JEE Exam > JEE Questions > Two identical non-conducting solid spheres of...
Start Learning for Free
Two identical non-conducting solid spheres of same mass and charge are suspended in air from a common point by two non-conducting, massless strings of same length. At equilibrium, the angle between the strings is α. The spheres are now immersed in a dielectric liquid of density 800 kg m−3 and dielectric constant 21. If the angle between the strings remains the same after the immersion, then
- a)electric force between the spheres remains unchanged
- b)electric force between the spheres reduces
- c)mass density of the spheres is 840 kg m−3
- d)the tension in the strings holding the spheres remains unchanged
Correct answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Two identical non-conducting solid spheres of same mass and charge are...
The net electric force on any sphere is lesser but by Coulomb law the force due to one sphere to another remain the same.
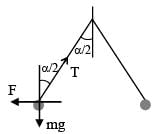
In equilibrium
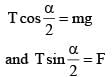
After immersed is dielectric liquid.
As given no change in angle α.
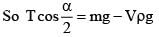
when ρ = 800 Kg/m3
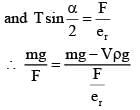
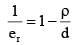
d = density of sphere
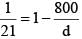
d = 840

In equilibrium
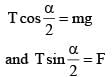
After immersed is dielectric liquid.
As given no change in angle α.
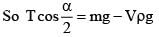
when ρ = 800 Kg/m3
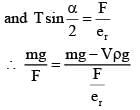
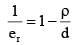
d = density of sphere
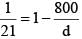
d = 840
Most Upvoted Answer
Two identical non-conducting solid spheres of same mass and charge are...
Since the spheres are identical and have the same charge, they will repel each other with equal force in all directions. This means that the tension in each string will be equal, and the system will be in equilibrium when the two strings form equal angles with the vertical axis.
Let's call this angle θ. Then, we can draw a free body diagram for one of the spheres:
[asy]
size(100);
draw((0,0)--(-1,0));
draw((-1,0)--(-1,-1));
draw((-1,0)--(-1,1));
draw((-1,-1)--(-1,-2));
draw((-1,1)--(-1,2));
draw((-1,-2)--(-1,-3));
draw((-1,2)--(-1,3));
draw((-1,-3)--(-1,-4));
draw((-1,3)--(-1,4));
label("$\theta$",(-0.3,-0.3),NE);
label("$T$",(0,-0.5),N);
label("$T$",(0,0.5),S);
label("$mg$",(0,-2),S);
draw(circle((0,-2),0.5));
[/asy]
The forces acting on the sphere are its weight (mg) and the tension in the strings (T). Since the sphere is in equilibrium, the net force on it must be zero. This means that the vertical components of the tension forces must balance the weight of the sphere:
2T cosθ = mg
Similarly, the horizontal components of the tension forces must balance each other:
T sinθ = T sin(180° - θ) = T sinθ
Therefore,
2T cosθ = T sinθ
2 cosθ = sinθ
tanθ = 2
θ = tan⁻¹(2) ≈ 63.4°
So the angle between the strings is approximately 63.4°.
Let's call this angle θ. Then, we can draw a free body diagram for one of the spheres:
[asy]
size(100);
draw((0,0)--(-1,0));
draw((-1,0)--(-1,-1));
draw((-1,0)--(-1,1));
draw((-1,-1)--(-1,-2));
draw((-1,1)--(-1,2));
draw((-1,-2)--(-1,-3));
draw((-1,2)--(-1,3));
draw((-1,-3)--(-1,-4));
draw((-1,3)--(-1,4));
label("$\theta$",(-0.3,-0.3),NE);
label("$T$",(0,-0.5),N);
label("$T$",(0,0.5),S);
label("$mg$",(0,-2),S);
draw(circle((0,-2),0.5));
[/asy]
The forces acting on the sphere are its weight (mg) and the tension in the strings (T). Since the sphere is in equilibrium, the net force on it must be zero. This means that the vertical components of the tension forces must balance the weight of the sphere:
2T cosθ = mg
Similarly, the horizontal components of the tension forces must balance each other:
T sinθ = T sin(180° - θ) = T sinθ
Therefore,
2T cosθ = T sinθ
2 cosθ = sinθ
tanθ = 2
θ = tan⁻¹(2) ≈ 63.4°
So the angle between the strings is approximately 63.4°.
Attention JEE Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed JEE study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in JEE.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
Two identical non-conducting solid spheres of same mass and charge are suspended in air from a common point by two non-conducting, massless strings of same length. At equilibrium, the angle between the strings is α. The spheres are now immersed in a dielectric liquid of density 800 kg m−3 and dielectric constant 21. If the angle between the strings remains the same after the immersion, then a)electric force between the spheres remains unchanged b)electric force between the spheres reduces c)mass density of the spheres is 840 kg m−3d)the tension in the strings holding the spheres remains unchangedCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Two identical non-conducting solid spheres of same mass and charge are suspended in air from a common point by two non-conducting, massless strings of same length. At equilibrium, the angle between the strings is α. The spheres are now immersed in a dielectric liquid of density 800 kg m−3 and dielectric constant 21. If the angle between the strings remains the same after the immersion, then a)electric force between the spheres remains unchanged b)electric force between the spheres reduces c)mass density of the spheres is 840 kg m−3d)the tension in the strings holding the spheres remains unchangedCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Two identical non-conducting solid spheres of same mass and charge are suspended in air from a common point by two non-conducting, massless strings of same length. At equilibrium, the angle between the strings is α. The spheres are now immersed in a dielectric liquid of density 800 kg m−3 and dielectric constant 21. If the angle between the strings remains the same after the immersion, then a)electric force between the spheres remains unchanged b)electric force between the spheres reduces c)mass density of the spheres is 840 kg m−3d)the tension in the strings holding the spheres remains unchangedCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Two identical non-conducting solid spheres of same mass and charge are suspended in air from a common point by two non-conducting, massless strings of same length. At equilibrium, the angle between the strings is α. The spheres are now immersed in a dielectric liquid of density 800 kg m−3 and dielectric constant 21. If the angle between the strings remains the same after the immersion, then a)electric force between the spheres remains unchanged b)electric force between the spheres reduces c)mass density of the spheres is 840 kg m−3d)the tension in the strings holding the spheres remains unchangedCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Two identical non-conducting solid spheres of same mass and charge are suspended in air from a common point by two non-conducting, massless strings of same length. At equilibrium, the angle between the strings is α. The spheres are now immersed in a dielectric liquid of density 800 kg m−3 and dielectric constant 21. If the angle between the strings remains the same after the immersion, then a)electric force between the spheres remains unchanged b)electric force between the spheres reduces c)mass density of the spheres is 840 kg m−3d)the tension in the strings holding the spheres remains unchangedCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Two identical non-conducting solid spheres of same mass and charge are suspended in air from a common point by two non-conducting, massless strings of same length. At equilibrium, the angle between the strings is α. The spheres are now immersed in a dielectric liquid of density 800 kg m−3 and dielectric constant 21. If the angle between the strings remains the same after the immersion, then a)electric force between the spheres remains unchanged b)electric force between the spheres reduces c)mass density of the spheres is 840 kg m−3d)the tension in the strings holding the spheres remains unchangedCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Two identical non-conducting solid spheres of same mass and charge are suspended in air from a common point by two non-conducting, massless strings of same length. At equilibrium, the angle between the strings is α. The spheres are now immersed in a dielectric liquid of density 800 kg m−3 and dielectric constant 21. If the angle between the strings remains the same after the immersion, then a)electric force between the spheres remains unchanged b)electric force between the spheres reduces c)mass density of the spheres is 840 kg m−3d)the tension in the strings holding the spheres remains unchangedCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Two identical non-conducting solid spheres of same mass and charge are suspended in air from a common point by two non-conducting, massless strings of same length. At equilibrium, the angle between the strings is α. The spheres are now immersed in a dielectric liquid of density 800 kg m−3 and dielectric constant 21. If the angle between the strings remains the same after the immersion, then a)electric force between the spheres remains unchanged b)electric force between the spheres reduces c)mass density of the spheres is 840 kg m−3d)the tension in the strings holding the spheres remains unchangedCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Two identical non-conducting solid spheres of same mass and charge are suspended in air from a common point by two non-conducting, massless strings of same length. At equilibrium, the angle between the strings is α. The spheres are now immersed in a dielectric liquid of density 800 kg m−3 and dielectric constant 21. If the angle between the strings remains the same after the immersion, then a)electric force between the spheres remains unchanged b)electric force between the spheres reduces c)mass density of the spheres is 840 kg m−3d)the tension in the strings holding the spheres remains unchangedCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Two identical non-conducting solid spheres of same mass and charge are suspended in air from a common point by two non-conducting, massless strings of same length. At equilibrium, the angle between the strings is α. The spheres are now immersed in a dielectric liquid of density 800 kg m−3 and dielectric constant 21. If the angle between the strings remains the same after the immersion, then a)electric force between the spheres remains unchanged b)electric force between the spheres reduces c)mass density of the spheres is 840 kg m−3d)the tension in the strings holding the spheres remains unchangedCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Two identical non-conducting solid spheres of same mass and charge are suspended in air from a common point by two non-conducting, massless strings of same length. At equilibrium, the angle between the strings is α. The spheres are now immersed in a dielectric liquid of density 800 kg m−3 and dielectric constant 21. If the angle between the strings remains the same after the immersion, then a)electric force between the spheres remains unchanged b)electric force between the spheres reduces c)mass density of the spheres is 840 kg m−3d)the tension in the strings holding the spheres remains unchangedCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Two identical non-conducting solid spheres of same mass and charge are suspended in air from a common point by two non-conducting, massless strings of same length. At equilibrium, the angle between the strings is α. The spheres are now immersed in a dielectric liquid of density 800 kg m−3 and dielectric constant 21. If the angle between the strings remains the same after the immersion, then a)electric force between the spheres remains unchanged b)electric force between the spheres reduces c)mass density of the spheres is 840 kg m−3d)the tension in the strings holding the spheres remains unchangedCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Two identical non-conducting solid spheres of same mass and charge are suspended in air from a common point by two non-conducting, massless strings of same length. At equilibrium, the angle between the strings is α. The spheres are now immersed in a dielectric liquid of density 800 kg m−3 and dielectric constant 21. If the angle between the strings remains the same after the immersion, then a)electric force between the spheres remains unchanged b)electric force between the spheres reduces c)mass density of the spheres is 840 kg m−3d)the tension in the strings holding the spheres remains unchangedCorrect answer is option 'A,C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























