JEE Exam > JEE Questions > Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Bea...
Start Learning for Free
Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Beaker A initially contained 0.15 mol of naphthalene (non-volatile) in 117 g of benzene and beaker B initially contained 31 g of an unknown compound (non-volatile, non-electrolytic) in 117 g of benzene. At equilibrium, beaker A is found to have lost 7.8 g of weight. Assume ideal behaviour of both solutions to answer the following question.
Now beaker B, at equilibrium, is replaced by another beaker C which contain 31 g of same solute as in B, but in different solvent X. Also moles of X in solution C is same as mol of benzene in solution B at equilibrium. When the container containing beakers A and C is closed again and allowed to attain equilibrium, beaker C has lost some weight. Which of the following can be said with guarantee ?
- a)The weight loss in C will be 7.8 g
- b)Vapour pressure of X is greater than the vapour pressure of benzene
- c)Moles of benzene migrated from C to A will be equal to the moles of benzene migrated from A to B in the first experiment
- d)Boiling point of solution C is greater than boiling point of solution A
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Beaker A initially contained...
for beaker A,
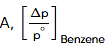
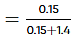
= 0.0967 (before equilibrium)
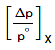 for solvent x
for solvent x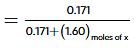
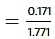
= 0.0965 (before equilibrium)
Relative lowering in vapour pressure is less over beaker C i.e., vapour pressure of X is more than vapour pressure of benzene.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Beaker A initially contained...
Understanding the Problem
In this scenario, we have two beakers with non-volatile solutes in benzene, and we analyze the vapor pressure changes as they reach equilibrium.
Beaker A Details
- Contains naphthalene, a non-volatile solute.
- Initially has 0.15 mol of naphthalene in 117 g of benzene.
- Weight loss of 7.8 g indicates the evaporation of benzene.
Beaker B to Beaker C Transition
- Beaker B is replaced with Beaker C, which contains the same solute as B but dissolved in a different solvent (X).
- The moles of X equal the moles of benzene in Beaker B at equilibrium.
Why Option B is Correct
- When Beaker C is introduced, it will also lose weight as the solvent (X) evaporates.
- The key point here is that since Beaker C has the same amount of solute but in a different solvent, the vapor pressure of solvent X must be higher than that of benzene for C to lose weight.
Key Reasons for the Answer
- **Vapor Pressure**: Since Beaker A lost weight due to the evaporation of benzene, for Beaker C to also lose weight, the vapor pressure of solvent X must be higher than that of benzene.
- **Weight Loss**: The weight loss in C will not necessarily be equal to 7.8 g, as it depends on the specific properties of solvent X.
Conclusion
In summary, the vapor pressure of solvent X must be greater than that of benzene for Beaker C to lose weight, confirming that option B is the correct answer.
In this scenario, we have two beakers with non-volatile solutes in benzene, and we analyze the vapor pressure changes as they reach equilibrium.
Beaker A Details
- Contains naphthalene, a non-volatile solute.
- Initially has 0.15 mol of naphthalene in 117 g of benzene.
- Weight loss of 7.8 g indicates the evaporation of benzene.
Beaker B to Beaker C Transition
- Beaker B is replaced with Beaker C, which contains the same solute as B but dissolved in a different solvent (X).
- The moles of X equal the moles of benzene in Beaker B at equilibrium.
Why Option B is Correct
- When Beaker C is introduced, it will also lose weight as the solvent (X) evaporates.
- The key point here is that since Beaker C has the same amount of solute but in a different solvent, the vapor pressure of solvent X must be higher than that of benzene for C to lose weight.
Key Reasons for the Answer
- **Vapor Pressure**: Since Beaker A lost weight due to the evaporation of benzene, for Beaker C to also lose weight, the vapor pressure of solvent X must be higher than that of benzene.
- **Weight Loss**: The weight loss in C will not necessarily be equal to 7.8 g, as it depends on the specific properties of solvent X.
Conclusion
In summary, the vapor pressure of solvent X must be greater than that of benzene for Beaker C to lose weight, confirming that option B is the correct answer.
Attention JEE Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed JEE study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in JEE.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Beaker A initially contained 0.15 mol of naphthalene (non-volatile) in 117 g of benzene and beaker B initially contained 31 g of an unknown compound (non-volatile, non-electrolytic) in 117 g of benzene. At equilibrium, beaker A is found to have lost 7.8 g of weight. Assume ideal behaviour of both solutions to answer the following question.Now beaker B, at equilibrium, is replaced by another beaker C which contain 31 g of same solute as in B, but in different solvent X. Also moles of X in solution C is same as mol of benzene in solution B at equilibrium. When the container containing beakers A and C is closed again and allowed to attain equilibrium, beaker C has lost some weight. Which of the following can be said with guarantee ?a)The weight loss in C will be 7.8 gb)Vapour pressure of X is greater than the vapour pressure of benzenec)Moles of benzene migrated from C to A will be equal to the moles of benzene migrated from A to B in the first experimentd)Boiling point of solution C is greater than boiling point of solution ACorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Beaker A initially contained 0.15 mol of naphthalene (non-volatile) in 117 g of benzene and beaker B initially contained 31 g of an unknown compound (non-volatile, non-electrolytic) in 117 g of benzene. At equilibrium, beaker A is found to have lost 7.8 g of weight. Assume ideal behaviour of both solutions to answer the following question.Now beaker B, at equilibrium, is replaced by another beaker C which contain 31 g of same solute as in B, but in different solvent X. Also moles of X in solution C is same as mol of benzene in solution B at equilibrium. When the container containing beakers A and C is closed again and allowed to attain equilibrium, beaker C has lost some weight. Which of the following can be said with guarantee ?a)The weight loss in C will be 7.8 gb)Vapour pressure of X is greater than the vapour pressure of benzenec)Moles of benzene migrated from C to A will be equal to the moles of benzene migrated from A to B in the first experimentd)Boiling point of solution C is greater than boiling point of solution ACorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Beaker A initially contained 0.15 mol of naphthalene (non-volatile) in 117 g of benzene and beaker B initially contained 31 g of an unknown compound (non-volatile, non-electrolytic) in 117 g of benzene. At equilibrium, beaker A is found to have lost 7.8 g of weight. Assume ideal behaviour of both solutions to answer the following question.Now beaker B, at equilibrium, is replaced by another beaker C which contain 31 g of same solute as in B, but in different solvent X. Also moles of X in solution C is same as mol of benzene in solution B at equilibrium. When the container containing beakers A and C is closed again and allowed to attain equilibrium, beaker C has lost some weight. Which of the following can be said with guarantee ?a)The weight loss in C will be 7.8 gb)Vapour pressure of X is greater than the vapour pressure of benzenec)Moles of benzene migrated from C to A will be equal to the moles of benzene migrated from A to B in the first experimentd)Boiling point of solution C is greater than boiling point of solution ACorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Beaker A initially contained 0.15 mol of naphthalene (non-volatile) in 117 g of benzene and beaker B initially contained 31 g of an unknown compound (non-volatile, non-electrolytic) in 117 g of benzene. At equilibrium, beaker A is found to have lost 7.8 g of weight. Assume ideal behaviour of both solutions to answer the following question.Now beaker B, at equilibrium, is replaced by another beaker C which contain 31 g of same solute as in B, but in different solvent X. Also moles of X in solution C is same as mol of benzene in solution B at equilibrium. When the container containing beakers A and C is closed again and allowed to attain equilibrium, beaker C has lost some weight. Which of the following can be said with guarantee ?a)The weight loss in C will be 7.8 gb)Vapour pressure of X is greater than the vapour pressure of benzenec)Moles of benzene migrated from C to A will be equal to the moles of benzene migrated from A to B in the first experimentd)Boiling point of solution C is greater than boiling point of solution ACorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Beaker A initially contained 0.15 mol of naphthalene (non-volatile) in 117 g of benzene and beaker B initially contained 31 g of an unknown compound (non-volatile, non-electrolytic) in 117 g of benzene. At equilibrium, beaker A is found to have lost 7.8 g of weight. Assume ideal behaviour of both solutions to answer the following question.Now beaker B, at equilibrium, is replaced by another beaker C which contain 31 g of same solute as in B, but in different solvent X. Also moles of X in solution C is same as mol of benzene in solution B at equilibrium. When the container containing beakers A and C is closed again and allowed to attain equilibrium, beaker C has lost some weight. Which of the following can be said with guarantee ?a)The weight loss in C will be 7.8 gb)Vapour pressure of X is greater than the vapour pressure of benzenec)Moles of benzene migrated from C to A will be equal to the moles of benzene migrated from A to B in the first experimentd)Boiling point of solution C is greater than boiling point of solution ACorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Beaker A initially contained 0.15 mol of naphthalene (non-volatile) in 117 g of benzene and beaker B initially contained 31 g of an unknown compound (non-volatile, non-electrolytic) in 117 g of benzene. At equilibrium, beaker A is found to have lost 7.8 g of weight. Assume ideal behaviour of both solutions to answer the following question.Now beaker B, at equilibrium, is replaced by another beaker C which contain 31 g of same solute as in B, but in different solvent X. Also moles of X in solution C is same as mol of benzene in solution B at equilibrium. When the container containing beakers A and C is closed again and allowed to attain equilibrium, beaker C has lost some weight. Which of the following can be said with guarantee ?a)The weight loss in C will be 7.8 gb)Vapour pressure of X is greater than the vapour pressure of benzenec)Moles of benzene migrated from C to A will be equal to the moles of benzene migrated from A to B in the first experimentd)Boiling point of solution C is greater than boiling point of solution ACorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Beaker A initially contained 0.15 mol of naphthalene (non-volatile) in 117 g of benzene and beaker B initially contained 31 g of an unknown compound (non-volatile, non-electrolytic) in 117 g of benzene. At equilibrium, beaker A is found to have lost 7.8 g of weight. Assume ideal behaviour of both solutions to answer the following question.Now beaker B, at equilibrium, is replaced by another beaker C which contain 31 g of same solute as in B, but in different solvent X. Also moles of X in solution C is same as mol of benzene in solution B at equilibrium. When the container containing beakers A and C is closed again and allowed to attain equilibrium, beaker C has lost some weight. Which of the following can be said with guarantee ?a)The weight loss in C will be 7.8 gb)Vapour pressure of X is greater than the vapour pressure of benzenec)Moles of benzene migrated from C to A will be equal to the moles of benzene migrated from A to B in the first experimentd)Boiling point of solution C is greater than boiling point of solution ACorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Beaker A initially contained 0.15 mol of naphthalene (non-volatile) in 117 g of benzene and beaker B initially contained 31 g of an unknown compound (non-volatile, non-electrolytic) in 117 g of benzene. At equilibrium, beaker A is found to have lost 7.8 g of weight. Assume ideal behaviour of both solutions to answer the following question.Now beaker B, at equilibrium, is replaced by another beaker C which contain 31 g of same solute as in B, but in different solvent X. Also moles of X in solution C is same as mol of benzene in solution B at equilibrium. When the container containing beakers A and C is closed again and allowed to attain equilibrium, beaker C has lost some weight. Which of the following can be said with guarantee ?a)The weight loss in C will be 7.8 gb)Vapour pressure of X is greater than the vapour pressure of benzenec)Moles of benzene migrated from C to A will be equal to the moles of benzene migrated from A to B in the first experimentd)Boiling point of solution C is greater than boiling point of solution ACorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Beaker A initially contained 0.15 mol of naphthalene (non-volatile) in 117 g of benzene and beaker B initially contained 31 g of an unknown compound (non-volatile, non-electrolytic) in 117 g of benzene. At equilibrium, beaker A is found to have lost 7.8 g of weight. Assume ideal behaviour of both solutions to answer the following question.Now beaker B, at equilibrium, is replaced by another beaker C which contain 31 g of same solute as in B, but in different solvent X. Also moles of X in solution C is same as mol of benzene in solution B at equilibrium. When the container containing beakers A and C is closed again and allowed to attain equilibrium, beaker C has lost some weight. Which of the following can be said with guarantee ?a)The weight loss in C will be 7.8 gb)Vapour pressure of X is greater than the vapour pressure of benzenec)Moles of benzene migrated from C to A will be equal to the moles of benzene migrated from A to B in the first experimentd)Boiling point of solution C is greater than boiling point of solution ACorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Beaker A initially contained 0.15 mol of naphthalene (non-volatile) in 117 g of benzene and beaker B initially contained 31 g of an unknown compound (non-volatile, non-electrolytic) in 117 g of benzene. At equilibrium, beaker A is found to have lost 7.8 g of weight. Assume ideal behaviour of both solutions to answer the following question.Now beaker B, at equilibrium, is replaced by another beaker C which contain 31 g of same solute as in B, but in different solvent X. Also moles of X in solution C is same as mol of benzene in solution B at equilibrium. When the container containing beakers A and C is closed again and allowed to attain equilibrium, beaker C has lost some weight. Which of the following can be said with guarantee ?a)The weight loss in C will be 7.8 gb)Vapour pressure of X is greater than the vapour pressure of benzenec)Moles of benzene migrated from C to A will be equal to the moles of benzene migrated from A to B in the first experimentd)Boiling point of solution C is greater than boiling point of solution ACorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Beaker A initially contained 0.15 mol of naphthalene (non-volatile) in 117 g of benzene and beaker B initially contained 31 g of an unknown compound (non-volatile, non-electrolytic) in 117 g of benzene. At equilibrium, beaker A is found to have lost 7.8 g of weight. Assume ideal behaviour of both solutions to answer the following question.Now beaker B, at equilibrium, is replaced by another beaker C which contain 31 g of same solute as in B, but in different solvent X. Also moles of X in solution C is same as mol of benzene in solution B at equilibrium. When the container containing beakers A and C is closed again and allowed to attain equilibrium, beaker C has lost some weight. Which of the following can be said with guarantee ?a)The weight loss in C will be 7.8 gb)Vapour pressure of X is greater than the vapour pressure of benzenec)Moles of benzene migrated from C to A will be equal to the moles of benzene migrated from A to B in the first experimentd)Boiling point of solution C is greater than boiling point of solution ACorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Beaker A initially contained 0.15 mol of naphthalene (non-volatile) in 117 g of benzene and beaker B initially contained 31 g of an unknown compound (non-volatile, non-electrolytic) in 117 g of benzene. At equilibrium, beaker A is found to have lost 7.8 g of weight. Assume ideal behaviour of both solutions to answer the following question.Now beaker B, at equilibrium, is replaced by another beaker C which contain 31 g of same solute as in B, but in different solvent X. Also moles of X in solution C is same as mol of benzene in solution B at equilibrium. When the container containing beakers A and C is closed again and allowed to attain equilibrium, beaker C has lost some weight. Which of the following can be said with guarantee ?a)The weight loss in C will be 7.8 gb)Vapour pressure of X is greater than the vapour pressure of benzenec)Moles of benzene migrated from C to A will be equal to the moles of benzene migrated from A to B in the first experimentd)Boiling point of solution C is greater than boiling point of solution ACorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Two beaker are placed in a sealed flask. Beaker A initially contained 0.15 mol of naphthalene (non-volatile) in 117 g of benzene and beaker B initially contained 31 g of an unknown compound (non-volatile, non-electrolytic) in 117 g of benzene. At equilibrium, beaker A is found to have lost 7.8 g of weight. Assume ideal behaviour of both solutions to answer the following question.Now beaker B, at equilibrium, is replaced by another beaker C which contain 31 g of same solute as in B, but in different solvent X. Also moles of X in solution C is same as mol of benzene in solution B at equilibrium. When the container containing beakers A and C is closed again and allowed to attain equilibrium, beaker C has lost some weight. Which of the following can be said with guarantee ?a)The weight loss in C will be 7.8 gb)Vapour pressure of X is greater than the vapour pressure of benzenec)Moles of benzene migrated from C to A will be equal to the moles of benzene migrated from A to B in the first experimentd)Boiling point of solution C is greater than boiling point of solution ACorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.






















