JEE Exam > JEE Questions > Amphoteric oxides,such as aluminium oxide, ar...
Start Learning for Free
Amphoteric oxides,such as aluminium oxide, are soluble both in strongly acidic and in strongly basic solutions. 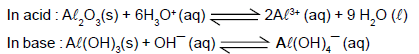
Dissolution of Al(OH)3 in excess base is just a special case of the effect of complex-ion formation on solubility.Al(OH)3 dissolves because excess OH- ions convert it to the soluble complex ion (aluminate ion). The effect of pH on the solubility of Al(OH)3 is shown in figure.
(aluminate ion). The effect of pH on the solubility of Al(OH)3 is shown in figure.
Dissolution of Al(OH)3 in excess base is just a special case of the effect of complex-ion formation on solubility.Al(OH)3 dissolves because excess OH- ions convert it to the soluble complex ion
Other examples of amphoteric hydroxides include Zn(OH)2, Cr(OH)2, Sn(OH)2 and Pb(OH)2, which react with excess OH- ions to from the soluble complex ions Zn(OH)42- (zincate ion), Cr(OH)4¯ (chromite ion), Sn(OH)3¯
(stannite ion), and Pb(OH3)¯ (plumbite ion),respectively.By contrast, basic hydroxides, such as Mn(OH)2,
Fe(OH)2,and Fe(OH)3, dissolve in strong acid but not in strong base.
(stannite ion), and Pb(OH3)¯ (plumbite ion),respectively.By contrast, basic hydroxides, such as Mn(OH)2,
Fe(OH)2,and Fe(OH)3, dissolve in strong acid but not in strong base.
Aluminium is mined as bauxite (Al2O3.xH2O) a hydrated oxide that is always contaminated with Fe2O3 and SiO2. In Bayer process, Al2O3 is purified by some reagents, which of the following reagents will be the best for this purification (Note : Strong heating of precipitate of Al(OH)3 produces Al2O3)
- a)First treat bauxite with a weak acid (like CO2) and then treat the remaining solution with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.
- b)First treat the bauxite with strong NaOH solution and filter it, then neutralise the remaining filterate with a weak acid (like CO2) and heat the precipitate obtained.
- c)First treat bauxite with a strong acid solution (like HCl) and filter it, then treat the remaining filterate with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.
- d)First treat bauxite solution with a strong alkali like NaOH and filter it, then to filtrate add a strong acid like HCl and heat the precipitate obtained.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Amphoteric oxides,such as aluminium oxide, are soluble both in strongl...
First heat bauxite with NaOH so, Al2O3 get dissolved in it (SiO2 will also get dissolved as it is an acidic oxide but not Fe2O3 (basic acidic),then filter lt. To filterate add a weak acid like CO2 so Al(OH)3 forms Al3+ ions). On heating the ppt. of Al(OH)3 we will get pure Al2O3.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
Amphoteric oxides,such as aluminium oxide, are soluble both in strongly acidic and in strongly basic solutions. Dissolution of Al(OH)3 in excess base is just a special case of the effect of complex-ion formation on solubility.Al(OH)3 dissolves because excess OH-ions convert it to the soluble complex ion(aluminate ion). The effect of pH on the solubility of Al(OH)3 is shown in figure.Other examples of amphoteric hydroxides include Zn(OH)2,Cr(OH)2,Sn(OH)2 andPb(OH)2, which react with excess OH- ions to from the soluble complexions Zn(OH)42-(zincate ion), Cr(OH)4¯ (chromite ion), Sn(OH)3¯(stannite ion), and Pb(OH3)¯ (plumbite ion),respectively.By contrast, basic hydroxides, such as Mn(OH)2,Fe(OH)2,and Fe(OH)3, dissolve in strong acid but not in strong base.Aluminium is mined as bauxite (Al2O3.xH2O) a hydrated oxide that is always contaminated with Fe2O3 and SiO2. In Bayer process, Al2O3 is purified by some reagents, which of the following reagents will be the best for this purification (Note : Strong heating of precipitate of Al(OH)3 produces Al2O3)a)First treat bauxite with a weak acid (like CO2) and then treat the remaining solution with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.b)First treat the bauxite with strong NaOH solution and filter it, then neutralise the remaining filterate with a weak acid (like CO2) and heat the precipitate obtained. c)First treat bauxite with a strong acid solution (like HCl) and filter it, then treat the remaining filterate with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.d)First treat bauxite solution with a strong alkali like NaOH and filter it, then to filtrate add a strong acid like HCl and heat the precipitate obtained.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Amphoteric oxides,such as aluminium oxide, are soluble both in strongly acidic and in strongly basic solutions. Dissolution of Al(OH)3 in excess base is just a special case of the effect of complex-ion formation on solubility.Al(OH)3 dissolves because excess OH-ions convert it to the soluble complex ion(aluminate ion). The effect of pH on the solubility of Al(OH)3 is shown in figure.Other examples of amphoteric hydroxides include Zn(OH)2,Cr(OH)2,Sn(OH)2 andPb(OH)2, which react with excess OH- ions to from the soluble complexions Zn(OH)42-(zincate ion), Cr(OH)4¯ (chromite ion), Sn(OH)3¯(stannite ion), and Pb(OH3)¯ (plumbite ion),respectively.By contrast, basic hydroxides, such as Mn(OH)2,Fe(OH)2,and Fe(OH)3, dissolve in strong acid but not in strong base.Aluminium is mined as bauxite (Al2O3.xH2O) a hydrated oxide that is always contaminated with Fe2O3 and SiO2. In Bayer process, Al2O3 is purified by some reagents, which of the following reagents will be the best for this purification (Note : Strong heating of precipitate of Al(OH)3 produces Al2O3)a)First treat bauxite with a weak acid (like CO2) and then treat the remaining solution with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.b)First treat the bauxite with strong NaOH solution and filter it, then neutralise the remaining filterate with a weak acid (like CO2) and heat the precipitate obtained. c)First treat bauxite with a strong acid solution (like HCl) and filter it, then treat the remaining filterate with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.d)First treat bauxite solution with a strong alkali like NaOH and filter it, then to filtrate add a strong acid like HCl and heat the precipitate obtained.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Amphoteric oxides,such as aluminium oxide, are soluble both in strongly acidic and in strongly basic solutions. Dissolution of Al(OH)3 in excess base is just a special case of the effect of complex-ion formation on solubility.Al(OH)3 dissolves because excess OH-ions convert it to the soluble complex ion(aluminate ion). The effect of pH on the solubility of Al(OH)3 is shown in figure.Other examples of amphoteric hydroxides include Zn(OH)2,Cr(OH)2,Sn(OH)2 andPb(OH)2, which react with excess OH- ions to from the soluble complexions Zn(OH)42-(zincate ion), Cr(OH)4¯ (chromite ion), Sn(OH)3¯(stannite ion), and Pb(OH3)¯ (plumbite ion),respectively.By contrast, basic hydroxides, such as Mn(OH)2,Fe(OH)2,and Fe(OH)3, dissolve in strong acid but not in strong base.Aluminium is mined as bauxite (Al2O3.xH2O) a hydrated oxide that is always contaminated with Fe2O3 and SiO2. In Bayer process, Al2O3 is purified by some reagents, which of the following reagents will be the best for this purification (Note : Strong heating of precipitate of Al(OH)3 produces Al2O3)a)First treat bauxite with a weak acid (like CO2) and then treat the remaining solution with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.b)First treat the bauxite with strong NaOH solution and filter it, then neutralise the remaining filterate with a weak acid (like CO2) and heat the precipitate obtained. c)First treat bauxite with a strong acid solution (like HCl) and filter it, then treat the remaining filterate with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.d)First treat bauxite solution with a strong alkali like NaOH and filter it, then to filtrate add a strong acid like HCl and heat the precipitate obtained.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Amphoteric oxides,such as aluminium oxide, are soluble both in strongly acidic and in strongly basic solutions. Dissolution of Al(OH)3 in excess base is just a special case of the effect of complex-ion formation on solubility.Al(OH)3 dissolves because excess OH-ions convert it to the soluble complex ion(aluminate ion). The effect of pH on the solubility of Al(OH)3 is shown in figure.Other examples of amphoteric hydroxides include Zn(OH)2,Cr(OH)2,Sn(OH)2 andPb(OH)2, which react with excess OH- ions to from the soluble complexions Zn(OH)42-(zincate ion), Cr(OH)4¯ (chromite ion), Sn(OH)3¯(stannite ion), and Pb(OH3)¯ (plumbite ion),respectively.By contrast, basic hydroxides, such as Mn(OH)2,Fe(OH)2,and Fe(OH)3, dissolve in strong acid but not in strong base.Aluminium is mined as bauxite (Al2O3.xH2O) a hydrated oxide that is always contaminated with Fe2O3 and SiO2. In Bayer process, Al2O3 is purified by some reagents, which of the following reagents will be the best for this purification (Note : Strong heating of precipitate of Al(OH)3 produces Al2O3)a)First treat bauxite with a weak acid (like CO2) and then treat the remaining solution with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.b)First treat the bauxite with strong NaOH solution and filter it, then neutralise the remaining filterate with a weak acid (like CO2) and heat the precipitate obtained. c)First treat bauxite with a strong acid solution (like HCl) and filter it, then treat the remaining filterate with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.d)First treat bauxite solution with a strong alkali like NaOH and filter it, then to filtrate add a strong acid like HCl and heat the precipitate obtained.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Amphoteric oxides,such as aluminium oxide, are soluble both in strongly acidic and in strongly basic solutions. Dissolution of Al(OH)3 in excess base is just a special case of the effect of complex-ion formation on solubility.Al(OH)3 dissolves because excess OH-ions convert it to the soluble complex ion(aluminate ion). The effect of pH on the solubility of Al(OH)3 is shown in figure.Other examples of amphoteric hydroxides include Zn(OH)2,Cr(OH)2,Sn(OH)2 andPb(OH)2, which react with excess OH- ions to from the soluble complexions Zn(OH)42-(zincate ion), Cr(OH)4¯ (chromite ion), Sn(OH)3¯(stannite ion), and Pb(OH3)¯ (plumbite ion),respectively.By contrast, basic hydroxides, such as Mn(OH)2,Fe(OH)2,and Fe(OH)3, dissolve in strong acid but not in strong base.Aluminium is mined as bauxite (Al2O3.xH2O) a hydrated oxide that is always contaminated with Fe2O3 and SiO2. In Bayer process, Al2O3 is purified by some reagents, which of the following reagents will be the best for this purification (Note : Strong heating of precipitate of Al(OH)3 produces Al2O3)a)First treat bauxite with a weak acid (like CO2) and then treat the remaining solution with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.b)First treat the bauxite with strong NaOH solution and filter it, then neutralise the remaining filterate with a weak acid (like CO2) and heat the precipitate obtained. c)First treat bauxite with a strong acid solution (like HCl) and filter it, then treat the remaining filterate with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.d)First treat bauxite solution with a strong alkali like NaOH and filter it, then to filtrate add a strong acid like HCl and heat the precipitate obtained.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Amphoteric oxides,such as aluminium oxide, are soluble both in strongly acidic and in strongly basic solutions. Dissolution of Al(OH)3 in excess base is just a special case of the effect of complex-ion formation on solubility.Al(OH)3 dissolves because excess OH-ions convert it to the soluble complex ion(aluminate ion). The effect of pH on the solubility of Al(OH)3 is shown in figure.Other examples of amphoteric hydroxides include Zn(OH)2,Cr(OH)2,Sn(OH)2 andPb(OH)2, which react with excess OH- ions to from the soluble complexions Zn(OH)42-(zincate ion), Cr(OH)4¯ (chromite ion), Sn(OH)3¯(stannite ion), and Pb(OH3)¯ (plumbite ion),respectively.By contrast, basic hydroxides, such as Mn(OH)2,Fe(OH)2,and Fe(OH)3, dissolve in strong acid but not in strong base.Aluminium is mined as bauxite (Al2O3.xH2O) a hydrated oxide that is always contaminated with Fe2O3 and SiO2. In Bayer process, Al2O3 is purified by some reagents, which of the following reagents will be the best for this purification (Note : Strong heating of precipitate of Al(OH)3 produces Al2O3)a)First treat bauxite with a weak acid (like CO2) and then treat the remaining solution with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.b)First treat the bauxite with strong NaOH solution and filter it, then neutralise the remaining filterate with a weak acid (like CO2) and heat the precipitate obtained. c)First treat bauxite with a strong acid solution (like HCl) and filter it, then treat the remaining filterate with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.d)First treat bauxite solution with a strong alkali like NaOH and filter it, then to filtrate add a strong acid like HCl and heat the precipitate obtained.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Amphoteric oxides,such as aluminium oxide, are soluble both in strongly acidic and in strongly basic solutions. Dissolution of Al(OH)3 in excess base is just a special case of the effect of complex-ion formation on solubility.Al(OH)3 dissolves because excess OH-ions convert it to the soluble complex ion(aluminate ion). The effect of pH on the solubility of Al(OH)3 is shown in figure.Other examples of amphoteric hydroxides include Zn(OH)2,Cr(OH)2,Sn(OH)2 andPb(OH)2, which react with excess OH- ions to from the soluble complexions Zn(OH)42-(zincate ion), Cr(OH)4¯ (chromite ion), Sn(OH)3¯(stannite ion), and Pb(OH3)¯ (plumbite ion),respectively.By contrast, basic hydroxides, such as Mn(OH)2,Fe(OH)2,and Fe(OH)3, dissolve in strong acid but not in strong base.Aluminium is mined as bauxite (Al2O3.xH2O) a hydrated oxide that is always contaminated with Fe2O3 and SiO2. In Bayer process, Al2O3 is purified by some reagents, which of the following reagents will be the best for this purification (Note : Strong heating of precipitate of Al(OH)3 produces Al2O3)a)First treat bauxite with a weak acid (like CO2) and then treat the remaining solution with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.b)First treat the bauxite with strong NaOH solution and filter it, then neutralise the remaining filterate with a weak acid (like CO2) and heat the precipitate obtained. c)First treat bauxite with a strong acid solution (like HCl) and filter it, then treat the remaining filterate with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.d)First treat bauxite solution with a strong alkali like NaOH and filter it, then to filtrate add a strong acid like HCl and heat the precipitate obtained.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Amphoteric oxides,such as aluminium oxide, are soluble both in strongly acidic and in strongly basic solutions. Dissolution of Al(OH)3 in excess base is just a special case of the effect of complex-ion formation on solubility.Al(OH)3 dissolves because excess OH-ions convert it to the soluble complex ion(aluminate ion). The effect of pH on the solubility of Al(OH)3 is shown in figure.Other examples of amphoteric hydroxides include Zn(OH)2,Cr(OH)2,Sn(OH)2 andPb(OH)2, which react with excess OH- ions to from the soluble complexions Zn(OH)42-(zincate ion), Cr(OH)4¯ (chromite ion), Sn(OH)3¯(stannite ion), and Pb(OH3)¯ (plumbite ion),respectively.By contrast, basic hydroxides, such as Mn(OH)2,Fe(OH)2,and Fe(OH)3, dissolve in strong acid but not in strong base.Aluminium is mined as bauxite (Al2O3.xH2O) a hydrated oxide that is always contaminated with Fe2O3 and SiO2. In Bayer process, Al2O3 is purified by some reagents, which of the following reagents will be the best for this purification (Note : Strong heating of precipitate of Al(OH)3 produces Al2O3)a)First treat bauxite with a weak acid (like CO2) and then treat the remaining solution with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.b)First treat the bauxite with strong NaOH solution and filter it, then neutralise the remaining filterate with a weak acid (like CO2) and heat the precipitate obtained. c)First treat bauxite with a strong acid solution (like HCl) and filter it, then treat the remaining filterate with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.d)First treat bauxite solution with a strong alkali like NaOH and filter it, then to filtrate add a strong acid like HCl and heat the precipitate obtained.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Amphoteric oxides,such as aluminium oxide, are soluble both in strongly acidic and in strongly basic solutions. Dissolution of Al(OH)3 in excess base is just a special case of the effect of complex-ion formation on solubility.Al(OH)3 dissolves because excess OH-ions convert it to the soluble complex ion(aluminate ion). The effect of pH on the solubility of Al(OH)3 is shown in figure.Other examples of amphoteric hydroxides include Zn(OH)2,Cr(OH)2,Sn(OH)2 andPb(OH)2, which react with excess OH- ions to from the soluble complexions Zn(OH)42-(zincate ion), Cr(OH)4¯ (chromite ion), Sn(OH)3¯(stannite ion), and Pb(OH3)¯ (plumbite ion),respectively.By contrast, basic hydroxides, such as Mn(OH)2,Fe(OH)2,and Fe(OH)3, dissolve in strong acid but not in strong base.Aluminium is mined as bauxite (Al2O3.xH2O) a hydrated oxide that is always contaminated with Fe2O3 and SiO2. In Bayer process, Al2O3 is purified by some reagents, which of the following reagents will be the best for this purification (Note : Strong heating of precipitate of Al(OH)3 produces Al2O3)a)First treat bauxite with a weak acid (like CO2) and then treat the remaining solution with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.b)First treat the bauxite with strong NaOH solution and filter it, then neutralise the remaining filterate with a weak acid (like CO2) and heat the precipitate obtained. c)First treat bauxite with a strong acid solution (like HCl) and filter it, then treat the remaining filterate with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.d)First treat bauxite solution with a strong alkali like NaOH and filter it, then to filtrate add a strong acid like HCl and heat the precipitate obtained.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Amphoteric oxides,such as aluminium oxide, are soluble both in strongly acidic and in strongly basic solutions. Dissolution of Al(OH)3 in excess base is just a special case of the effect of complex-ion formation on solubility.Al(OH)3 dissolves because excess OH-ions convert it to the soluble complex ion(aluminate ion). The effect of pH on the solubility of Al(OH)3 is shown in figure.Other examples of amphoteric hydroxides include Zn(OH)2,Cr(OH)2,Sn(OH)2 andPb(OH)2, which react with excess OH- ions to from the soluble complexions Zn(OH)42-(zincate ion), Cr(OH)4¯ (chromite ion), Sn(OH)3¯(stannite ion), and Pb(OH3)¯ (plumbite ion),respectively.By contrast, basic hydroxides, such as Mn(OH)2,Fe(OH)2,and Fe(OH)3, dissolve in strong acid but not in strong base.Aluminium is mined as bauxite (Al2O3.xH2O) a hydrated oxide that is always contaminated with Fe2O3 and SiO2. In Bayer process, Al2O3 is purified by some reagents, which of the following reagents will be the best for this purification (Note : Strong heating of precipitate of Al(OH)3 produces Al2O3)a)First treat bauxite with a weak acid (like CO2) and then treat the remaining solution with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.b)First treat the bauxite with strong NaOH solution and filter it, then neutralise the remaining filterate with a weak acid (like CO2) and heat the precipitate obtained. c)First treat bauxite with a strong acid solution (like HCl) and filter it, then treat the remaining filterate with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.d)First treat bauxite solution with a strong alkali like NaOH and filter it, then to filtrate add a strong acid like HCl and heat the precipitate obtained.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Amphoteric oxides,such as aluminium oxide, are soluble both in strongly acidic and in strongly basic solutions. Dissolution of Al(OH)3 in excess base is just a special case of the effect of complex-ion formation on solubility.Al(OH)3 dissolves because excess OH-ions convert it to the soluble complex ion(aluminate ion). The effect of pH on the solubility of Al(OH)3 is shown in figure.Other examples of amphoteric hydroxides include Zn(OH)2,Cr(OH)2,Sn(OH)2 andPb(OH)2, which react with excess OH- ions to from the soluble complexions Zn(OH)42-(zincate ion), Cr(OH)4¯ (chromite ion), Sn(OH)3¯(stannite ion), and Pb(OH3)¯ (plumbite ion),respectively.By contrast, basic hydroxides, such as Mn(OH)2,Fe(OH)2,and Fe(OH)3, dissolve in strong acid but not in strong base.Aluminium is mined as bauxite (Al2O3.xH2O) a hydrated oxide that is always contaminated with Fe2O3 and SiO2. In Bayer process, Al2O3 is purified by some reagents, which of the following reagents will be the best for this purification (Note : Strong heating of precipitate of Al(OH)3 produces Al2O3)a)First treat bauxite with a weak acid (like CO2) and then treat the remaining solution with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.b)First treat the bauxite with strong NaOH solution and filter it, then neutralise the remaining filterate with a weak acid (like CO2) and heat the precipitate obtained. c)First treat bauxite with a strong acid solution (like HCl) and filter it, then treat the remaining filterate with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.d)First treat bauxite solution with a strong alkali like NaOH and filter it, then to filtrate add a strong acid like HCl and heat the precipitate obtained.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Amphoteric oxides,such as aluminium oxide, are soluble both in strongly acidic and in strongly basic solutions. Dissolution of Al(OH)3 in excess base is just a special case of the effect of complex-ion formation on solubility.Al(OH)3 dissolves because excess OH-ions convert it to the soluble complex ion(aluminate ion). The effect of pH on the solubility of Al(OH)3 is shown in figure.Other examples of amphoteric hydroxides include Zn(OH)2,Cr(OH)2,Sn(OH)2 andPb(OH)2, which react with excess OH- ions to from the soluble complexions Zn(OH)42-(zincate ion), Cr(OH)4¯ (chromite ion), Sn(OH)3¯(stannite ion), and Pb(OH3)¯ (plumbite ion),respectively.By contrast, basic hydroxides, such as Mn(OH)2,Fe(OH)2,and Fe(OH)3, dissolve in strong acid but not in strong base.Aluminium is mined as bauxite (Al2O3.xH2O) a hydrated oxide that is always contaminated with Fe2O3 and SiO2. In Bayer process, Al2O3 is purified by some reagents, which of the following reagents will be the best for this purification (Note : Strong heating of precipitate of Al(OH)3 produces Al2O3)a)First treat bauxite with a weak acid (like CO2) and then treat the remaining solution with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.b)First treat the bauxite with strong NaOH solution and filter it, then neutralise the remaining filterate with a weak acid (like CO2) and heat the precipitate obtained. c)First treat bauxite with a strong acid solution (like HCl) and filter it, then treat the remaining filterate with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.d)First treat bauxite solution with a strong alkali like NaOH and filter it, then to filtrate add a strong acid like HCl and heat the precipitate obtained.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Amphoteric oxides,such as aluminium oxide, are soluble both in strongly acidic and in strongly basic solutions. Dissolution of Al(OH)3 in excess base is just a special case of the effect of complex-ion formation on solubility.Al(OH)3 dissolves because excess OH-ions convert it to the soluble complex ion(aluminate ion). The effect of pH on the solubility of Al(OH)3 is shown in figure.Other examples of amphoteric hydroxides include Zn(OH)2,Cr(OH)2,Sn(OH)2 andPb(OH)2, which react with excess OH- ions to from the soluble complexions Zn(OH)42-(zincate ion), Cr(OH)4¯ (chromite ion), Sn(OH)3¯(stannite ion), and Pb(OH3)¯ (plumbite ion),respectively.By contrast, basic hydroxides, such as Mn(OH)2,Fe(OH)2,and Fe(OH)3, dissolve in strong acid but not in strong base.Aluminium is mined as bauxite (Al2O3.xH2O) a hydrated oxide that is always contaminated with Fe2O3 and SiO2. In Bayer process, Al2O3 is purified by some reagents, which of the following reagents will be the best for this purification (Note : Strong heating of precipitate of Al(OH)3 produces Al2O3)a)First treat bauxite with a weak acid (like CO2) and then treat the remaining solution with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.b)First treat the bauxite with strong NaOH solution and filter it, then neutralise the remaining filterate with a weak acid (like CO2) and heat the precipitate obtained. c)First treat bauxite with a strong acid solution (like HCl) and filter it, then treat the remaining filterate with NaOH solution and heat the precipitate obtained.d)First treat bauxite solution with a strong alkali like NaOH and filter it, then to filtrate add a strong acid like HCl and heat the precipitate obtained.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.























