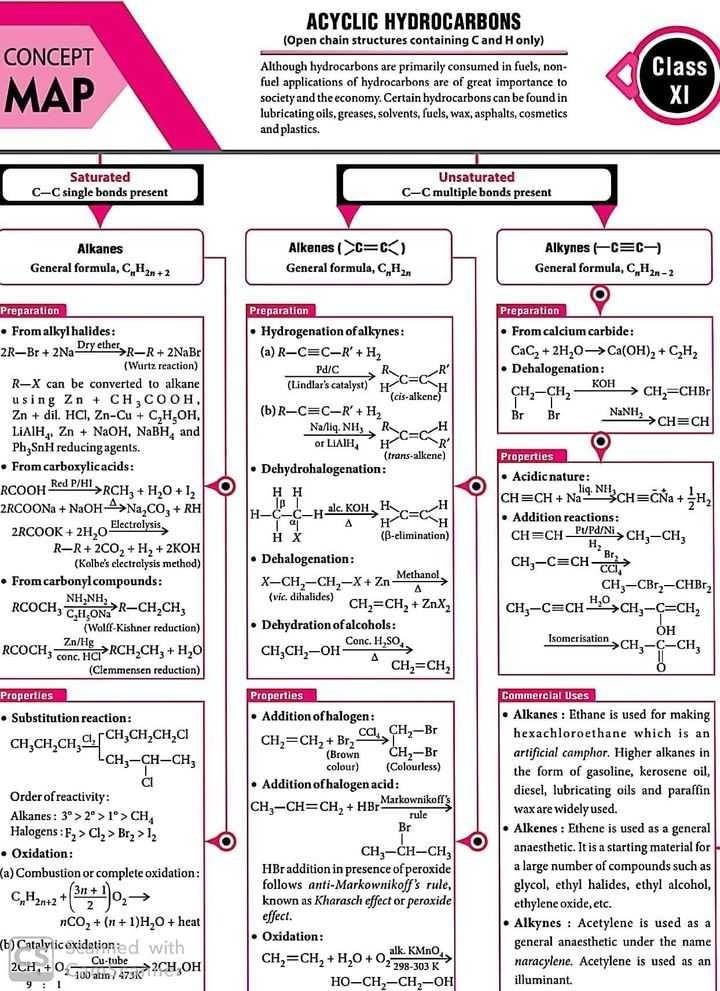
Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > Concept map for acyclic hydrocarbon ?
Start Learning for Free
Concept map for acyclic hydrocarbon ?
Community Answer
Concept map for acyclic hydrocarbon ?
Acyclic Hydrocarbon:
Acyclic hydrocarbons, also known as aliphatic hydrocarbons, are a class of organic compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms arranged in an open chain or a branched structure. These hydrocarbons do not have any cyclic or ring structures. They are the simplest form of hydrocarbons and serve as the building blocks for many other organic compounds.
Types of Acyclic Hydrocarbons:
There are two main types of acyclic hydrocarbons:
1. Alkanes:
- Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with single bonds between carbon atoms.
- They have the general formula CnH2n+2, where "n" represents the number of carbon atoms.
- Alkanes are relatively unreactive and are commonly used as fuels.
- Examples include methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), and butane (C4H10).
2. Alkenes:
- Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with at least one carbon-carbon double bond.
- They have the general formula CnH2n, where "n" represents the number of carbon atoms.
- Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes and undergo addition reactions.
- Examples include ethene (C2H4), propene (C3H6), and butene (C4H8).
Properties of Acyclic Hydrocarbons:
- Acyclic hydrocarbons are nonpolar due to the similar electronegativity of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
- They have low boiling points and melting points, as they are held together by relatively weak London dispersion forces.
- Acyclic hydrocarbons are generally insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar solvents such as benzene and ether.
- The physical properties of acyclic hydrocarbons depend on factors such as molecular size, shape, and branching.
Uses of Acyclic Hydrocarbons:
- Alkanes are widely used as fuels for heating, cooking, and transportation.
- Alkenes are essential in the production of various plastics, synthetic fibers, and rubber.
- Acyclic hydrocarbons are used as solvents in industrial processes.
- They serve as starting materials for the synthesis of numerous organic compounds.
In conclusion, acyclic hydrocarbons are organic compounds that lack cyclic structures. They include alkanes and alkenes, which have distinct properties and applications. Acyclic hydrocarbons are fundamental in the field of organic chemistry and find extensive use in various industries.
Acyclic hydrocarbons, also known as aliphatic hydrocarbons, are a class of organic compounds that contain only carbon and hydrogen atoms arranged in an open chain or a branched structure. These hydrocarbons do not have any cyclic or ring structures. They are the simplest form of hydrocarbons and serve as the building blocks for many other organic compounds.
Types of Acyclic Hydrocarbons:
There are two main types of acyclic hydrocarbons:
1. Alkanes:
- Alkanes are saturated hydrocarbons with single bonds between carbon atoms.
- They have the general formula CnH2n+2, where "n" represents the number of carbon atoms.
- Alkanes are relatively unreactive and are commonly used as fuels.
- Examples include methane (CH4), ethane (C2H6), propane (C3H8), and butane (C4H10).
2. Alkenes:
- Alkenes are unsaturated hydrocarbons with at least one carbon-carbon double bond.
- They have the general formula CnH2n, where "n" represents the number of carbon atoms.
- Alkenes are more reactive than alkanes and undergo addition reactions.
- Examples include ethene (C2H4), propene (C3H6), and butene (C4H8).
Properties of Acyclic Hydrocarbons:
- Acyclic hydrocarbons are nonpolar due to the similar electronegativity of carbon and hydrogen atoms.
- They have low boiling points and melting points, as they are held together by relatively weak London dispersion forces.
- Acyclic hydrocarbons are generally insoluble in water but soluble in nonpolar solvents such as benzene and ether.
- The physical properties of acyclic hydrocarbons depend on factors such as molecular size, shape, and branching.
Uses of Acyclic Hydrocarbons:
- Alkanes are widely used as fuels for heating, cooking, and transportation.
- Alkenes are essential in the production of various plastics, synthetic fibers, and rubber.
- Acyclic hydrocarbons are used as solvents in industrial processes.
- They serve as starting materials for the synthesis of numerous organic compounds.
In conclusion, acyclic hydrocarbons are organic compounds that lack cyclic structures. They include alkanes and alkenes, which have distinct properties and applications. Acyclic hydrocarbons are fundamental in the field of organic chemistry and find extensive use in various industries.
Attention Class 11 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 11 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 11.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Similar Class 11 Doubts
Concept map for acyclic hydrocarbon ?
Question Description
Concept map for acyclic hydrocarbon ? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Concept map for acyclic hydrocarbon ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Concept map for acyclic hydrocarbon ?.
Concept map for acyclic hydrocarbon ? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Concept map for acyclic hydrocarbon ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Concept map for acyclic hydrocarbon ?.
Solutions for Concept map for acyclic hydrocarbon ? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Concept map for acyclic hydrocarbon ? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Concept map for acyclic hydrocarbon ?, a detailed solution for Concept map for acyclic hydrocarbon ? has been provided alongside types of Concept map for acyclic hydrocarbon ? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Concept map for acyclic hydrocarbon ? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.