Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > which time PPC curve is convex?
Start Learning for Free
which time PPC curve is convex?
Verified Answer
which time PPC curve is convex?
A PPC curve generally refers to the representation of amount of two different goods that can be obtained by foregoing an estimate of a certain unit required in terms of another. As the amount of one good increases by foregoing the required proportion of other,the opportunity cost of the foregone good increases. This increase in the opportunity cost causes the curve shape concave to the origin. (Maximum utilisation of resources)
Therefore the PPC curve can be convex to the origin when the opportunity cost decreases. This can happen only when less and less units are forgone of first commodity for the introduction of additional unit of another commodity. This can prove realistic practically. For example, when you are about to produce 10000 units of food against an estimation of 5000 units of cloth. But unfortunately you have only 4000 units of cloth to forgo,so you will either forgo less units of cloth or forgo it proportionately. Further even when the opportunity cost is zero, you will continue to produce more units of food maybe by the introduction of another commodity. This will lead the Production Possibility Curve to be convex to origin.
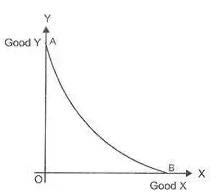
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 12 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 12 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
which time PPC curve is convex?
Convex PPC Curve
A Production Possibility Curve (PPC), also known as a Production Possibility Frontier (PPF), represents the maximum combination of goods and services that an economy can produce given its resources and technology. The shape of the PPC curve can provide important insights into the economy's efficiency and opportunity costs. In this response, we will discuss the concept of a convex PPC curve and explain why it occurs.
Definition of Convex PPC Curve
A convex PPC curve is one that is bowed outwards from the origin, forming a curve that is concave to the origin. It means that as the economy moves from one point to another on the curve, the opportunity cost of producing more of one good increases.
Reasons for Convex PPC Curve
There are several reasons why a convex PPC curve occurs:
1. Increasing Marginal Opportunity Cost: As an economy produces more of one good, it usually needs to sacrifice increasing amounts of the other good. This is due to the principle of increasing marginal opportunity cost, which states that to produce more of a good, resources specialized in the production of the other good must be reallocated. These reallocated resources are likely to be less efficient in producing the second good, resulting in a higher opportunity cost.
2. Resource Allocation: The shape of the PPC curve also reflects the allocation of resources in the economy. When resources are allocated evenly between the production of two goods, the PPC curve tends to be linear. However, if resources are specialized in the production of a particular good, the PPC curve becomes concave. This specialization can be driven by differences in factor endowments, technology, or comparative advantage.
3. Diminishing Returns: Another reason for a convex PPC curve is the principle of diminishing marginal returns. This principle states that as more units of a variable input (e.g., labor or capital) are added to a fixed input (e.g., land or machinery), the additional output produced by each additional unit of the variable input will eventually decrease. This leads to a decrease in the rate at which the economy can switch between producing one good and the other.
Implications of Convex PPC Curve
The convex shape of the PPC curve has important implications for the economy:
1. Opportunity Cost: The increasing opportunity cost along the curve indicates that resources are not perfectly adaptable between the production of different goods. This highlights the concept of trade-offs, where producing more of one good requires sacrificing the production of another good.
2. Economic Efficiency: The shape of the PPC curve can provide insights into the economy's efficiency. If the economy is operating inside the curve, it indicates that resources are not fully utilized, resulting in inefficiency. On the other hand, if the economy is operating on the curve, it suggests that resources are allocated efficiently given the available technology and resources.
In conclusion, a convex PPC curve occurs due to increasing marginal opportunity cost, resource allocation, and diminishing returns. The shape of the curve highlights the trade-offs faced by the economy and provides insights into its efficiency. Understanding the concept of a convex PPC curve is essential in analyzing an economy's production capabilities and decision-making processes.
A Production Possibility Curve (PPC), also known as a Production Possibility Frontier (PPF), represents the maximum combination of goods and services that an economy can produce given its resources and technology. The shape of the PPC curve can provide important insights into the economy's efficiency and opportunity costs. In this response, we will discuss the concept of a convex PPC curve and explain why it occurs.
Definition of Convex PPC Curve
A convex PPC curve is one that is bowed outwards from the origin, forming a curve that is concave to the origin. It means that as the economy moves from one point to another on the curve, the opportunity cost of producing more of one good increases.
Reasons for Convex PPC Curve
There are several reasons why a convex PPC curve occurs:
1. Increasing Marginal Opportunity Cost: As an economy produces more of one good, it usually needs to sacrifice increasing amounts of the other good. This is due to the principle of increasing marginal opportunity cost, which states that to produce more of a good, resources specialized in the production of the other good must be reallocated. These reallocated resources are likely to be less efficient in producing the second good, resulting in a higher opportunity cost.
2. Resource Allocation: The shape of the PPC curve also reflects the allocation of resources in the economy. When resources are allocated evenly between the production of two goods, the PPC curve tends to be linear. However, if resources are specialized in the production of a particular good, the PPC curve becomes concave. This specialization can be driven by differences in factor endowments, technology, or comparative advantage.
3. Diminishing Returns: Another reason for a convex PPC curve is the principle of diminishing marginal returns. This principle states that as more units of a variable input (e.g., labor or capital) are added to a fixed input (e.g., land or machinery), the additional output produced by each additional unit of the variable input will eventually decrease. This leads to a decrease in the rate at which the economy can switch between producing one good and the other.
Implications of Convex PPC Curve
The convex shape of the PPC curve has important implications for the economy:
1. Opportunity Cost: The increasing opportunity cost along the curve indicates that resources are not perfectly adaptable between the production of different goods. This highlights the concept of trade-offs, where producing more of one good requires sacrificing the production of another good.
2. Economic Efficiency: The shape of the PPC curve can provide insights into the economy's efficiency. If the economy is operating inside the curve, it indicates that resources are not fully utilized, resulting in inefficiency. On the other hand, if the economy is operating on the curve, it suggests that resources are allocated efficiently given the available technology and resources.
In conclusion, a convex PPC curve occurs due to increasing marginal opportunity cost, resource allocation, and diminishing returns. The shape of the curve highlights the trade-offs faced by the economy and provides insights into its efficiency. Understanding the concept of a convex PPC curve is essential in analyzing an economy's production capabilities and decision-making processes.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
which time PPC curve is convex?
Question Description
which time PPC curve is convex? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about which time PPC curve is convex? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for which time PPC curve is convex?.
which time PPC curve is convex? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about which time PPC curve is convex? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for which time PPC curve is convex?.
Solutions for which time PPC curve is convex? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of which time PPC curve is convex? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
which time PPC curve is convex?, a detailed solution for which time PPC curve is convex? has been provided alongside types of which time PPC curve is convex? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice which time PPC curve is convex? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















