(b) Give molecular formula and structure of the compound formed by reaction of Be(OH)2 with acetic acid.Correct answer is '(a) Unit cell of NaCl Cl– = F.C.C arrangement Na+ = All octahedral voids.'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about (a) Draw the unit cell structure of NaCl. Calculate the limiting radius ratio of any ionic solid having NaCl like structure.(b) Give molecular formula and structure of the compound formed by reaction of Be(OH)2 with acetic acid.Correct answer is '(a) Unit cell of NaCl Cl– = F.C.C arrangement Na+ = All octahedral voids.'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for (a) Draw the unit cell structure of NaCl. Calculate the limiting radius ratio of any ionic solid having NaCl like structure.(b) Give molecular formula and structure of the compound formed by reaction of Be(OH)2 with acetic acid.Correct answer is '(a) Unit cell of NaCl Cl– = F.C.C arrangement Na+ = All octahedral voids.'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for (a) Draw the unit cell structure of NaCl. Calculate the limiting radius ratio of any ionic solid having NaCl like structure.(b) Give molecular formula and structure of the compound formed by reaction of Be(OH)2 with acetic acid.Correct answer is '(a) Unit cell of NaCl Cl– = F.C.C arrangement Na+ = All octahedral voids.'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for IIT JAM.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of (a) Draw the unit cell structure of NaCl. Calculate the limiting radius ratio of any ionic solid having NaCl like structure.(b) Give molecular formula and structure of the compound formed by reaction of Be(OH)2 with acetic acid.Correct answer is '(a) Unit cell of NaCl Cl– = F.C.C arrangement Na+ = All octahedral voids.'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
(a) Draw the unit cell structure of NaCl. Calculate the limiting radius ratio of any ionic solid having NaCl like structure.(b) Give molecular formula and structure of the compound formed by reaction of Be(OH)2 with acetic acid.Correct answer is '(a) Unit cell of NaCl Cl– = F.C.C arrangement Na+ = All octahedral voids.'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for (a) Draw the unit cell structure of NaCl. Calculate the limiting radius ratio of any ionic solid having NaCl like structure.(b) Give molecular formula and structure of the compound formed by reaction of Be(OH)2 with acetic acid.Correct answer is '(a) Unit cell of NaCl Cl– = F.C.C arrangement Na+ = All octahedral voids.'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of (a) Draw the unit cell structure of NaCl. Calculate the limiting radius ratio of any ionic solid having NaCl like structure.(b) Give molecular formula and structure of the compound formed by reaction of Be(OH)2 with acetic acid.Correct answer is '(a) Unit cell of NaCl Cl– = F.C.C arrangement Na+ = All octahedral voids.'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice (a) Draw the unit cell structure of NaCl. Calculate the limiting radius ratio of any ionic solid having NaCl like structure.(b) Give molecular formula and structure of the compound formed by reaction of Be(OH)2 with acetic acid.Correct answer is '(a) Unit cell of NaCl Cl– = F.C.C arrangement Na+ = All octahedral voids.'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice IIT JAM tests.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















