Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Brain map for ray optics ?
Start Learning for Free
Brain map for ray optics ?
Most Upvoted Answer
Brain map for ray optics ?
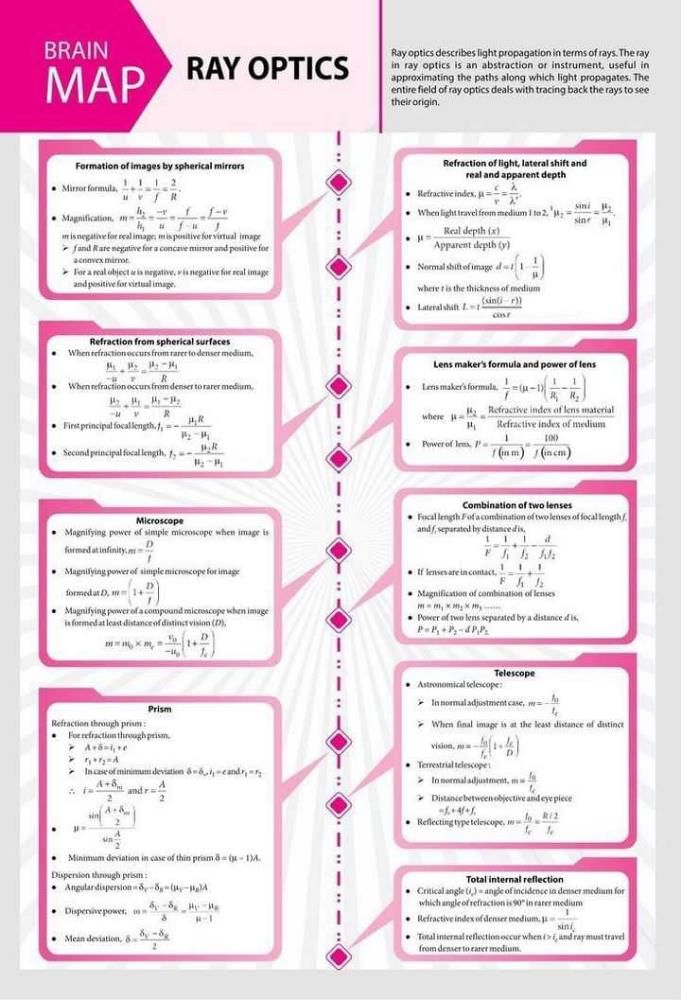
Community Answer
Brain map for ray optics ?
Brain Map for Ray Optics
Introduction:
Ray optics is the branch of optics that deals with the study of light in terms of rays. It is concerned with the behavior of light when it passes through different media such as air, water, glass, etc.
Key Concepts:
There are several key concepts that are important to understand in ray optics. These include:
1. Reflection: This is the process by which light bounces off a surface. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
2. Refraction: This is the process by which light changes direction as it passes through a medium of different refractive index. The amount of refraction depends on the angle of incidence and the refractive indices of the two media.
3. Snell's Law: This law describes the relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for a given pair of media. It is given by n1 sin(theta1) = n2 sin(theta2), where n1 and n2 are the refractive indices of the two media and theta1 and theta2 are the angles of incidence and refraction, respectively.
4. Total Internal Reflection: This occurs when light is incident on a boundary between two media and the angle of incidence is greater than a certain critical angle. The light is then reflected back into the first medium rather than being refracted into the second medium.
5. Lenses: These are optical devices that are used to focus or diverge light. There are two main types of lenses: convex (converging) and concave (diverging).
6. Mirrors: These are optical devices that reflect light. There are two main types of mirrors: plane mirrors and curved mirrors (such as concave and convex mirrors).
7. Optical Instruments: There are several optical instruments that make use of the principles of ray optics, including microscopes, telescopes, and cameras.
Applications:
Ray optics has many practical applications, including:
1. Designing and manufacturing lenses and mirrors for use in optical instruments.
2. Understanding how light behaves in the atmosphere, which is important for weather forecasting and climate modeling.
3. Developing optical fibers for use in telecommunications.
4. Designing and optimizing solar panels to maximize the amount of light they can capture.
5. Developing optical sensors for use in medical imaging and other applications.
Conclusion:
Ray optics is an important branch of optics that deals with the behavior of light in terms of rays. Understanding the key concepts of reflection, refraction, Snell's law, total internal reflection, lenses, mirrors, and optical instruments is essential for anyone studying or working in this field. Ray optics has many practical applications in fields such as telecommunications, weather forecasting, solar energy, and medical imaging.
Introduction:
Ray optics is the branch of optics that deals with the study of light in terms of rays. It is concerned with the behavior of light when it passes through different media such as air, water, glass, etc.
Key Concepts:
There are several key concepts that are important to understand in ray optics. These include:
1. Reflection: This is the process by which light bounces off a surface. The angle of incidence is equal to the angle of reflection.
2. Refraction: This is the process by which light changes direction as it passes through a medium of different refractive index. The amount of refraction depends on the angle of incidence and the refractive indices of the two media.
3. Snell's Law: This law describes the relationship between the angle of incidence and the angle of refraction for a given pair of media. It is given by n1 sin(theta1) = n2 sin(theta2), where n1 and n2 are the refractive indices of the two media and theta1 and theta2 are the angles of incidence and refraction, respectively.
4. Total Internal Reflection: This occurs when light is incident on a boundary between two media and the angle of incidence is greater than a certain critical angle. The light is then reflected back into the first medium rather than being refracted into the second medium.
5. Lenses: These are optical devices that are used to focus or diverge light. There are two main types of lenses: convex (converging) and concave (diverging).
6. Mirrors: These are optical devices that reflect light. There are two main types of mirrors: plane mirrors and curved mirrors (such as concave and convex mirrors).
7. Optical Instruments: There are several optical instruments that make use of the principles of ray optics, including microscopes, telescopes, and cameras.
Applications:
Ray optics has many practical applications, including:
1. Designing and manufacturing lenses and mirrors for use in optical instruments.
2. Understanding how light behaves in the atmosphere, which is important for weather forecasting and climate modeling.
3. Developing optical fibers for use in telecommunications.
4. Designing and optimizing solar panels to maximize the amount of light they can capture.
5. Developing optical sensors for use in medical imaging and other applications.
Conclusion:
Ray optics is an important branch of optics that deals with the behavior of light in terms of rays. Understanding the key concepts of reflection, refraction, Snell's law, total internal reflection, lenses, mirrors, and optical instruments is essential for anyone studying or working in this field. Ray optics has many practical applications in fields such as telecommunications, weather forecasting, solar energy, and medical imaging.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Brain map for ray optics ?
Question Description
Brain map for ray optics ? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Brain map for ray optics ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Brain map for ray optics ?.
Brain map for ray optics ? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Brain map for ray optics ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Brain map for ray optics ?.
Solutions for Brain map for ray optics ? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Brain map for ray optics ? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Brain map for ray optics ?, a detailed solution for Brain map for ray optics ? has been provided alongside types of Brain map for ray optics ? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Brain map for ray optics ? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















