Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Read the following text and answer the follo...
Start Learning for Free
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:
Atomic Absorption Spectrometer: The atomic absorption (AA) spectrometer is used to analyze metals at very low concentrations, typically in the parts per million (ppm) or parts per billion (ppb) ranges. A liquid sample containing dissolved material whose concentration is to be measured is aspirated into a thin, wide AA flame, or is introduced into a small carbon furnace which is heated to a high temperature.
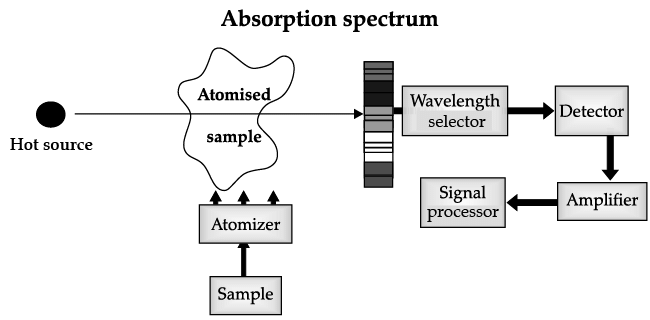
Basic Principle of AAS is the measurement of absorption of radiation by free atoms. The total amount of absorption depends on the number of free atoms present and the degree to which the free atoms absorb the radiation. At the high temperature of the AA flame, the sample is broken down into atoms using an atomizer and it is the concentration of these atoms that is measured.
Sample in the form of solution is used. It is broken up into a fine mist with the help of an atomizer.
When the mist reaches the flame, the intense heat breaks up the sample into its individual atoms.
When a photon coming out from the hot source hits an atom and the energy of the photon is equal to the gap between two electron energy levels of the atom, then the electron in the lower energy level absorb the photon and jumps up to the higher energy level. If the photon energy does not correspond to the difference between two energy levels, then the photon will not be absorbed (it may be scattered away).
Hence in the spectrum, the wavelength corresponding to the absorbed photons is observed as black lines as shown in the following spectrum of Hydrogen. The dark lines correspond to the frequencies of light those have been absorbed by the sample element.

Using this process, a source of photons (generally a white light) of various energies is used to obtain the absorption spectra of different materials and to identify them.
Q. How the sample for analysis is driven to atomic state in AAS?
- a)At a very high temperature, the sample is driven to its gaseous state
- b)Using an atomizer and then intense heating.
- c)By rotating the solution of the sample at a very high speed.
- d)None of the above
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the bas...
Sample in the form of solution is used. It is broken up into a fine mist with the help of an atomizer. When the mist reaches the flame, the intense heat breaks up the sample into its individual atoms.
View all questions of this test

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:Atomic Absorption Spectrometer: The atomic absorption (AA) spectrometer is used to analyze metals at very low concentrations, typically in the parts per million (ppm) or parts per billion (ppb) ranges. A liquid sample containing dissolved material whose concentration is to be measured is aspirated into a thin, wide AA flame, or is introduced into a small carbon furnace which is heated to a high temperature.Basic Principle of AAS is the measurement of absorption of radiation by free atoms. The total amount of absorption depends on the number of free atoms present and the degree to which the free atoms absorb the radiation. At the high temperature of the AA flame, the sample is broken down into atoms using an atomizer and it is the concentration of these atoms that is measured.Sample in the form of solution is used. It is broken up into a fine mist with the help of an atomizer.When the mist reaches the flame, the intense heat breaks up the sample into its individual atoms.When a photon coming out from the hot source hits an atom and the energy of the photon is equal to the gap between two electron energy levels of the atom, then the electron in the lower energy level absorb the photon and jumps up to the higher energy level. If the photon energy does not correspond to the difference between two energy levels, then the photon will not be absorbed (it may be scattered away).Hence in the spectrum, the wavelength corresponding to the absorbed photons is observed as black lines as shown in the following spectrum of Hydrogen. The dark lines correspond to the frequencies of light those have been absorbed by the sample element.Using this process, a source of photons (generally a white light) of various energies is used to obtain the absorption spectra of different materials and to identify them.Q. How the sample for analysis is driven to atomic state in AAS?a)At a very high temperature, the sample is driven to its gaseous stateb)Using an atomizer and then intense heating.c)By rotating the solution of the sample at a very high speed.d)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:Atomic Absorption Spectrometer: The atomic absorption (AA) spectrometer is used to analyze metals at very low concentrations, typically in the parts per million (ppm) or parts per billion (ppb) ranges. A liquid sample containing dissolved material whose concentration is to be measured is aspirated into a thin, wide AA flame, or is introduced into a small carbon furnace which is heated to a high temperature.Basic Principle of AAS is the measurement of absorption of radiation by free atoms. The total amount of absorption depends on the number of free atoms present and the degree to which the free atoms absorb the radiation. At the high temperature of the AA flame, the sample is broken down into atoms using an atomizer and it is the concentration of these atoms that is measured.Sample in the form of solution is used. It is broken up into a fine mist with the help of an atomizer.When the mist reaches the flame, the intense heat breaks up the sample into its individual atoms.When a photon coming out from the hot source hits an atom and the energy of the photon is equal to the gap between two electron energy levels of the atom, then the electron in the lower energy level absorb the photon and jumps up to the higher energy level. If the photon energy does not correspond to the difference between two energy levels, then the photon will not be absorbed (it may be scattered away).Hence in the spectrum, the wavelength corresponding to the absorbed photons is observed as black lines as shown in the following spectrum of Hydrogen. The dark lines correspond to the frequencies of light those have been absorbed by the sample element.Using this process, a source of photons (generally a white light) of various energies is used to obtain the absorption spectra of different materials and to identify them.Q. How the sample for analysis is driven to atomic state in AAS?a)At a very high temperature, the sample is driven to its gaseous stateb)Using an atomizer and then intense heating.c)By rotating the solution of the sample at a very high speed.d)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:Atomic Absorption Spectrometer: The atomic absorption (AA) spectrometer is used to analyze metals at very low concentrations, typically in the parts per million (ppm) or parts per billion (ppb) ranges. A liquid sample containing dissolved material whose concentration is to be measured is aspirated into a thin, wide AA flame, or is introduced into a small carbon furnace which is heated to a high temperature.Basic Principle of AAS is the measurement of absorption of radiation by free atoms. The total amount of absorption depends on the number of free atoms present and the degree to which the free atoms absorb the radiation. At the high temperature of the AA flame, the sample is broken down into atoms using an atomizer and it is the concentration of these atoms that is measured.Sample in the form of solution is used. It is broken up into a fine mist with the help of an atomizer.When the mist reaches the flame, the intense heat breaks up the sample into its individual atoms.When a photon coming out from the hot source hits an atom and the energy of the photon is equal to the gap between two electron energy levels of the atom, then the electron in the lower energy level absorb the photon and jumps up to the higher energy level. If the photon energy does not correspond to the difference between two energy levels, then the photon will not be absorbed (it may be scattered away).Hence in the spectrum, the wavelength corresponding to the absorbed photons is observed as black lines as shown in the following spectrum of Hydrogen. The dark lines correspond to the frequencies of light those have been absorbed by the sample element.Using this process, a source of photons (generally a white light) of various energies is used to obtain the absorption spectra of different materials and to identify them.Q. How the sample for analysis is driven to atomic state in AAS?a)At a very high temperature, the sample is driven to its gaseous stateb)Using an atomizer and then intense heating.c)By rotating the solution of the sample at a very high speed.d)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:Atomic Absorption Spectrometer: The atomic absorption (AA) spectrometer is used to analyze metals at very low concentrations, typically in the parts per million (ppm) or parts per billion (ppb) ranges. A liquid sample containing dissolved material whose concentration is to be measured is aspirated into a thin, wide AA flame, or is introduced into a small carbon furnace which is heated to a high temperature.Basic Principle of AAS is the measurement of absorption of radiation by free atoms. The total amount of absorption depends on the number of free atoms present and the degree to which the free atoms absorb the radiation. At the high temperature of the AA flame, the sample is broken down into atoms using an atomizer and it is the concentration of these atoms that is measured.Sample in the form of solution is used. It is broken up into a fine mist with the help of an atomizer.When the mist reaches the flame, the intense heat breaks up the sample into its individual atoms.When a photon coming out from the hot source hits an atom and the energy of the photon is equal to the gap between two electron energy levels of the atom, then the electron in the lower energy level absorb the photon and jumps up to the higher energy level. If the photon energy does not correspond to the difference between two energy levels, then the photon will not be absorbed (it may be scattered away).Hence in the spectrum, the wavelength corresponding to the absorbed photons is observed as black lines as shown in the following spectrum of Hydrogen. The dark lines correspond to the frequencies of light those have been absorbed by the sample element.Using this process, a source of photons (generally a white light) of various energies is used to obtain the absorption spectra of different materials and to identify them.Q. How the sample for analysis is driven to atomic state in AAS?a)At a very high temperature, the sample is driven to its gaseous stateb)Using an atomizer and then intense heating.c)By rotating the solution of the sample at a very high speed.d)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:Atomic Absorption Spectrometer: The atomic absorption (AA) spectrometer is used to analyze metals at very low concentrations, typically in the parts per million (ppm) or parts per billion (ppb) ranges. A liquid sample containing dissolved material whose concentration is to be measured is aspirated into a thin, wide AA flame, or is introduced into a small carbon furnace which is heated to a high temperature.Basic Principle of AAS is the measurement of absorption of radiation by free atoms. The total amount of absorption depends on the number of free atoms present and the degree to which the free atoms absorb the radiation. At the high temperature of the AA flame, the sample is broken down into atoms using an atomizer and it is the concentration of these atoms that is measured.Sample in the form of solution is used. It is broken up into a fine mist with the help of an atomizer.When the mist reaches the flame, the intense heat breaks up the sample into its individual atoms.When a photon coming out from the hot source hits an atom and the energy of the photon is equal to the gap between two electron energy levels of the atom, then the electron in the lower energy level absorb the photon and jumps up to the higher energy level. If the photon energy does not correspond to the difference between two energy levels, then the photon will not be absorbed (it may be scattered away).Hence in the spectrum, the wavelength corresponding to the absorbed photons is observed as black lines as shown in the following spectrum of Hydrogen. The dark lines correspond to the frequencies of light those have been absorbed by the sample element.Using this process, a source of photons (generally a white light) of various energies is used to obtain the absorption spectra of different materials and to identify them.Q. How the sample for analysis is driven to atomic state in AAS?a)At a very high temperature, the sample is driven to its gaseous stateb)Using an atomizer and then intense heating.c)By rotating the solution of the sample at a very high speed.d)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:Atomic Absorption Spectrometer: The atomic absorption (AA) spectrometer is used to analyze metals at very low concentrations, typically in the parts per million (ppm) or parts per billion (ppb) ranges. A liquid sample containing dissolved material whose concentration is to be measured is aspirated into a thin, wide AA flame, or is introduced into a small carbon furnace which is heated to a high temperature.Basic Principle of AAS is the measurement of absorption of radiation by free atoms. The total amount of absorption depends on the number of free atoms present and the degree to which the free atoms absorb the radiation. At the high temperature of the AA flame, the sample is broken down into atoms using an atomizer and it is the concentration of these atoms that is measured.Sample in the form of solution is used. It is broken up into a fine mist with the help of an atomizer.When the mist reaches the flame, the intense heat breaks up the sample into its individual atoms.When a photon coming out from the hot source hits an atom and the energy of the photon is equal to the gap between two electron energy levels of the atom, then the electron in the lower energy level absorb the photon and jumps up to the higher energy level. If the photon energy does not correspond to the difference between two energy levels, then the photon will not be absorbed (it may be scattered away).Hence in the spectrum, the wavelength corresponding to the absorbed photons is observed as black lines as shown in the following spectrum of Hydrogen. The dark lines correspond to the frequencies of light those have been absorbed by the sample element.Using this process, a source of photons (generally a white light) of various energies is used to obtain the absorption spectra of different materials and to identify them.Q. How the sample for analysis is driven to atomic state in AAS?a)At a very high temperature, the sample is driven to its gaseous stateb)Using an atomizer and then intense heating.c)By rotating the solution of the sample at a very high speed.d)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:Atomic Absorption Spectrometer: The atomic absorption (AA) spectrometer is used to analyze metals at very low concentrations, typically in the parts per million (ppm) or parts per billion (ppb) ranges. A liquid sample containing dissolved material whose concentration is to be measured is aspirated into a thin, wide AA flame, or is introduced into a small carbon furnace which is heated to a high temperature.Basic Principle of AAS is the measurement of absorption of radiation by free atoms. The total amount of absorption depends on the number of free atoms present and the degree to which the free atoms absorb the radiation. At the high temperature of the AA flame, the sample is broken down into atoms using an atomizer and it is the concentration of these atoms that is measured.Sample in the form of solution is used. It is broken up into a fine mist with the help of an atomizer.When the mist reaches the flame, the intense heat breaks up the sample into its individual atoms.When a photon coming out from the hot source hits an atom and the energy of the photon is equal to the gap between two electron energy levels of the atom, then the electron in the lower energy level absorb the photon and jumps up to the higher energy level. If the photon energy does not correspond to the difference between two energy levels, then the photon will not be absorbed (it may be scattered away).Hence in the spectrum, the wavelength corresponding to the absorbed photons is observed as black lines as shown in the following spectrum of Hydrogen. The dark lines correspond to the frequencies of light those have been absorbed by the sample element.Using this process, a source of photons (generally a white light) of various energies is used to obtain the absorption spectra of different materials and to identify them.Q. How the sample for analysis is driven to atomic state in AAS?a)At a very high temperature, the sample is driven to its gaseous stateb)Using an atomizer and then intense heating.c)By rotating the solution of the sample at a very high speed.d)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:Atomic Absorption Spectrometer: The atomic absorption (AA) spectrometer is used to analyze metals at very low concentrations, typically in the parts per million (ppm) or parts per billion (ppb) ranges. A liquid sample containing dissolved material whose concentration is to be measured is aspirated into a thin, wide AA flame, or is introduced into a small carbon furnace which is heated to a high temperature.Basic Principle of AAS is the measurement of absorption of radiation by free atoms. The total amount of absorption depends on the number of free atoms present and the degree to which the free atoms absorb the radiation. At the high temperature of the AA flame, the sample is broken down into atoms using an atomizer and it is the concentration of these atoms that is measured.Sample in the form of solution is used. It is broken up into a fine mist with the help of an atomizer.When the mist reaches the flame, the intense heat breaks up the sample into its individual atoms.When a photon coming out from the hot source hits an atom and the energy of the photon is equal to the gap between two electron energy levels of the atom, then the electron in the lower energy level absorb the photon and jumps up to the higher energy level. If the photon energy does not correspond to the difference between two energy levels, then the photon will not be absorbed (it may be scattered away).Hence in the spectrum, the wavelength corresponding to the absorbed photons is observed as black lines as shown in the following spectrum of Hydrogen. The dark lines correspond to the frequencies of light those have been absorbed by the sample element.Using this process, a source of photons (generally a white light) of various energies is used to obtain the absorption spectra of different materials and to identify them.Q. How the sample for analysis is driven to atomic state in AAS?a)At a very high temperature, the sample is driven to its gaseous stateb)Using an atomizer and then intense heating.c)By rotating the solution of the sample at a very high speed.d)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:Atomic Absorption Spectrometer: The atomic absorption (AA) spectrometer is used to analyze metals at very low concentrations, typically in the parts per million (ppm) or parts per billion (ppb) ranges. A liquid sample containing dissolved material whose concentration is to be measured is aspirated into a thin, wide AA flame, or is introduced into a small carbon furnace which is heated to a high temperature.Basic Principle of AAS is the measurement of absorption of radiation by free atoms. The total amount of absorption depends on the number of free atoms present and the degree to which the free atoms absorb the radiation. At the high temperature of the AA flame, the sample is broken down into atoms using an atomizer and it is the concentration of these atoms that is measured.Sample in the form of solution is used. It is broken up into a fine mist with the help of an atomizer.When the mist reaches the flame, the intense heat breaks up the sample into its individual atoms.When a photon coming out from the hot source hits an atom and the energy of the photon is equal to the gap between two electron energy levels of the atom, then the electron in the lower energy level absorb the photon and jumps up to the higher energy level. If the photon energy does not correspond to the difference between two energy levels, then the photon will not be absorbed (it may be scattered away).Hence in the spectrum, the wavelength corresponding to the absorbed photons is observed as black lines as shown in the following spectrum of Hydrogen. The dark lines correspond to the frequencies of light those have been absorbed by the sample element.Using this process, a source of photons (generally a white light) of various energies is used to obtain the absorption spectra of different materials and to identify them.Q. How the sample for analysis is driven to atomic state in AAS?a)At a very high temperature, the sample is driven to its gaseous stateb)Using an atomizer and then intense heating.c)By rotating the solution of the sample at a very high speed.d)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:Atomic Absorption Spectrometer: The atomic absorption (AA) spectrometer is used to analyze metals at very low concentrations, typically in the parts per million (ppm) or parts per billion (ppb) ranges. A liquid sample containing dissolved material whose concentration is to be measured is aspirated into a thin, wide AA flame, or is introduced into a small carbon furnace which is heated to a high temperature.Basic Principle of AAS is the measurement of absorption of radiation by free atoms. The total amount of absorption depends on the number of free atoms present and the degree to which the free atoms absorb the radiation. At the high temperature of the AA flame, the sample is broken down into atoms using an atomizer and it is the concentration of these atoms that is measured.Sample in the form of solution is used. It is broken up into a fine mist with the help of an atomizer.When the mist reaches the flame, the intense heat breaks up the sample into its individual atoms.When a photon coming out from the hot source hits an atom and the energy of the photon is equal to the gap between two electron energy levels of the atom, then the electron in the lower energy level absorb the photon and jumps up to the higher energy level. If the photon energy does not correspond to the difference between two energy levels, then the photon will not be absorbed (it may be scattered away).Hence in the spectrum, the wavelength corresponding to the absorbed photons is observed as black lines as shown in the following spectrum of Hydrogen. The dark lines correspond to the frequencies of light those have been absorbed by the sample element.Using this process, a source of photons (generally a white light) of various energies is used to obtain the absorption spectra of different materials and to identify them.Q. How the sample for analysis is driven to atomic state in AAS?a)At a very high temperature, the sample is driven to its gaseous stateb)Using an atomizer and then intense heating.c)By rotating the solution of the sample at a very high speed.d)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:Atomic Absorption Spectrometer: The atomic absorption (AA) spectrometer is used to analyze metals at very low concentrations, typically in the parts per million (ppm) or parts per billion (ppb) ranges. A liquid sample containing dissolved material whose concentration is to be measured is aspirated into a thin, wide AA flame, or is introduced into a small carbon furnace which is heated to a high temperature.Basic Principle of AAS is the measurement of absorption of radiation by free atoms. The total amount of absorption depends on the number of free atoms present and the degree to which the free atoms absorb the radiation. At the high temperature of the AA flame, the sample is broken down into atoms using an atomizer and it is the concentration of these atoms that is measured.Sample in the form of solution is used. It is broken up into a fine mist with the help of an atomizer.When the mist reaches the flame, the intense heat breaks up the sample into its individual atoms.When a photon coming out from the hot source hits an atom and the energy of the photon is equal to the gap between two electron energy levels of the atom, then the electron in the lower energy level absorb the photon and jumps up to the higher energy level. If the photon energy does not correspond to the difference between two energy levels, then the photon will not be absorbed (it may be scattered away).Hence in the spectrum, the wavelength corresponding to the absorbed photons is observed as black lines as shown in the following spectrum of Hydrogen. The dark lines correspond to the frequencies of light those have been absorbed by the sample element.Using this process, a source of photons (generally a white light) of various energies is used to obtain the absorption spectra of different materials and to identify them.Q. How the sample for analysis is driven to atomic state in AAS?a)At a very high temperature, the sample is driven to its gaseous stateb)Using an atomizer and then intense heating.c)By rotating the solution of the sample at a very high speed.d)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:Atomic Absorption Spectrometer: The atomic absorption (AA) spectrometer is used to analyze metals at very low concentrations, typically in the parts per million (ppm) or parts per billion (ppb) ranges. A liquid sample containing dissolved material whose concentration is to be measured is aspirated into a thin, wide AA flame, or is introduced into a small carbon furnace which is heated to a high temperature.Basic Principle of AAS is the measurement of absorption of radiation by free atoms. The total amount of absorption depends on the number of free atoms present and the degree to which the free atoms absorb the radiation. At the high temperature of the AA flame, the sample is broken down into atoms using an atomizer and it is the concentration of these atoms that is measured.Sample in the form of solution is used. It is broken up into a fine mist with the help of an atomizer.When the mist reaches the flame, the intense heat breaks up the sample into its individual atoms.When a photon coming out from the hot source hits an atom and the energy of the photon is equal to the gap between two electron energy levels of the atom, then the electron in the lower energy level absorb the photon and jumps up to the higher energy level. If the photon energy does not correspond to the difference between two energy levels, then the photon will not be absorbed (it may be scattered away).Hence in the spectrum, the wavelength corresponding to the absorbed photons is observed as black lines as shown in the following spectrum of Hydrogen. The dark lines correspond to the frequencies of light those have been absorbed by the sample element.Using this process, a source of photons (generally a white light) of various energies is used to obtain the absorption spectra of different materials and to identify them.Q. How the sample for analysis is driven to atomic state in AAS?a)At a very high temperature, the sample is driven to its gaseous stateb)Using an atomizer and then intense heating.c)By rotating the solution of the sample at a very high speed.d)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Read the following text and answer the following questions on the basis of the same:Atomic Absorption Spectrometer: The atomic absorption (AA) spectrometer is used to analyze metals at very low concentrations, typically in the parts per million (ppm) or parts per billion (ppb) ranges. A liquid sample containing dissolved material whose concentration is to be measured is aspirated into a thin, wide AA flame, or is introduced into a small carbon furnace which is heated to a high temperature.Basic Principle of AAS is the measurement of absorption of radiation by free atoms. The total amount of absorption depends on the number of free atoms present and the degree to which the free atoms absorb the radiation. At the high temperature of the AA flame, the sample is broken down into atoms using an atomizer and it is the concentration of these atoms that is measured.Sample in the form of solution is used. It is broken up into a fine mist with the help of an atomizer.When the mist reaches the flame, the intense heat breaks up the sample into its individual atoms.When a photon coming out from the hot source hits an atom and the energy of the photon is equal to the gap between two electron energy levels of the atom, then the electron in the lower energy level absorb the photon and jumps up to the higher energy level. If the photon energy does not correspond to the difference between two energy levels, then the photon will not be absorbed (it may be scattered away).Hence in the spectrum, the wavelength corresponding to the absorbed photons is observed as black lines as shown in the following spectrum of Hydrogen. The dark lines correspond to the frequencies of light those have been absorbed by the sample element.Using this process, a source of photons (generally a white light) of various energies is used to obtain the absorption spectra of different materials and to identify them.Q. How the sample for analysis is driven to atomic state in AAS?a)At a very high temperature, the sample is driven to its gaseous stateb)Using an atomizer and then intense heating.c)By rotating the solution of the sample at a very high speed.d)None of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















