Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > A reversible heat transfer demands:[1993]a)Th...
Start Learning for Free
A reversible heat transfer demands:
[1993]
- a)The temperature difference causing heat transfer tends to zero
- b)The system receiving heat must be at a constant temperature
- c)The system transferring out heat must be at a constant temperature
- d)Both interacting systems must beat constant temperatures
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
A reversible heat transfer demands:[1993]a)The temperature difference ...
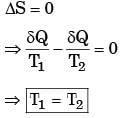
Most Upvoted Answer
A reversible heat transfer demands:[1993]a)The temperature difference ...
Reversible Heat Transfer
Introduction:
Reversible heat transfer refers to a process where heat is transferred between two systems without any irreversibilities. In other words, the system can be restored to its original state without any loss of energy or increase in entropy. To achieve reversible heat transfer, certain conditions must be met.
Temperature Difference Tending to Zero:
The first condition for reversible heat transfer is that the temperature difference causing the heat transfer tends to zero. This means that the temperature gradient between the two systems involved should be minimized as much as possible.
- The temperature difference can be reduced by minimizing the temperature difference between the system receiving heat and the system transferring out heat.
- As the temperature difference approaches zero, the heat transfer becomes more reversible because the driving force for heat transfer decreases.
Constant Temperature of the Receiving System:
The second condition for reversible heat transfer is that the system receiving heat must be at a constant temperature. This means that the temperature of the receiving system should remain constant throughout the heat transfer process.
- If the temperature of the receiving system changes, it will result in a temperature gradient and non-reversible heat transfer.
- By maintaining a constant temperature, the heat transfer can be reversible as there are no fluctuations in temperature.
Constant Temperature of the Transferring System:
The third condition for reversible heat transfer is that the system transferring out heat must be at a constant temperature. This means that the temperature of the transferring system should also remain constant during the heat transfer process.
- Similar to the receiving system, any fluctuations in the temperature of the transferring system will result in non-reversible heat transfer.
- By maintaining a constant temperature, the heat transfer can be reversible as there are no temperature fluctuations.
Interaction of Systems at Constant Temperatures:
The final condition for reversible heat transfer is that both interacting systems must be at constant temperatures. This means that both the receiving and transferring systems should maintain a constant temperature throughout the heat transfer process.
- If either system experiences a change in temperature, the heat transfer will become non-reversible.
- By ensuring that both systems are at constant temperatures, the heat transfer can be reversible as there are no temperature fluctuations or gradients.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, option A is the correct answer because it states that the temperature difference causing heat transfer tends to zero. This condition is essential for achieving reversible heat transfer. The other options (B, C, and D) are not sufficient on their own to ensure reversible heat transfer and do not encompass all the necessary conditions.
Introduction:
Reversible heat transfer refers to a process where heat is transferred between two systems without any irreversibilities. In other words, the system can be restored to its original state without any loss of energy or increase in entropy. To achieve reversible heat transfer, certain conditions must be met.
Temperature Difference Tending to Zero:
The first condition for reversible heat transfer is that the temperature difference causing the heat transfer tends to zero. This means that the temperature gradient between the two systems involved should be minimized as much as possible.
- The temperature difference can be reduced by minimizing the temperature difference between the system receiving heat and the system transferring out heat.
- As the temperature difference approaches zero, the heat transfer becomes more reversible because the driving force for heat transfer decreases.
Constant Temperature of the Receiving System:
The second condition for reversible heat transfer is that the system receiving heat must be at a constant temperature. This means that the temperature of the receiving system should remain constant throughout the heat transfer process.
- If the temperature of the receiving system changes, it will result in a temperature gradient and non-reversible heat transfer.
- By maintaining a constant temperature, the heat transfer can be reversible as there are no fluctuations in temperature.
Constant Temperature of the Transferring System:
The third condition for reversible heat transfer is that the system transferring out heat must be at a constant temperature. This means that the temperature of the transferring system should also remain constant during the heat transfer process.
- Similar to the receiving system, any fluctuations in the temperature of the transferring system will result in non-reversible heat transfer.
- By maintaining a constant temperature, the heat transfer can be reversible as there are no temperature fluctuations.
Interaction of Systems at Constant Temperatures:
The final condition for reversible heat transfer is that both interacting systems must be at constant temperatures. This means that both the receiving and transferring systems should maintain a constant temperature throughout the heat transfer process.
- If either system experiences a change in temperature, the heat transfer will become non-reversible.
- By ensuring that both systems are at constant temperatures, the heat transfer can be reversible as there are no temperature fluctuations or gradients.
Conclusion:
Among the given options, option A is the correct answer because it states that the temperature difference causing heat transfer tends to zero. This condition is essential for achieving reversible heat transfer. The other options (B, C, and D) are not sufficient on their own to ensure reversible heat transfer and do not encompass all the necessary conditions.
Free Test
| FREE | Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A reversible heat transfer demands:[1993]a)The temperature difference ...
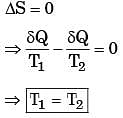
Attention Mechanical Engineering Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Mechanical Engineering study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Mechanical Engineering.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Mechanical Engineering Doubts
A reversible heat transfer demands:[1993]a)The temperature difference causing heat transfer tends to zerob)The system receiving heat must be at a constant temperaturec)The system transferring out heat must be at a constant temperatured)Both interacting systems must beat constant temperaturesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A reversible heat transfer demands:[1993]a)The temperature difference causing heat transfer tends to zerob)The system receiving heat must be at a constant temperaturec)The system transferring out heat must be at a constant temperatured)Both interacting systems must beat constant temperaturesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A reversible heat transfer demands:[1993]a)The temperature difference causing heat transfer tends to zerob)The system receiving heat must be at a constant temperaturec)The system transferring out heat must be at a constant temperatured)Both interacting systems must beat constant temperaturesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A reversible heat transfer demands:[1993]a)The temperature difference causing heat transfer tends to zerob)The system receiving heat must be at a constant temperaturec)The system transferring out heat must be at a constant temperatured)Both interacting systems must beat constant temperaturesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
A reversible heat transfer demands:[1993]a)The temperature difference causing heat transfer tends to zerob)The system receiving heat must be at a constant temperaturec)The system transferring out heat must be at a constant temperatured)Both interacting systems must beat constant temperaturesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A reversible heat transfer demands:[1993]a)The temperature difference causing heat transfer tends to zerob)The system receiving heat must be at a constant temperaturec)The system transferring out heat must be at a constant temperatured)Both interacting systems must beat constant temperaturesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A reversible heat transfer demands:[1993]a)The temperature difference causing heat transfer tends to zerob)The system receiving heat must be at a constant temperaturec)The system transferring out heat must be at a constant temperatured)Both interacting systems must beat constant temperaturesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A reversible heat transfer demands:[1993]a)The temperature difference causing heat transfer tends to zerob)The system receiving heat must be at a constant temperaturec)The system transferring out heat must be at a constant temperatured)Both interacting systems must beat constant temperaturesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A reversible heat transfer demands:[1993]a)The temperature difference causing heat transfer tends to zerob)The system receiving heat must be at a constant temperaturec)The system transferring out heat must be at a constant temperatured)Both interacting systems must beat constant temperaturesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A reversible heat transfer demands:[1993]a)The temperature difference causing heat transfer tends to zerob)The system receiving heat must be at a constant temperaturec)The system transferring out heat must be at a constant temperatured)Both interacting systems must beat constant temperaturesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A reversible heat transfer demands:[1993]a)The temperature difference causing heat transfer tends to zerob)The system receiving heat must be at a constant temperaturec)The system transferring out heat must be at a constant temperatured)Both interacting systems must beat constant temperaturesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A reversible heat transfer demands:[1993]a)The temperature difference causing heat transfer tends to zerob)The system receiving heat must be at a constant temperaturec)The system transferring out heat must be at a constant temperatured)Both interacting systems must beat constant temperaturesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A reversible heat transfer demands:[1993]a)The temperature difference causing heat transfer tends to zerob)The system receiving heat must be at a constant temperaturec)The system transferring out heat must be at a constant temperatured)Both interacting systems must beat constant temperaturesCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























