IIT JAM Exam > IIT JAM Questions > The technique that involves impacting samples...
Start Learning for Free
The technique that involves impacting samples with electrons is _______.
- a)NMR spectroscopy
- b)ESI mass spectrometry
- c)IR spectroscopy
- d)UV-vis spectroscopy
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The technique that involves impacting samples with electrons is ______...
Answer :
View all questions of this test
- b)ESI mass spectrometry
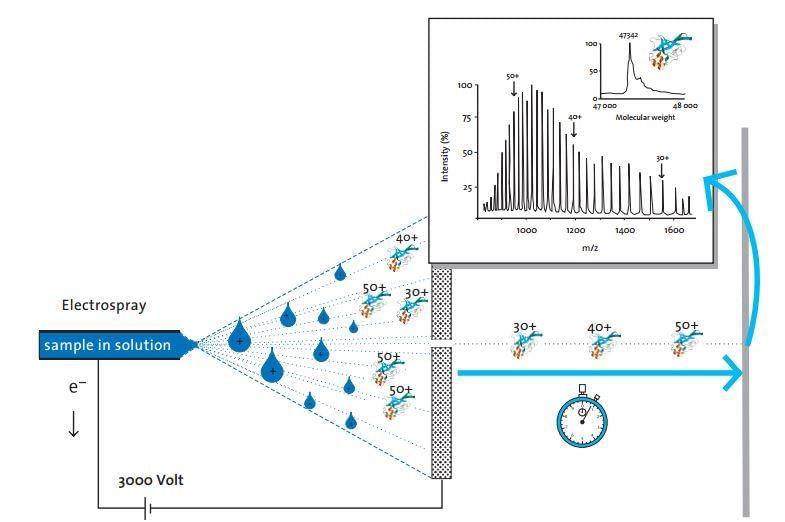
Electrospray ionization (ESI) is a
technique to generate ions for mass spectrometry using electrospray by applying a high voltage to a liquid to produce an aerosol. ... ESI overcomes the tendency of these molecules to fragment upon ionization.
Most Upvoted Answer
The technique that involves impacting samples with electrons is ______...
ESI mass spectrometry
ESI stands for Electrospray Ionization, which is a technique used in mass spectrometry. Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique used to determine the molecular weight and structure of a sample. It involves the ionization of molecules and the separation of these ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio.
Principle of ESI Mass Spectrometry:
Electrospray ionization involves the generation of charged droplets from a liquid sample. These droplets are then subjected to a strong electric field, causing them to break apart into smaller droplets. During this process, the solvent molecules evaporate, and the remaining charged analyte molecules are transferred into the gas phase as ions.
The Process:
1. Sample preparation: The sample is dissolved in a suitable solvent and introduced into the mass spectrometer through a capillary.
2. Electrospray: The sample solution is passed through a needle connected to a high voltage power supply. The high voltage creates a strong electric field that causes the formation of a fine aerosol of charged droplets.
3. Desolvation: As the droplets travel through the mass spectrometer, the solvent molecules evaporate, leaving behind the analyte ions.
4. Ionization: The analyte molecules acquire a charge by either gaining or losing electrons. This can be achieved by introducing a reagent gas, such as ammonia or acetonitrile, into the mass spectrometer.
5. Ion separation: The ions are then guided into the mass analyzer, where they are separated based on their mass-to-charge ratio. This separation can be achieved using various techniques, such as time-of-flight (TOF), quadrupole, or ion trap.
6. Ion detection: The separated ions are detected by a detector, which generates an electrical signal proportional to the abundance of each ion.
7. Data analysis: The recorded data is analyzed to determine the mass-to-charge ratio of the ions and their relative abundance. This information can be used to identify the molecular weight and structure of the sample.
Advantages of ESI Mass Spectrometry:
- ESI is compatible with a wide range of analytes, including small organic molecules, peptides, proteins, and nucleic acids.
- It can provide information about the molecular weight, structure, and fragmentation patterns of the analyte.
- ESI is a soft ionization technique, meaning it produces minimal fragmentation of the analyte ions, allowing for the detection of intact molecular ions.
- It is highly sensitive, capable of detecting analytes in the picogram to femtogram range.
In conclusion, ESI mass spectrometry is a technique that involves impacting samples with electrons to generate ions for analysis. It is widely used in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine, for the identification and characterization of molecules.
ESI stands for Electrospray Ionization, which is a technique used in mass spectrometry. Mass spectrometry is an analytical technique used to determine the molecular weight and structure of a sample. It involves the ionization of molecules and the separation of these ions based on their mass-to-charge ratio.
Principle of ESI Mass Spectrometry:
Electrospray ionization involves the generation of charged droplets from a liquid sample. These droplets are then subjected to a strong electric field, causing them to break apart into smaller droplets. During this process, the solvent molecules evaporate, and the remaining charged analyte molecules are transferred into the gas phase as ions.
The Process:
1. Sample preparation: The sample is dissolved in a suitable solvent and introduced into the mass spectrometer through a capillary.
2. Electrospray: The sample solution is passed through a needle connected to a high voltage power supply. The high voltage creates a strong electric field that causes the formation of a fine aerosol of charged droplets.
3. Desolvation: As the droplets travel through the mass spectrometer, the solvent molecules evaporate, leaving behind the analyte ions.
4. Ionization: The analyte molecules acquire a charge by either gaining or losing electrons. This can be achieved by introducing a reagent gas, such as ammonia or acetonitrile, into the mass spectrometer.
5. Ion separation: The ions are then guided into the mass analyzer, where they are separated based on their mass-to-charge ratio. This separation can be achieved using various techniques, such as time-of-flight (TOF), quadrupole, or ion trap.
6. Ion detection: The separated ions are detected by a detector, which generates an electrical signal proportional to the abundance of each ion.
7. Data analysis: The recorded data is analyzed to determine the mass-to-charge ratio of the ions and their relative abundance. This information can be used to identify the molecular weight and structure of the sample.
Advantages of ESI Mass Spectrometry:
- ESI is compatible with a wide range of analytes, including small organic molecules, peptides, proteins, and nucleic acids.
- It can provide information about the molecular weight, structure, and fragmentation patterns of the analyte.
- ESI is a soft ionization technique, meaning it produces minimal fragmentation of the analyte ions, allowing for the detection of intact molecular ions.
- It is highly sensitive, capable of detecting analytes in the picogram to femtogram range.
In conclusion, ESI mass spectrometry is a technique that involves impacting samples with electrons to generate ions for analysis. It is widely used in various fields, including chemistry, biology, and medicine, for the identification and characterization of molecules.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Similar IIT JAM Doubts
The technique that involves impacting samples with electrons is _______.a)NMR spectroscopyb)ESI mass spectrometryc)IR spectroscopyd)UV-vis spectroscopyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The technique that involves impacting samples with electrons is _______.a)NMR spectroscopyb)ESI mass spectrometryc)IR spectroscopyd)UV-vis spectroscopyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about The technique that involves impacting samples with electrons is _______.a)NMR spectroscopyb)ESI mass spectrometryc)IR spectroscopyd)UV-vis spectroscopyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The technique that involves impacting samples with electrons is _______.a)NMR spectroscopyb)ESI mass spectrometryc)IR spectroscopyd)UV-vis spectroscopyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
The technique that involves impacting samples with electrons is _______.a)NMR spectroscopyb)ESI mass spectrometryc)IR spectroscopyd)UV-vis spectroscopyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about The technique that involves impacting samples with electrons is _______.a)NMR spectroscopyb)ESI mass spectrometryc)IR spectroscopyd)UV-vis spectroscopyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The technique that involves impacting samples with electrons is _______.a)NMR spectroscopyb)ESI mass spectrometryc)IR spectroscopyd)UV-vis spectroscopyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The technique that involves impacting samples with electrons is _______.a)NMR spectroscopyb)ESI mass spectrometryc)IR spectroscopyd)UV-vis spectroscopyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for IIT JAM.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The technique that involves impacting samples with electrons is _______.a)NMR spectroscopyb)ESI mass spectrometryc)IR spectroscopyd)UV-vis spectroscopyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The technique that involves impacting samples with electrons is _______.a)NMR spectroscopyb)ESI mass spectrometryc)IR spectroscopyd)UV-vis spectroscopyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The technique that involves impacting samples with electrons is _______.a)NMR spectroscopyb)ESI mass spectrometryc)IR spectroscopyd)UV-vis spectroscopyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The technique that involves impacting samples with electrons is _______.a)NMR spectroscopyb)ESI mass spectrometryc)IR spectroscopyd)UV-vis spectroscopyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The technique that involves impacting samples with electrons is _______.a)NMR spectroscopyb)ESI mass spectrometryc)IR spectroscopyd)UV-vis spectroscopyCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice IIT JAM tests.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















