Railways Exam > Railways Questions > The shear modulus of resilience of a materia...
Start Learning for Free
The shear modulus of resilience of a material is proportional to
- a)Shear Stress (Ss)
- b)S2s
- c)S3s
- d)√Ss
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The shear modulus of resilience of a material is proportional toa)She...
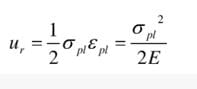
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The shear modulus of resilience of a material is proportional toa)She...
The shear modulus of resilience of a material is a measure of its ability to absorb and store energy when subjected to shear stress. It is defined as the amount of energy per unit volume that can be absorbed by a material without causing permanent deformation. The shear modulus of resilience is denoted as Rs.
The relationship between the shear modulus of resilience (Rs) and shear stress (Ss) can be expressed as:
Rs ∝ S^2s
This means that the shear modulus of resilience is directly proportional to the square of the shear stress. In other words, as the shear stress increases, the shear modulus of resilience also increases, and vice versa.
Explanation:
1. Shear Modulus of Resilience:
- The shear modulus of resilience is a material property that quantifies its ability to absorb and store energy when subjected to shear stress.
- It measures the amount of energy per unit volume that a material can absorb without undergoing permanent deformation.
2. Shear Stress:
- Shear stress is the force per unit area that acts parallel to the cross-section of a material.
- It is responsible for causing deformation or displacement of material layers along a plane parallel to the applied force.
3. Relationship:
- The relationship between the shear modulus of resilience and shear stress is determined by experimental observations and theoretical models.
- It has been found that the shear modulus of resilience is directly proportional to the square of the shear stress.
- Mathematically, this relationship can be expressed as: Rs ∝ S^2s, where Rs is the shear modulus of resilience and Ss is the shear stress.
4. Proportional Relationship:
- The proportional relationship between the shear modulus of resilience and the square of shear stress implies that an increase in shear stress will result in a corresponding increase in the shear modulus of resilience.
- This means that a material with a higher shear stress will have a higher ability to absorb and store energy without undergoing permanent deformation.
In conclusion, the shear modulus of resilience is proportional to the square of shear stress. This relationship indicates that as shear stress increases, the shear modulus of resilience also increases. It is important to note that this relationship is based on experimental observations and theoretical models, and the proportionality constant may vary for different materials.
The relationship between the shear modulus of resilience (Rs) and shear stress (Ss) can be expressed as:
Rs ∝ S^2s
This means that the shear modulus of resilience is directly proportional to the square of the shear stress. In other words, as the shear stress increases, the shear modulus of resilience also increases, and vice versa.
Explanation:
1. Shear Modulus of Resilience:
- The shear modulus of resilience is a material property that quantifies its ability to absorb and store energy when subjected to shear stress.
- It measures the amount of energy per unit volume that a material can absorb without undergoing permanent deformation.
2. Shear Stress:
- Shear stress is the force per unit area that acts parallel to the cross-section of a material.
- It is responsible for causing deformation or displacement of material layers along a plane parallel to the applied force.
3. Relationship:
- The relationship between the shear modulus of resilience and shear stress is determined by experimental observations and theoretical models.
- It has been found that the shear modulus of resilience is directly proportional to the square of the shear stress.
- Mathematically, this relationship can be expressed as: Rs ∝ S^2s, where Rs is the shear modulus of resilience and Ss is the shear stress.
4. Proportional Relationship:
- The proportional relationship between the shear modulus of resilience and the square of shear stress implies that an increase in shear stress will result in a corresponding increase in the shear modulus of resilience.
- This means that a material with a higher shear stress will have a higher ability to absorb and store energy without undergoing permanent deformation.
In conclusion, the shear modulus of resilience is proportional to the square of shear stress. This relationship indicates that as shear stress increases, the shear modulus of resilience also increases. It is important to note that this relationship is based on experimental observations and theoretical models, and the proportionality constant may vary for different materials.

|
Explore Courses for Railways exam
|

|
Similar Railways Doubts
The shear modulus of resilience of a material is proportional toa)Shear Stress (Ss)b)S2sc)S3sd)√SsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The shear modulus of resilience of a material is proportional toa)Shear Stress (Ss)b)S2sc)S3sd)√SsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Railways 2025 is part of Railways preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Railways exam syllabus. Information about The shear modulus of resilience of a material is proportional toa)Shear Stress (Ss)b)S2sc)S3sd)√SsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Railways 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The shear modulus of resilience of a material is proportional toa)Shear Stress (Ss)b)S2sc)S3sd)√SsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
The shear modulus of resilience of a material is proportional toa)Shear Stress (Ss)b)S2sc)S3sd)√SsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Railways 2025 is part of Railways preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Railways exam syllabus. Information about The shear modulus of resilience of a material is proportional toa)Shear Stress (Ss)b)S2sc)S3sd)√SsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Railways 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The shear modulus of resilience of a material is proportional toa)Shear Stress (Ss)b)S2sc)S3sd)√SsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The shear modulus of resilience of a material is proportional toa)Shear Stress (Ss)b)S2sc)S3sd)√SsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Railways.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Railways Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The shear modulus of resilience of a material is proportional toa)Shear Stress (Ss)b)S2sc)S3sd)√SsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The shear modulus of resilience of a material is proportional toa)Shear Stress (Ss)b)S2sc)S3sd)√SsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The shear modulus of resilience of a material is proportional toa)Shear Stress (Ss)b)S2sc)S3sd)√SsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The shear modulus of resilience of a material is proportional toa)Shear Stress (Ss)b)S2sc)S3sd)√SsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The shear modulus of resilience of a material is proportional toa)Shear Stress (Ss)b)S2sc)S3sd)√SsCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Railways tests.

|
Explore Courses for Railways exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























