Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > Differentiate between the phenomenon of adsor...
Start Learning for Free
Differentiate between the phenomenon of adsorption and absorption. Give one example for each.?
Most Upvoted Answer
Differentiate between the phenomenon of adsorption and absorption. Giv...
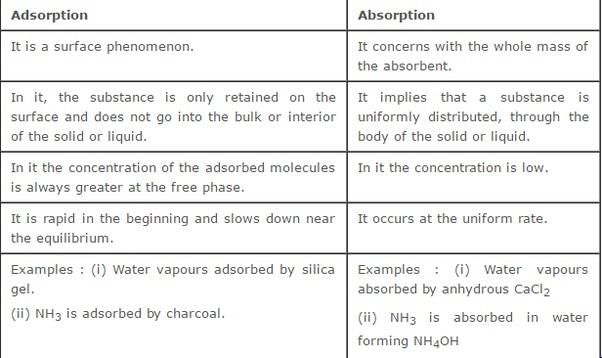
Adsorption:
Adsorption is the process in which atoms, ions, or molecules from a substance (gas, liquid, or dissolved solid) adhere to a surface of a solid or liquid. The substance that gets adsorbed is called the adsorbate, and the surface to which it adheres is called the adsorbent. The phenomenon of adsorption occurs due to the attractive forces between the adsorbate and the adsorbent surface.
Example of Adsorption:
An example of adsorption is the use of activated charcoal to remove impurities from water or air. Activated charcoal has a highly porous structure with a large surface area, which allows it to effectively adsorb contaminants. When water or air passes through the activated charcoal, the contaminants adhere to its surface through adsorption, resulting in cleaner water or air.
Absorption:
Absorption is the process in which atoms, ions, or molecules penetrate and distribute evenly within the volume of a solid, liquid, or gas. Unlike adsorption, absorption involves the uptake of substances into the bulk of another substance rather than just adhering to its surface. Absorption occurs due to the interaction between the absorbing substance and the substance being absorbed.
Example of Absorption:
An example of absorption is the process of plants absorbing water and nutrients from the soil. The roots of plants have tiny root hairs that increase their surface area, allowing for more efficient absorption. As water and nutrients in the soil come into contact with the root hairs, they are absorbed and distributed throughout the plant's tissues, providing essential nourishment for growth and survival.
Comparison:
1. Surface Interaction: Adsorption occurs on the surface of the adsorbent, while absorption involves the penetration and distribution within the bulk of the absorbing substance.
2. Nature of Interaction: Adsorption is a surface phenomenon and involves weak van der Waals forces or electrostatic interactions between the adsorbate and adsorbent. Absorption involves stronger chemical or physical interactions between the substances being absorbed and the absorbing substance.
3. Depth of Penetration: Adsorption occurs only on the surface of the adsorbent, while absorption involves the uptake of substances into the bulk of the absorbing substance.
4. Reversibility: Adsorption is often reversible, meaning the adsorbate can be desorbed from the adsorbent surface. Absorption is generally irreversible, as the absorbed substances become part of the absorbing substance.
In summary, adsorption and absorption are two distinct processes. Adsorption occurs on the surface of a material, while absorption involves the penetration and distribution within the bulk of a substance. Understanding the differences between these phenomena is essential in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science.
Adsorption is the process in which atoms, ions, or molecules from a substance (gas, liquid, or dissolved solid) adhere to a surface of a solid or liquid. The substance that gets adsorbed is called the adsorbate, and the surface to which it adheres is called the adsorbent. The phenomenon of adsorption occurs due to the attractive forces between the adsorbate and the adsorbent surface.
Example of Adsorption:
An example of adsorption is the use of activated charcoal to remove impurities from water or air. Activated charcoal has a highly porous structure with a large surface area, which allows it to effectively adsorb contaminants. When water or air passes through the activated charcoal, the contaminants adhere to its surface through adsorption, resulting in cleaner water or air.
Absorption:
Absorption is the process in which atoms, ions, or molecules penetrate and distribute evenly within the volume of a solid, liquid, or gas. Unlike adsorption, absorption involves the uptake of substances into the bulk of another substance rather than just adhering to its surface. Absorption occurs due to the interaction between the absorbing substance and the substance being absorbed.
Example of Absorption:
An example of absorption is the process of plants absorbing water and nutrients from the soil. The roots of plants have tiny root hairs that increase their surface area, allowing for more efficient absorption. As water and nutrients in the soil come into contact with the root hairs, they are absorbed and distributed throughout the plant's tissues, providing essential nourishment for growth and survival.
Comparison:
1. Surface Interaction: Adsorption occurs on the surface of the adsorbent, while absorption involves the penetration and distribution within the bulk of the absorbing substance.
2. Nature of Interaction: Adsorption is a surface phenomenon and involves weak van der Waals forces or electrostatic interactions between the adsorbate and adsorbent. Absorption involves stronger chemical or physical interactions between the substances being absorbed and the absorbing substance.
3. Depth of Penetration: Adsorption occurs only on the surface of the adsorbent, while absorption involves the uptake of substances into the bulk of the absorbing substance.
4. Reversibility: Adsorption is often reversible, meaning the adsorbate can be desorbed from the adsorbent surface. Absorption is generally irreversible, as the absorbed substances become part of the absorbing substance.
In summary, adsorption and absorption are two distinct processes. Adsorption occurs on the surface of a material, while absorption involves the penetration and distribution within the bulk of a substance. Understanding the differences between these phenomena is essential in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and environmental science.
Community Answer
Differentiate between the phenomenon of adsorption and absorption. Giv...
Attention Class 11 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 11 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 11.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Similar Class 11 Doubts
Differentiate between the phenomenon of adsorption and absorption. Give one example for each.?
Question Description
Differentiate between the phenomenon of adsorption and absorption. Give one example for each.? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Differentiate between the phenomenon of adsorption and absorption. Give one example for each.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Differentiate between the phenomenon of adsorption and absorption. Give one example for each.?.
Differentiate between the phenomenon of adsorption and absorption. Give one example for each.? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Differentiate between the phenomenon of adsorption and absorption. Give one example for each.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Differentiate between the phenomenon of adsorption and absorption. Give one example for each.?.
Solutions for Differentiate between the phenomenon of adsorption and absorption. Give one example for each.? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Differentiate between the phenomenon of adsorption and absorption. Give one example for each.? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Differentiate between the phenomenon of adsorption and absorption. Give one example for each.?, a detailed solution for Differentiate between the phenomenon of adsorption and absorption. Give one example for each.? has been provided alongside types of Differentiate between the phenomenon of adsorption and absorption. Give one example for each.? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Differentiate between the phenomenon of adsorption and absorption. Give one example for each.? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























