Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > During inelastic collision of two particles, ...
Start Learning for Free
During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the following is conserved ?
- a)total linear momentum only
- b)total kinetic energy only
- c)both linear momentum and kinetic energy
- d)neither linear momentum nor kinetic energy
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the followin...
Conservation of Linear Momentum in Inelastic Collisions
In an inelastic collision, two particles collide and stick together, resulting in a loss of kinetic energy. During this type of collision, the total linear momentum is conserved, but the total kinetic energy is not conserved.
Definition of Linear Momentum
Linear momentum is a vector quantity that depends on the mass and velocity of an object. Mathematically, it is given by the product of mass and velocity:
Momentum (p) = mass (m) * velocity (v)
Conservation of Linear Momentum
According to Newton's third law of motion, the total linear momentum of an isolated system remains constant before and after the collision, provided no external forces act on the system. This principle is known as the conservation of linear momentum.
In an inelastic collision, the two particles collide and stick together, forming a single object. Since the particles stick together, they move with the same final velocity after the collision. As a result, the total momentum of the system before and after the collision remains the same.
Mathematical Representation
Let's consider two particles with masses m1 and m2, initially moving with velocities u1 and u2, respectively. After the collision, they stick together and move with a final velocity v. The conservation of linear momentum can be expressed as follows:
Initial momentum = Final momentum
(m1 * u1) + (m2 * u2) = (m1 + m2) * v
Conservation of Kinetic Energy
In an inelastic collision, the total kinetic energy of the system before the collision is not equal to the total kinetic energy after the collision. Some kinetic energy is lost during the collision, typically transforming into other forms of energy such as heat, sound, or deformation.
This loss of kinetic energy is primarily due to the fact that the two particles stick together instead of bouncing off each other. The energy required to permanently deform the particles or overcome intermolecular forces results in a decrease in kinetic energy.
Conclusion
In summary, during an inelastic collision of two particles, the total linear momentum is conserved, but the total kinetic energy is not conserved. This is because the particles stick together and move with a common final velocity, resulting in a loss of kinetic energy.
In an inelastic collision, two particles collide and stick together, resulting in a loss of kinetic energy. During this type of collision, the total linear momentum is conserved, but the total kinetic energy is not conserved.
Definition of Linear Momentum
Linear momentum is a vector quantity that depends on the mass and velocity of an object. Mathematically, it is given by the product of mass and velocity:
Momentum (p) = mass (m) * velocity (v)
Conservation of Linear Momentum
According to Newton's third law of motion, the total linear momentum of an isolated system remains constant before and after the collision, provided no external forces act on the system. This principle is known as the conservation of linear momentum.
In an inelastic collision, the two particles collide and stick together, forming a single object. Since the particles stick together, they move with the same final velocity after the collision. As a result, the total momentum of the system before and after the collision remains the same.
Mathematical Representation
Let's consider two particles with masses m1 and m2, initially moving with velocities u1 and u2, respectively. After the collision, they stick together and move with a final velocity v. The conservation of linear momentum can be expressed as follows:
Initial momentum = Final momentum
(m1 * u1) + (m2 * u2) = (m1 + m2) * v
Conservation of Kinetic Energy
In an inelastic collision, the total kinetic energy of the system before the collision is not equal to the total kinetic energy after the collision. Some kinetic energy is lost during the collision, typically transforming into other forms of energy such as heat, sound, or deformation.
This loss of kinetic energy is primarily due to the fact that the two particles stick together instead of bouncing off each other. The energy required to permanently deform the particles or overcome intermolecular forces results in a decrease in kinetic energy.
Conclusion
In summary, during an inelastic collision of two particles, the total linear momentum is conserved, but the total kinetic energy is not conserved. This is because the particles stick together and move with a common final velocity, resulting in a loss of kinetic energy.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the followin...
- Momentum is conserved in all collisions.
- In elastic collision, kinetic energy is also conserved.
- In inelastic collision, kinetic energy is not conserved. In perfectly inelastic collision, objects stick together after collision.
Perfectly elastic collision:
If law of conservation of momentum and that of kinetic energy hold good during the collision.
Inelastic collision:
If law of conservation of momentum holds good during collision while that of kinetic energy is not.
Coefficient of restitution (e)
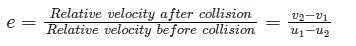
If law of conservation of momentum and that of kinetic energy hold good during the collision.
Inelastic collision:
If law of conservation of momentum holds good during collision while that of kinetic energy is not.
Coefficient of restitution (e)
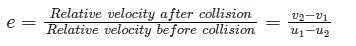
- For perfectly elastic collision, e = 1
- For inelastic collision, e < 1
- For perfectly inelastic collision, e = 0
Attention Mechanical Engineering Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Mechanical Engineering study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Mechanical Engineering.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Mechanical Engineering Doubts
During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the following is conserved ?a)total linear momentum onlyb)total kinetic energy onlyc)both linear momentum and kinetic energyd)neither linear momentum nor kinetic energyCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the following is conserved ?a)total linear momentum onlyb)total kinetic energy onlyc)both linear momentum and kinetic energyd)neither linear momentum nor kinetic energyCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the following is conserved ?a)total linear momentum onlyb)total kinetic energy onlyc)both linear momentum and kinetic energyd)neither linear momentum nor kinetic energyCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the following is conserved ?a)total linear momentum onlyb)total kinetic energy onlyc)both linear momentum and kinetic energyd)neither linear momentum nor kinetic energyCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the following is conserved ?a)total linear momentum onlyb)total kinetic energy onlyc)both linear momentum and kinetic energyd)neither linear momentum nor kinetic energyCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the following is conserved ?a)total linear momentum onlyb)total kinetic energy onlyc)both linear momentum and kinetic energyd)neither linear momentum nor kinetic energyCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the following is conserved ?a)total linear momentum onlyb)total kinetic energy onlyc)both linear momentum and kinetic energyd)neither linear momentum nor kinetic energyCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the following is conserved ?a)total linear momentum onlyb)total kinetic energy onlyc)both linear momentum and kinetic energyd)neither linear momentum nor kinetic energyCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the following is conserved ?a)total linear momentum onlyb)total kinetic energy onlyc)both linear momentum and kinetic energyd)neither linear momentum nor kinetic energyCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the following is conserved ?a)total linear momentum onlyb)total kinetic energy onlyc)both linear momentum and kinetic energyd)neither linear momentum nor kinetic energyCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the following is conserved ?a)total linear momentum onlyb)total kinetic energy onlyc)both linear momentum and kinetic energyd)neither linear momentum nor kinetic energyCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the following is conserved ?a)total linear momentum onlyb)total kinetic energy onlyc)both linear momentum and kinetic energyd)neither linear momentum nor kinetic energyCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice During inelastic collision of two particles, which one of the following is conserved ?a)total linear momentum onlyb)total kinetic energy onlyc)both linear momentum and kinetic energyd)neither linear momentum nor kinetic energyCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























