Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > difference between trade ,commerce and indust...
Start Learning for Free
difference between trade ,commerce and industry
Verified Answer
difference between trade ,commerce and industry
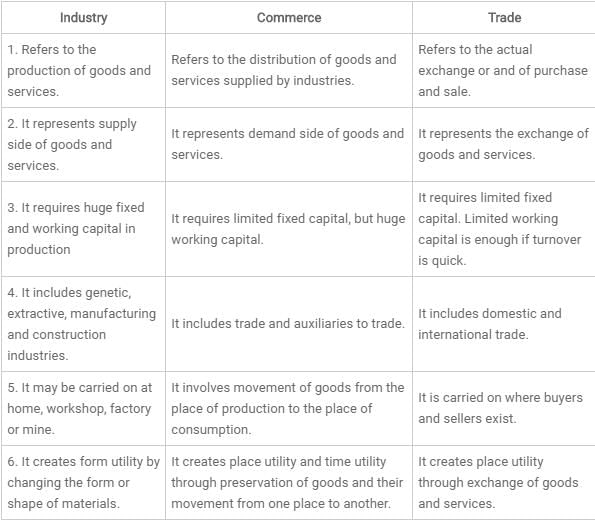
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 11 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 11 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
difference between trade ,commerce and industry
Trade:
Trade refers to the buying and selling of goods and services between two or more parties. It involves the exchange of goods and services for money or other goods and services. Trade can occur within a country or between countries. It plays a crucial role in the economy as it facilitates the flow of goods and services, promotes specialization, and allows countries to acquire the goods they cannot produce themselves.
Commerce:
Commerce is a broader term that encompasses various activities related to the exchange of goods and services. It includes trade, along with other activities such as transportation, banking, insurance, advertising, warehousing, and distribution. Commerce involves the entire process of buying and selling, from the production and marketing of goods to their distribution and consumption. It focuses on the overall management and organization of trade activities.
Industry:
Industry refers to the production of goods or the provision of services on a large scale. It involves the transformation of raw materials into finished products through various processes. Industries can be classified into different sectors such as manufacturing, construction, agriculture, mining, and services. They play a vital role in economic development by creating employment opportunities, generating income, and contributing to the country's GDP. Industries rely on trade and commerce to market and distribute their products to consumers.
Differences:
1. Scope: Trade specifically deals with the buying and selling of goods and services, while commerce encompasses a broader range of activities related to trade, including transportation, banking, and distribution. Industry, on the other hand, focuses on the production of goods or services.
2. Activities: Trade involves the exchange of goods or services for money or other goods and services. Commerce involves various activities such as advertising, warehousing, and transportation, which facilitate trade. Industry involves the production or provision of goods or services through manufacturing, construction, or other processes.
3. Scale: Trade can occur on a small scale, such as between individuals or local businesses, or on a large scale, such as international trade between countries. Commerce and industry generally operate on a larger scale, involving multiple businesses, organizations, and even countries.
4. Focus: Trade focuses on the exchange of goods and services between parties. Commerce focuses on the overall management and organization of trade activities. Industry focuses on the production or provision of goods or services.
5. Interdependence: Trade relies on commerce for various activities such as transportation, advertising, and distribution. Industry relies on trade and commerce for marketing and distributing its products to consumers.
In conclusion, trade, commerce, and industry are interconnected but have distinct differences. Trade involves the buying and selling of goods and services, while commerce encompasses a broader range of activities related to trade. Industry focuses on the production or provision of goods or services. They all play essential roles in the economy, contributing to economic growth, employment, and the overall well-being of societies.
Trade refers to the buying and selling of goods and services between two or more parties. It involves the exchange of goods and services for money or other goods and services. Trade can occur within a country or between countries. It plays a crucial role in the economy as it facilitates the flow of goods and services, promotes specialization, and allows countries to acquire the goods they cannot produce themselves.
Commerce:
Commerce is a broader term that encompasses various activities related to the exchange of goods and services. It includes trade, along with other activities such as transportation, banking, insurance, advertising, warehousing, and distribution. Commerce involves the entire process of buying and selling, from the production and marketing of goods to their distribution and consumption. It focuses on the overall management and organization of trade activities.
Industry:
Industry refers to the production of goods or the provision of services on a large scale. It involves the transformation of raw materials into finished products through various processes. Industries can be classified into different sectors such as manufacturing, construction, agriculture, mining, and services. They play a vital role in economic development by creating employment opportunities, generating income, and contributing to the country's GDP. Industries rely on trade and commerce to market and distribute their products to consumers.
Differences:
1. Scope: Trade specifically deals with the buying and selling of goods and services, while commerce encompasses a broader range of activities related to trade, including transportation, banking, and distribution. Industry, on the other hand, focuses on the production of goods or services.
2. Activities: Trade involves the exchange of goods or services for money or other goods and services. Commerce involves various activities such as advertising, warehousing, and transportation, which facilitate trade. Industry involves the production or provision of goods or services through manufacturing, construction, or other processes.
3. Scale: Trade can occur on a small scale, such as between individuals or local businesses, or on a large scale, such as international trade between countries. Commerce and industry generally operate on a larger scale, involving multiple businesses, organizations, and even countries.
4. Focus: Trade focuses on the exchange of goods and services between parties. Commerce focuses on the overall management and organization of trade activities. Industry focuses on the production or provision of goods or services.
5. Interdependence: Trade relies on commerce for various activities such as transportation, advertising, and distribution. Industry relies on trade and commerce for marketing and distributing its products to consumers.
In conclusion, trade, commerce, and industry are interconnected but have distinct differences. Trade involves the buying and selling of goods and services, while commerce encompasses a broader range of activities related to trade. Industry focuses on the production or provision of goods or services. They all play essential roles in the economy, contributing to economic growth, employment, and the overall well-being of societies.
Attention Class 11 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 11 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 11.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Similar Class 11 Doubts
difference between trade ,commerce and industry
Question Description
difference between trade ,commerce and industry for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about difference between trade ,commerce and industry covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for difference between trade ,commerce and industry.
difference between trade ,commerce and industry for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about difference between trade ,commerce and industry covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for difference between trade ,commerce and industry.
Solutions for difference between trade ,commerce and industry in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of difference between trade ,commerce and industry defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
difference between trade ,commerce and industry, a detailed solution for difference between trade ,commerce and industry has been provided alongside types of difference between trade ,commerce and industry theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice difference between trade ,commerce and industry tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























