Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > Phenol and benzyl alcohol area)functional iso...
Start Learning for Free
Phenol and benzyl alcohol are
- a)functional isomers
- b)Homologous
- c)Position isomers
- d)None of these
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Phenol and benzyl alcohol area)functional isomersb)Homologousc)Positio...
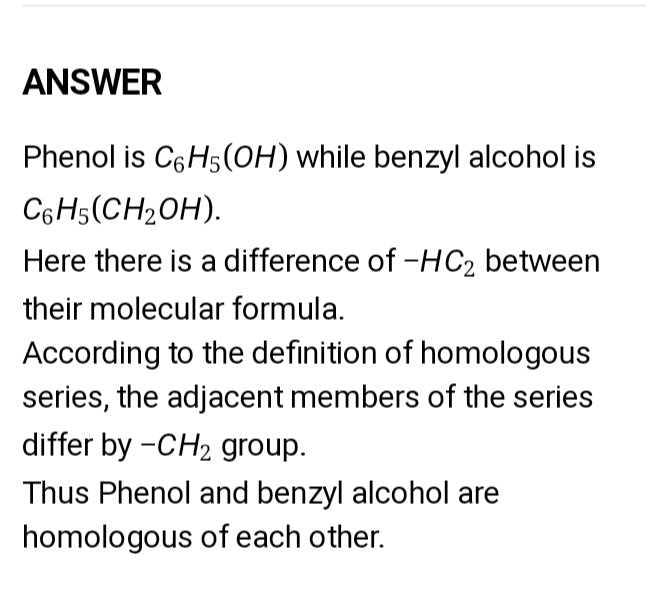
Phenol is C6H5(OH) while benzyl alcohol is C6H5(CH2OH).
Here there is a difference of −HC2 between their molecular formula.
According to the definition of homologous series, the adjacent members of the series differ by −CH2 group.
Thus, Phenol and benzyl alcohol are homologous of each other.
Here there is a difference of −HC2 between their molecular formula.
According to the definition of homologous series, the adjacent members of the series differ by −CH2 group.
Thus, Phenol and benzyl alcohol are homologous of each other.
Most Upvoted Answer
Phenol and benzyl alcohol area)functional isomersb)Homologousc)Positio...
Community Answer
Phenol and benzyl alcohol area)functional isomersb)Homologousc)Positio...
Phenol and benzyl alcohol are two different chemical compounds that have distinct chemical structures and properties. Let's analyze the given options one by one to understand why the correct answer is option 'D' (None of these).
a) Functional Isomers:
Functional isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the functional group present. In the case of phenol and benzyl alcohol, both compounds have the same functional group, which is an -OH group (hydroxyl group). Therefore, they cannot be considered functional isomers.
b) Homologous:
Homologous compounds are a series of organic compounds that have the same functional group and a similar chemical structure. They differ from each other by a common structural unit, such as a -CH2 group. Phenol and benzyl alcohol do not belong to the same homologous series as they have different structures and functional groups.
c) Position Isomers:
Position isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula and functional group but differ in the position of the functional group in the molecule. For example, in the case of butanol and isobutanol, both compounds have the same molecular formula C4H10O and the same functional group -OH, but the position of the -OH group is different in each compound. However, in the case of phenol and benzyl alcohol, the functional group -OH is attached to different parts of the molecule. In phenol, the -OH group is directly attached to the benzene ring, whereas in benzyl alcohol, the -OH group is attached to a methyl (-CH3) group attached to the benzene ring. Hence, they cannot be considered position isomers.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' (None of these) as neither functional isomers, homologous compounds, nor position isomers accurately describe the relationship between phenol and benzyl alcohol.
a) Functional Isomers:
Functional isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula but differ in the functional group present. In the case of phenol and benzyl alcohol, both compounds have the same functional group, which is an -OH group (hydroxyl group). Therefore, they cannot be considered functional isomers.
b) Homologous:
Homologous compounds are a series of organic compounds that have the same functional group and a similar chemical structure. They differ from each other by a common structural unit, such as a -CH2 group. Phenol and benzyl alcohol do not belong to the same homologous series as they have different structures and functional groups.
c) Position Isomers:
Position isomers are compounds that have the same molecular formula and functional group but differ in the position of the functional group in the molecule. For example, in the case of butanol and isobutanol, both compounds have the same molecular formula C4H10O and the same functional group -OH, but the position of the -OH group is different in each compound. However, in the case of phenol and benzyl alcohol, the functional group -OH is attached to different parts of the molecule. In phenol, the -OH group is directly attached to the benzene ring, whereas in benzyl alcohol, the -OH group is attached to a methyl (-CH3) group attached to the benzene ring. Hence, they cannot be considered position isomers.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'D' (None of these) as neither functional isomers, homologous compounds, nor position isomers accurately describe the relationship between phenol and benzyl alcohol.
Attention Class 11 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 11 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 11.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Similar Class 11 Doubts
Phenol and benzyl alcohol area)functional isomersb)Homologousc)Position isomersd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Phenol and benzyl alcohol area)functional isomersb)Homologousc)Position isomersd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Phenol and benzyl alcohol area)functional isomersb)Homologousc)Position isomersd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Phenol and benzyl alcohol area)functional isomersb)Homologousc)Position isomersd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Phenol and benzyl alcohol area)functional isomersb)Homologousc)Position isomersd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Phenol and benzyl alcohol area)functional isomersb)Homologousc)Position isomersd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Phenol and benzyl alcohol area)functional isomersb)Homologousc)Position isomersd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Phenol and benzyl alcohol area)functional isomersb)Homologousc)Position isomersd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Phenol and benzyl alcohol area)functional isomersb)Homologousc)Position isomersd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Phenol and benzyl alcohol area)functional isomersb)Homologousc)Position isomersd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Phenol and benzyl alcohol area)functional isomersb)Homologousc)Position isomersd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Phenol and benzyl alcohol area)functional isomersb)Homologousc)Position isomersd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Phenol and benzyl alcohol area)functional isomersb)Homologousc)Position isomersd)None of theseCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























