Defence Exam > Defence Questions > If the length of the Equator is about 40000 k...
Start Learning for Free
If the length of the Equator is about 40000 km and the velocity of rotation is about 1700 km per hour, what would be the velocity of rotation at the Pole?
- a)Zero
- b)850 km/hr
- c)1700 km/hr
- d)3400 km/hr
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
If the length of the Equator is about 40000 km and the velocity of rot...
Using Ve = ReW 1700
km/h=20000 xW
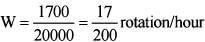
Velocity of rotation of pole,
Vp=Rp
Rp = 0 ⇒VP = 0
km/h=20000 xW
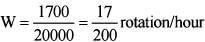
Velocity of rotation of pole,
Vp=Rp
Rp = 0 ⇒VP = 0
Most Upvoted Answer
If the length of the Equator is about 40000 km and the velocity of rot...
Velocity of Rotation at the Pole is Zero (a)
Explanation:
The rotation of the Earth causes the Equator to have a greater linear velocity compared to the poles. This is because the Earth rotates on its axis, completing one full rotation in approximately 24 hours.
1. Understanding the Equator and the Poles:
- The Equator is an imaginary line that divides the Earth into the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. It is the widest circumference of the Earth.
- The Poles are the points on the Earth's surface where the axis of rotation intersects the surface.
- The Earth rotates on its axis, which is an imaginary line passing through the North Pole and the South Pole.
2. Linear Velocity at the Equator:
- The length of the Earth's Equator is approximately 40,000 km.
- To calculate the linear velocity at the Equator, we need to divide the distance traveled by the time taken.
- Assuming the Earth completes one full rotation in 24 hours, the time taken for one rotation is 24 hours or 24 x 60 x 60 = 86,400 seconds.
- Therefore, the linear velocity at the Equator is 40,000 km / 86,400 s = 0.463 km/s or 1,674.24 km/hr.
3. Linear Velocity at the Poles:
- The Poles are located at the axis of rotation, which means they do not move in a circular path like the Equator.
- Since the Poles are stationary with respect to the rotation, their linear velocity is zero.
- This is because the distance traveled by the Poles in one rotation is zero, as they remain at the same point.
4. Conclusion:
- The velocity of rotation at the Pole is zero (a).
- This is because the Poles do not move in a circular path like the Equator, and they are stationary with respect to the Earth's rotation.
Explanation:
The rotation of the Earth causes the Equator to have a greater linear velocity compared to the poles. This is because the Earth rotates on its axis, completing one full rotation in approximately 24 hours.
1. Understanding the Equator and the Poles:
- The Equator is an imaginary line that divides the Earth into the Northern Hemisphere and the Southern Hemisphere. It is the widest circumference of the Earth.
- The Poles are the points on the Earth's surface where the axis of rotation intersects the surface.
- The Earth rotates on its axis, which is an imaginary line passing through the North Pole and the South Pole.
2. Linear Velocity at the Equator:
- The length of the Earth's Equator is approximately 40,000 km.
- To calculate the linear velocity at the Equator, we need to divide the distance traveled by the time taken.
- Assuming the Earth completes one full rotation in 24 hours, the time taken for one rotation is 24 hours or 24 x 60 x 60 = 86,400 seconds.
- Therefore, the linear velocity at the Equator is 40,000 km / 86,400 s = 0.463 km/s or 1,674.24 km/hr.
3. Linear Velocity at the Poles:
- The Poles are located at the axis of rotation, which means they do not move in a circular path like the Equator.
- Since the Poles are stationary with respect to the rotation, their linear velocity is zero.
- This is because the distance traveled by the Poles in one rotation is zero, as they remain at the same point.
4. Conclusion:
- The velocity of rotation at the Pole is zero (a).
- This is because the Poles do not move in a circular path like the Equator, and they are stationary with respect to the Earth's rotation.

|
Explore Courses for Defence exam
|

|
Similar Defence Doubts
If the length of the Equator is about 40000 km and the velocity of rotation is about 1700 km per hour, what would be the velocity of rotation at the Pole?a)Zerob)850 km/hrc)1700 km/hrd)3400 km/hrCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
If the length of the Equator is about 40000 km and the velocity of rotation is about 1700 km per hour, what would be the velocity of rotation at the Pole?a)Zerob)850 km/hrc)1700 km/hrd)3400 km/hrCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Defence 2025 is part of Defence preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Defence exam syllabus. Information about If the length of the Equator is about 40000 km and the velocity of rotation is about 1700 km per hour, what would be the velocity of rotation at the Pole?a)Zerob)850 km/hrc)1700 km/hrd)3400 km/hrCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Defence 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If the length of the Equator is about 40000 km and the velocity of rotation is about 1700 km per hour, what would be the velocity of rotation at the Pole?a)Zerob)850 km/hrc)1700 km/hrd)3400 km/hrCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
If the length of the Equator is about 40000 km and the velocity of rotation is about 1700 km per hour, what would be the velocity of rotation at the Pole?a)Zerob)850 km/hrc)1700 km/hrd)3400 km/hrCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Defence 2025 is part of Defence preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Defence exam syllabus. Information about If the length of the Equator is about 40000 km and the velocity of rotation is about 1700 km per hour, what would be the velocity of rotation at the Pole?a)Zerob)850 km/hrc)1700 km/hrd)3400 km/hrCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Defence 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for If the length of the Equator is about 40000 km and the velocity of rotation is about 1700 km per hour, what would be the velocity of rotation at the Pole?a)Zerob)850 km/hrc)1700 km/hrd)3400 km/hrCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for If the length of the Equator is about 40000 km and the velocity of rotation is about 1700 km per hour, what would be the velocity of rotation at the Pole?a)Zerob)850 km/hrc)1700 km/hrd)3400 km/hrCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Defence.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Defence Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of If the length of the Equator is about 40000 km and the velocity of rotation is about 1700 km per hour, what would be the velocity of rotation at the Pole?a)Zerob)850 km/hrc)1700 km/hrd)3400 km/hrCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
If the length of the Equator is about 40000 km and the velocity of rotation is about 1700 km per hour, what would be the velocity of rotation at the Pole?a)Zerob)850 km/hrc)1700 km/hrd)3400 km/hrCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for If the length of the Equator is about 40000 km and the velocity of rotation is about 1700 km per hour, what would be the velocity of rotation at the Pole?a)Zerob)850 km/hrc)1700 km/hrd)3400 km/hrCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of If the length of the Equator is about 40000 km and the velocity of rotation is about 1700 km per hour, what would be the velocity of rotation at the Pole?a)Zerob)850 km/hrc)1700 km/hrd)3400 km/hrCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice If the length of the Equator is about 40000 km and the velocity of rotation is about 1700 km per hour, what would be the velocity of rotation at the Pole?a)Zerob)850 km/hrc)1700 km/hrd)3400 km/hrCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Defence tests.

|
Explore Courses for Defence exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















