Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > An irreversible heat engine extracts heat fro...
Start Learning for Free
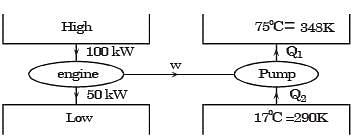
An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100 kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50 kW.The entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at 17°C and 75°C. The rate (in kW) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its high temperature sink is
[2009]
- a)50
- b)250
- c)300
- d)360
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature sour...
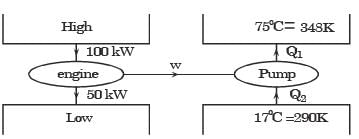
W = Q1 – Q2
= 100 – 50
= 50 kW
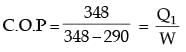
Q1 = 300 kW
Alternately
Work output from irreversible heat engine,
W = Q1 – Q2
= 100 –50 = 50 kW
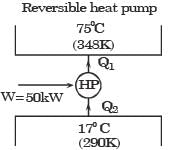
Also for irreversible heat engine
Q1 + W = Q2
∴ T1 ΔS + 50 = T2ΔS
or (T2 – T1) ΔS = 50
or (348 - 290) Δ S = 50
or ΔS = 50/58
∴ Rate of heat rejection,
Q2 = T2 ΔS
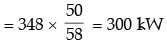
Most Upvoted Answer
An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature sour...
W = Q1 – Q2
= 100 – 50
= 50 kW
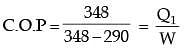
Q1 = 300 kW
Alternately
Work output from irreversible heat engine,
W = Q1 – Q2
= 100 –50 = 50 kW
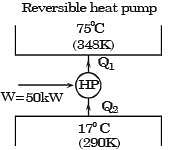
Also for irreversible heat engine
Q1 + W = Q2
∴ T1 ΔS + 50 = T2ΔS
or (T2 – T1) ΔS = 50
or (348 - 290) Δ S = 50
or ΔS = 50/58
∴ Rate of heat rejection,
Q2 = T2 ΔS
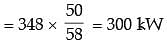
Free Test
| FREE | Start Free Test |
Community Answer
An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature sour...
°C and 127°C. Determine the rate at which heat is absorbed from the low-temperature reservoir and the rate at which heat is rejected to the high-temperature reservoir by the heat pump.
To solve this problem, we can use the principles of thermodynamics and the equation for the efficiency of a heat engine:
Efficiency = 1 - (T_low / T_high)
Given that the irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100 kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50 kW, we can determine the rate of work output:
Work output = Heat input - Heat rejection
100 kW = Heat input - 50 kW
Heat input = 150 kW
Now, we can calculate the efficiency of the heat engine:
Efficiency = 1 - (T_low / T_high)
Efficiency = 1 - (17 + 273) / (127 + 273)
Efficiency = 1 - 290 / 400
Efficiency = 0.275
Since the entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump, the rate of work input for the heat pump is equal to the rate of work output of the heat engine:
Work input (heat pump) = Work output (heat engine)
Work input (heat pump) = 100 kW
Now, we can determine the rate at which heat is absorbed from the low-temperature reservoir by the heat pump using the equation for the coefficient of performance (COP) of a heat pump:
COP = T_high / (T_high - T_low)
COP = 127 + 273 / (127 + 273 - 17 + 273)
COP = 400 / 756
COP = 0.529
Heat absorbed (low-temperature reservoir) = Work input (heat pump) / COP
Heat absorbed (low-temperature reservoir) = 100 kW / 0.529
Heat absorbed (low-temperature reservoir) = 188.9 kW
Finally, we can determine the rate at which heat is rejected to the high-temperature reservoir by the heat pump:
Heat rejected (high-temperature reservoir) = Heat absorbed (low-temperature reservoir) + Work input (heat pump)
Heat rejected (high-temperature reservoir) = 188.9 kW + 100 kW
Heat rejected (high-temperature reservoir) = 288.9 kW
Therefore, the rate at which heat is absorbed from the low-temperature reservoir by the heat pump is 188.9 kW, and the rate at which heat is rejected to the high-temperature reservoir by the heat pump is 288.9 kW.
To solve this problem, we can use the principles of thermodynamics and the equation for the efficiency of a heat engine:
Efficiency = 1 - (T_low / T_high)
Given that the irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100 kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50 kW, we can determine the rate of work output:
Work output = Heat input - Heat rejection
100 kW = Heat input - 50 kW
Heat input = 150 kW
Now, we can calculate the efficiency of the heat engine:
Efficiency = 1 - (T_low / T_high)
Efficiency = 1 - (17 + 273) / (127 + 273)
Efficiency = 1 - 290 / 400
Efficiency = 0.275
Since the entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump, the rate of work input for the heat pump is equal to the rate of work output of the heat engine:
Work input (heat pump) = Work output (heat engine)
Work input (heat pump) = 100 kW
Now, we can determine the rate at which heat is absorbed from the low-temperature reservoir by the heat pump using the equation for the coefficient of performance (COP) of a heat pump:
COP = T_high / (T_high - T_low)
COP = 127 + 273 / (127 + 273 - 17 + 273)
COP = 400 / 756
COP = 0.529
Heat absorbed (low-temperature reservoir) = Work input (heat pump) / COP
Heat absorbed (low-temperature reservoir) = 100 kW / 0.529
Heat absorbed (low-temperature reservoir) = 188.9 kW
Finally, we can determine the rate at which heat is rejected to the high-temperature reservoir by the heat pump:
Heat rejected (high-temperature reservoir) = Heat absorbed (low-temperature reservoir) + Work input (heat pump)
Heat rejected (high-temperature reservoir) = 188.9 kW + 100 kW
Heat rejected (high-temperature reservoir) = 288.9 kW
Therefore, the rate at which heat is absorbed from the low-temperature reservoir by the heat pump is 188.9 kW, and the rate at which heat is rejected to the high-temperature reservoir by the heat pump is 288.9 kW.
Attention Mechanical Engineering Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Mechanical Engineering study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Mechanical Engineering.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Mechanical Engineering Doubts
An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100 kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50 kW.The entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at 17°C and 75°C. The rate (in kW) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its high temperature sink is[2009]a)50b)250c)300d)360Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100 kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50 kW.The entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at 17°C and 75°C. The rate (in kW) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its high temperature sink is[2009]a)50b)250c)300d)360Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100 kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50 kW.The entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at 17°C and 75°C. The rate (in kW) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its high temperature sink is[2009]a)50b)250c)300d)360Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100 kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50 kW.The entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at 17°C and 75°C. The rate (in kW) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its high temperature sink is[2009]a)50b)250c)300d)360Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100 kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50 kW.The entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at 17°C and 75°C. The rate (in kW) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its high temperature sink is[2009]a)50b)250c)300d)360Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100 kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50 kW.The entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at 17°C and 75°C. The rate (in kW) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its high temperature sink is[2009]a)50b)250c)300d)360Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100 kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50 kW.The entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at 17°C and 75°C. The rate (in kW) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its high temperature sink is[2009]a)50b)250c)300d)360Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100 kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50 kW.The entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at 17°C and 75°C. The rate (in kW) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its high temperature sink is[2009]a)50b)250c)300d)360Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100 kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50 kW.The entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at 17°C and 75°C. The rate (in kW) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its high temperature sink is[2009]a)50b)250c)300d)360Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100 kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50 kW.The entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at 17°C and 75°C. The rate (in kW) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its high temperature sink is[2009]a)50b)250c)300d)360Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100 kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50 kW.The entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at 17°C and 75°C. The rate (in kW) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its high temperature sink is[2009]a)50b)250c)300d)360Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100 kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50 kW.The entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at 17°C and 75°C. The rate (in kW) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its high temperature sink is[2009]a)50b)250c)300d)360Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice An irreversible heat engine extracts heat from a high temperature source at a rate of 100 kW and rejects heat to a sink at a rate of 50 kW.The entire work output of the heat engine is used to drive a reversible heat pump operating between a set of independent isothermal heat reservoirs at 17°C and 75°C. The rate (in kW) at which the heat pump delivers heat to its high temperature sink is[2009]a)50b)250c)300d)360Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























