Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > what is the difference between centripetal an...
Start Learning for Free
what is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces?
Verified Answer
what is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces?
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 9 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
what is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces?
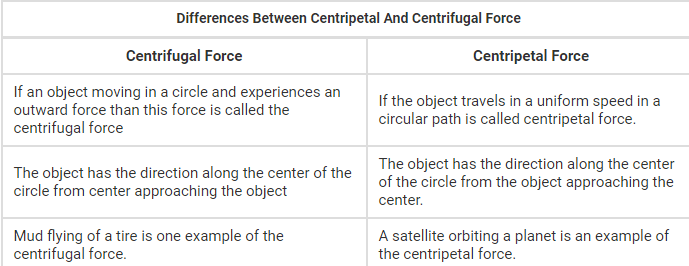
Centripetal and Centrifugal Forces
Centripetal and centrifugal forces are two opposing forces that arise in the context of circular motion. They are often misunderstood or used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings and effects. Let's delve into the differences between these two forces.
Centripetal Force
Centripetal force is a force that acts towards the center of a circular path, enabling an object to move in a curved trajectory. It is responsible for keeping an object in circular motion by constantly changing its direction. Some key points about centripetal force include:
1. Nature: Centripetal force is an inward force that pulls an object towards the center of the circular path it follows.
2. Direction: It always acts perpendicular to the velocity vector of the object at any point on the circular path.
3. Examples: Examples of centripetal forces include gravitational force acting on planets orbiting around the sun, tension in a string holding a ball in circular motion, or the force exerted by a car's tires on the road while taking a turn.
4. Role: Centripetal force is essential to maintain circular motion. Without it, an object would move in a straight line tangent to the circle at any given point.
Centrifugal Force
Centrifugal force is often regarded as a force, but it is actually a perceived force or a pseudo-force. It appears to act outwardly, away from the center of the circle, and is experienced by an object moving in a curved path. Understanding centrifugal force involves the following points:
1. Nature: Centrifugal force is not a real force but a result of inertia. It is a reaction force experienced by an object moving in a curved path, seemingly pushing it away from the center.
2. Direction: It acts radially outward, opposite to the centripetal force, and is directed away from the center of the circular path.
3. Examples: When a car takes a sharp turn, passengers might feel thrown outward due to the perceived centrifugal force. Similarly, a person spinning a bucket of water in a vertical circle experiences centrifugal force pushing the water out of the bucket.
4. Role: Centrifugal force is not a fundamental force and does not contribute to maintaining circular motion. It merely represents the inertia of an object that tends to move in a straight line tangential to the circular path.
Conclusion
In summary, centripetal force is the real force that keeps an object moving in a circular path towards the center, while centrifugal force is a perceived or pseudo-force that appears to push an object away from the center. Understanding these forces is crucial for comprehending circular motion and the dynamics involved.
Centripetal and centrifugal forces are two opposing forces that arise in the context of circular motion. They are often misunderstood or used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings and effects. Let's delve into the differences between these two forces.
Centripetal Force
Centripetal force is a force that acts towards the center of a circular path, enabling an object to move in a curved trajectory. It is responsible for keeping an object in circular motion by constantly changing its direction. Some key points about centripetal force include:
1. Nature: Centripetal force is an inward force that pulls an object towards the center of the circular path it follows.
2. Direction: It always acts perpendicular to the velocity vector of the object at any point on the circular path.
3. Examples: Examples of centripetal forces include gravitational force acting on planets orbiting around the sun, tension in a string holding a ball in circular motion, or the force exerted by a car's tires on the road while taking a turn.
4. Role: Centripetal force is essential to maintain circular motion. Without it, an object would move in a straight line tangent to the circle at any given point.
Centrifugal Force
Centrifugal force is often regarded as a force, but it is actually a perceived force or a pseudo-force. It appears to act outwardly, away from the center of the circle, and is experienced by an object moving in a curved path. Understanding centrifugal force involves the following points:
1. Nature: Centrifugal force is not a real force but a result of inertia. It is a reaction force experienced by an object moving in a curved path, seemingly pushing it away from the center.
2. Direction: It acts radially outward, opposite to the centripetal force, and is directed away from the center of the circular path.
3. Examples: When a car takes a sharp turn, passengers might feel thrown outward due to the perceived centrifugal force. Similarly, a person spinning a bucket of water in a vertical circle experiences centrifugal force pushing the water out of the bucket.
4. Role: Centrifugal force is not a fundamental force and does not contribute to maintaining circular motion. It merely represents the inertia of an object that tends to move in a straight line tangential to the circular path.
Conclusion
In summary, centripetal force is the real force that keeps an object moving in a circular path towards the center, while centrifugal force is a perceived or pseudo-force that appears to push an object away from the center. Understanding these forces is crucial for comprehending circular motion and the dynamics involved.
Attention Class 9 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 9 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 9.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
what is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces?
Question Description
what is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about what is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces?.
what is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces? for Class 9 2024 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about what is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces?.
Solutions for what is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of what is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
what is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces?, a detailed solution for what is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces? has been provided alongside types of what is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice what is the difference between centripetal and centrifugal forces? tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























