Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > Burmister considered the pavement structure a...
Start Learning for Free
Burmister considered the pavement structure as a homogeneous half space.
- a)infinite area with infinite depth
- b)finite area with infinite depth
- c)finite area with finite depth
- d)infinite area with finite depth
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
Burmister considered the pavement structure as a homogeneous half spac...
Burmister Method:
(i) This method is based on young's modulus of elasticity of different layers of pavement. As flexible pavement composed of layers and elastic modulus of top most layer is maximum.
Assumptions:
(i) This method is based on young's modulus of elasticity of different layers of pavement. As flexible pavement composed of layers and elastic modulus of top most layer is maximum.
Assumptions:
- Materials in each layer are isotropic, homogeneous, and elastic.
- Pavement forms a stiffer layer having higher value of E than that of subgrade.
- Layers are in constant contact.
- The surface layer is infinite in horizontal direction but finite in vertical direction means infinite area with finite depth.
This method gives the following design deflection values for pavements with different layers –
For flexible pavement:
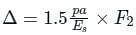
For rigid pavement:
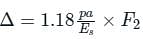
Where, p = contact pressure at road surface due to wheel load (kg/m2)
Es = modulus of elasticity of subgrade (kg/cm2), a = radius of contact area(cm) and
F2 = deflection factor which depends upon Es/EP and h/a, for single layer system F2 = 1.
For flexible pavement:
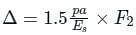
For rigid pavement:
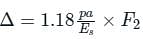
Where, p = contact pressure at road surface due to wheel load (kg/m2)
Es = modulus of elasticity of subgrade (kg/cm2), a = radius of contact area(cm) and
F2 = deflection factor which depends upon Es/EP and h/a, for single layer system F2 = 1.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Burmister considered the pavement structure as a homogeneous half spac...
Burmister's pavement structure assumption
In the field of pavement engineering, Burmister's assumption is a widely used simplification in the analysis of pavement structures. According to Burmister, the pavement structure can be considered as a homogeneous half space. This assumption helps in the mathematical modeling and analysis of the pavement response to various loading conditions.
Explanation of the answer
The correct answer to the given question is option 'D', which states that the pavement structure is considered to have an infinite area with finite depth. Let's understand why this option is the correct answer.
Infinite area
The assumption of an infinite area implies that the pavement structure extends indefinitely in all directions. This assumption is made to simplify the analysis and avoid the complexities of edge effects. In reality, pavement structures are typically constructed over a finite area, but for the purpose of analysis, an infinite area assumption is considered.
Finite depth
The assumption of a finite depth means that the pavement structure has a limited thickness or depth. This assumption is made to simplify the analysis and focus on the behavior of the pavement layers rather than considering the entire depth of the earth's crust. In reality, pavement structures consist of multiple layers with different thicknesses, but for the purpose of analysis, a simplified model with a finite depth is considered.
Significance of the assumption
The assumption of a homogeneous half space allows engineers to apply various mathematical and analytical methods to determine the response of the pavement structure under different loading conditions. By considering the pavement as a homogeneous half space, engineers can analyze the stress and strain distribution within the pavement layers, evaluate the pavement's structural capacity, and assess its performance under traffic loading.
Limitations of the assumption
While the assumption of a homogeneous half space simplifies the analysis, it does have certain limitations. In reality, pavement structures are subjected to non-uniform loading, temperature variations, moisture effects, and other environmental factors that can influence their behavior. Therefore, the assumption of a homogeneous half space may not fully capture the complex behavior of real pavements. Nonetheless, this assumption provides a useful starting point for pavement analysis and design.
Conclusion
In summary, Burmister's assumption considers the pavement structure as a homogeneous half space with an infinite area and finite depth. This assumption allows for simplified analysis and modeling of the pavement response to different loading conditions. While the assumption has its limitations, it provides a valuable framework for pavement engineers to evaluate the structural capacity and performance of pavements.
In the field of pavement engineering, Burmister's assumption is a widely used simplification in the analysis of pavement structures. According to Burmister, the pavement structure can be considered as a homogeneous half space. This assumption helps in the mathematical modeling and analysis of the pavement response to various loading conditions.
Explanation of the answer
The correct answer to the given question is option 'D', which states that the pavement structure is considered to have an infinite area with finite depth. Let's understand why this option is the correct answer.
Infinite area
The assumption of an infinite area implies that the pavement structure extends indefinitely in all directions. This assumption is made to simplify the analysis and avoid the complexities of edge effects. In reality, pavement structures are typically constructed over a finite area, but for the purpose of analysis, an infinite area assumption is considered.
Finite depth
The assumption of a finite depth means that the pavement structure has a limited thickness or depth. This assumption is made to simplify the analysis and focus on the behavior of the pavement layers rather than considering the entire depth of the earth's crust. In reality, pavement structures consist of multiple layers with different thicknesses, but for the purpose of analysis, a simplified model with a finite depth is considered.
Significance of the assumption
The assumption of a homogeneous half space allows engineers to apply various mathematical and analytical methods to determine the response of the pavement structure under different loading conditions. By considering the pavement as a homogeneous half space, engineers can analyze the stress and strain distribution within the pavement layers, evaluate the pavement's structural capacity, and assess its performance under traffic loading.
Limitations of the assumption
While the assumption of a homogeneous half space simplifies the analysis, it does have certain limitations. In reality, pavement structures are subjected to non-uniform loading, temperature variations, moisture effects, and other environmental factors that can influence their behavior. Therefore, the assumption of a homogeneous half space may not fully capture the complex behavior of real pavements. Nonetheless, this assumption provides a useful starting point for pavement analysis and design.
Conclusion
In summary, Burmister's assumption considers the pavement structure as a homogeneous half space with an infinite area and finite depth. This assumption allows for simplified analysis and modeling of the pavement response to different loading conditions. While the assumption has its limitations, it provides a valuable framework for pavement engineers to evaluate the structural capacity and performance of pavements.
Attention Civil Engineering (CE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Civil Engineering (CE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Civil Engineering (CE).

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
Burmister considered the pavement structure as a homogeneous half space.a)infinite area with infinite depthb)finite area with infinite depthc)finite area with finite depthd)infinite area with finite depthCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Burmister considered the pavement structure as a homogeneous half space.a)infinite area with infinite depthb)finite area with infinite depthc)finite area with finite depthd)infinite area with finite depthCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Burmister considered the pavement structure as a homogeneous half space.a)infinite area with infinite depthb)finite area with infinite depthc)finite area with finite depthd)infinite area with finite depthCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Burmister considered the pavement structure as a homogeneous half space.a)infinite area with infinite depthb)finite area with infinite depthc)finite area with finite depthd)infinite area with finite depthCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Burmister considered the pavement structure as a homogeneous half space.a)infinite area with infinite depthb)finite area with infinite depthc)finite area with finite depthd)infinite area with finite depthCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about Burmister considered the pavement structure as a homogeneous half space.a)infinite area with infinite depthb)finite area with infinite depthc)finite area with finite depthd)infinite area with finite depthCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Burmister considered the pavement structure as a homogeneous half space.a)infinite area with infinite depthb)finite area with infinite depthc)finite area with finite depthd)infinite area with finite depthCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Burmister considered the pavement structure as a homogeneous half space.a)infinite area with infinite depthb)finite area with infinite depthc)finite area with finite depthd)infinite area with finite depthCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Burmister considered the pavement structure as a homogeneous half space.a)infinite area with infinite depthb)finite area with infinite depthc)finite area with finite depthd)infinite area with finite depthCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Burmister considered the pavement structure as a homogeneous half space.a)infinite area with infinite depthb)finite area with infinite depthc)finite area with finite depthd)infinite area with finite depthCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Burmister considered the pavement structure as a homogeneous half space.a)infinite area with infinite depthb)finite area with infinite depthc)finite area with finite depthd)infinite area with finite depthCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Burmister considered the pavement structure as a homogeneous half space.a)infinite area with infinite depthb)finite area with infinite depthc)finite area with finite depthd)infinite area with finite depthCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Burmister considered the pavement structure as a homogeneous half space.a)infinite area with infinite depthb)finite area with infinite depthc)finite area with finite depthd)infinite area with finite depthCorrect answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























