Banking Exams Exam > Banking Exams Questions > Direction: The given caselet shows the stati...
Start Learning for Free
Direction: The given caselet shows the statistics of India’s literacy rate according to the 2011 census. Study the caselet and answer the questions that follow.
The literacy rate is the basic and an important measure to indicate the development in a developing nation like India. It indicates the quality of life and the level of skill and awareness in the people of the nation. Higher level of literacy leads to awareness and improves the social and economic conditions of the country. The effective literacy rate in India is computed relating the population with 7 years of age and above, that can read and write with understanding, while the crude literacy rate is computed relating the total population of the country. According to the 2011 census of India, India’s literacy rate is reported as 74.04%, in which the female literacy rate is 65.46% and the male literacy rate is 82.14%. The adult literacy rate (above the age of 15 years) for males is 78.8%, while that of females is 59.3%. From the year 2001, the female literacy rate has increased by 22% and that of male has increased by 9%, indicating the narrowing of gender gap, thereby, providing an increment of 14% in the total literacy rate. Out of 35 states and union territories, only 3 states have a literacy rate higher than 90%, in which Kerala has the highest literacy rate of 94%, followed by Lakshadweep and Mizoram with a literacy rate of 91.8% and 91.3% respectively. 14 states have a literacy rate higher than 80%, while only 8 states have a literacy rate below 70%, with Bihar having the lowest literacy rate of 61.8%. The highest male and the female literacy rate of 96.1% and 92.1% respectively is also reported from the state of Kerala.
Q. By how much percentage has the gender gap in the literacy rate declined from 2001 to 2011?
- a)13.6%
- b)16.2%
- c)21.7%
- d)23.1%
- e)27.9%
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Direction: The given caselet shows the statistics of India’s literacy...
Female literacy rate in 2011 = 65.46%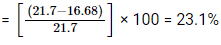
Increment from 2001 = 22%
⇒ (100 + 22)% of (Female literacy rate in 2001) = female literacy rate in 2011
⇒ Female literacy rate in 2001 = 65.46/1.22 = 53.66%
Male literacy rate in 2011 = 82.14%
Increment from 2001 = 9%
⇒ (100 + 9)% of (male literacy rate in 2001) = male literacy rate in 2011
⇒ Male literacy rate in 2001 = 82.14/1.09 = 75.36%
Gender gap in 2001 = 75.36 – 53.66 = 21.7
Gender gap in 2011 = 82.14 – 65.46 = 16.68
∴ Percentage decline in gender gap
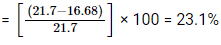
Hence, the correct option is (D).

|
Explore Courses for Banking Exams exam
|

|
Similar Banking Exams Doubts
Direction: The given caselet shows the statistics of India’s literacy rate according to the 2011 census. Study the caselet and answer the questions that follow.The literacy rate is the basic and an important measure to indicate the development in a developing nation like India. It indicates the quality of life and the level of skill and awareness in the people of the nation. Higher level of literacy leads to awareness and improves the social and economic conditions of the country. The effective literacy rate in India is computed relating the population with 7 years of age and above, that can read and write with understanding, while the crude literacy rate is computed relating the total population of the country. According to the 2011 census of India, India’s literacy rate is reported as 74.04%, in which the female literacy rate is 65.46% and the male literacy rate is 82.14%. The adult literacy rate (above the age of 15 years) for males is 78.8%, while that of females is 59.3%. From the year 2001, the female literacy rate has increased by 22% and that of male has increased by 9%, indicating the narrowing of gender gap, thereby, providing an increment of 14% in the total literacy rate. Out of 35 states and union territories, only 3 states have a literacy rate higher than 90%, in which Kerala has the highest literacy rate of 94%, followed by Lakshadweep and Mizoram with a literacy rate of 91.8% and 91.3% respectively. 14 states have a literacy rate higher than 80%, while only 8 states have a literacy rate below 70%, with Bihar having the lowest literacy rate of 61.8%. The highest male and the female literacy rate of 96.1% and 92.1% respectively is also reported from the state of Kerala.Q. By how much percentage has the gender gap in the literacy rate declined from 2001 to 2011?a)13.6%b)16.2%c)21.7%d)23.1%e)27.9%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Direction: The given caselet shows the statistics of India’s literacy rate according to the 2011 census. Study the caselet and answer the questions that follow.The literacy rate is the basic and an important measure to indicate the development in a developing nation like India. It indicates the quality of life and the level of skill and awareness in the people of the nation. Higher level of literacy leads to awareness and improves the social and economic conditions of the country. The effective literacy rate in India is computed relating the population with 7 years of age and above, that can read and write with understanding, while the crude literacy rate is computed relating the total population of the country. According to the 2011 census of India, India’s literacy rate is reported as 74.04%, in which the female literacy rate is 65.46% and the male literacy rate is 82.14%. The adult literacy rate (above the age of 15 years) for males is 78.8%, while that of females is 59.3%. From the year 2001, the female literacy rate has increased by 22% and that of male has increased by 9%, indicating the narrowing of gender gap, thereby, providing an increment of 14% in the total literacy rate. Out of 35 states and union territories, only 3 states have a literacy rate higher than 90%, in which Kerala has the highest literacy rate of 94%, followed by Lakshadweep and Mizoram with a literacy rate of 91.8% and 91.3% respectively. 14 states have a literacy rate higher than 80%, while only 8 states have a literacy rate below 70%, with Bihar having the lowest literacy rate of 61.8%. The highest male and the female literacy rate of 96.1% and 92.1% respectively is also reported from the state of Kerala.Q. By how much percentage has the gender gap in the literacy rate declined from 2001 to 2011?a)13.6%b)16.2%c)21.7%d)23.1%e)27.9%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Banking Exams 2025 is part of Banking Exams preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Banking Exams exam syllabus. Information about Direction: The given caselet shows the statistics of India’s literacy rate according to the 2011 census. Study the caselet and answer the questions that follow.The literacy rate is the basic and an important measure to indicate the development in a developing nation like India. It indicates the quality of life and the level of skill and awareness in the people of the nation. Higher level of literacy leads to awareness and improves the social and economic conditions of the country. The effective literacy rate in India is computed relating the population with 7 years of age and above, that can read and write with understanding, while the crude literacy rate is computed relating the total population of the country. According to the 2011 census of India, India’s literacy rate is reported as 74.04%, in which the female literacy rate is 65.46% and the male literacy rate is 82.14%. The adult literacy rate (above the age of 15 years) for males is 78.8%, while that of females is 59.3%. From the year 2001, the female literacy rate has increased by 22% and that of male has increased by 9%, indicating the narrowing of gender gap, thereby, providing an increment of 14% in the total literacy rate. Out of 35 states and union territories, only 3 states have a literacy rate higher than 90%, in which Kerala has the highest literacy rate of 94%, followed by Lakshadweep and Mizoram with a literacy rate of 91.8% and 91.3% respectively. 14 states have a literacy rate higher than 80%, while only 8 states have a literacy rate below 70%, with Bihar having the lowest literacy rate of 61.8%. The highest male and the female literacy rate of 96.1% and 92.1% respectively is also reported from the state of Kerala.Q. By how much percentage has the gender gap in the literacy rate declined from 2001 to 2011?a)13.6%b)16.2%c)21.7%d)23.1%e)27.9%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Banking Exams 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Direction: The given caselet shows the statistics of India’s literacy rate according to the 2011 census. Study the caselet and answer the questions that follow.The literacy rate is the basic and an important measure to indicate the development in a developing nation like India. It indicates the quality of life and the level of skill and awareness in the people of the nation. Higher level of literacy leads to awareness and improves the social and economic conditions of the country. The effective literacy rate in India is computed relating the population with 7 years of age and above, that can read and write with understanding, while the crude literacy rate is computed relating the total population of the country. According to the 2011 census of India, India’s literacy rate is reported as 74.04%, in which the female literacy rate is 65.46% and the male literacy rate is 82.14%. The adult literacy rate (above the age of 15 years) for males is 78.8%, while that of females is 59.3%. From the year 2001, the female literacy rate has increased by 22% and that of male has increased by 9%, indicating the narrowing of gender gap, thereby, providing an increment of 14% in the total literacy rate. Out of 35 states and union territories, only 3 states have a literacy rate higher than 90%, in which Kerala has the highest literacy rate of 94%, followed by Lakshadweep and Mizoram with a literacy rate of 91.8% and 91.3% respectively. 14 states have a literacy rate higher than 80%, while only 8 states have a literacy rate below 70%, with Bihar having the lowest literacy rate of 61.8%. The highest male and the female literacy rate of 96.1% and 92.1% respectively is also reported from the state of Kerala.Q. By how much percentage has the gender gap in the literacy rate declined from 2001 to 2011?a)13.6%b)16.2%c)21.7%d)23.1%e)27.9%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Direction: The given caselet shows the statistics of India’s literacy rate according to the 2011 census. Study the caselet and answer the questions that follow.The literacy rate is the basic and an important measure to indicate the development in a developing nation like India. It indicates the quality of life and the level of skill and awareness in the people of the nation. Higher level of literacy leads to awareness and improves the social and economic conditions of the country. The effective literacy rate in India is computed relating the population with 7 years of age and above, that can read and write with understanding, while the crude literacy rate is computed relating the total population of the country. According to the 2011 census of India, India’s literacy rate is reported as 74.04%, in which the female literacy rate is 65.46% and the male literacy rate is 82.14%. The adult literacy rate (above the age of 15 years) for males is 78.8%, while that of females is 59.3%. From the year 2001, the female literacy rate has increased by 22% and that of male has increased by 9%, indicating the narrowing of gender gap, thereby, providing an increment of 14% in the total literacy rate. Out of 35 states and union territories, only 3 states have a literacy rate higher than 90%, in which Kerala has the highest literacy rate of 94%, followed by Lakshadweep and Mizoram with a literacy rate of 91.8% and 91.3% respectively. 14 states have a literacy rate higher than 80%, while only 8 states have a literacy rate below 70%, with Bihar having the lowest literacy rate of 61.8%. The highest male and the female literacy rate of 96.1% and 92.1% respectively is also reported from the state of Kerala.Q. By how much percentage has the gender gap in the literacy rate declined from 2001 to 2011?a)13.6%b)16.2%c)21.7%d)23.1%e)27.9%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Banking Exams 2025 is part of Banking Exams preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Banking Exams exam syllabus. Information about Direction: The given caselet shows the statistics of India’s literacy rate according to the 2011 census. Study the caselet and answer the questions that follow.The literacy rate is the basic and an important measure to indicate the development in a developing nation like India. It indicates the quality of life and the level of skill and awareness in the people of the nation. Higher level of literacy leads to awareness and improves the social and economic conditions of the country. The effective literacy rate in India is computed relating the population with 7 years of age and above, that can read and write with understanding, while the crude literacy rate is computed relating the total population of the country. According to the 2011 census of India, India’s literacy rate is reported as 74.04%, in which the female literacy rate is 65.46% and the male literacy rate is 82.14%. The adult literacy rate (above the age of 15 years) for males is 78.8%, while that of females is 59.3%. From the year 2001, the female literacy rate has increased by 22% and that of male has increased by 9%, indicating the narrowing of gender gap, thereby, providing an increment of 14% in the total literacy rate. Out of 35 states and union territories, only 3 states have a literacy rate higher than 90%, in which Kerala has the highest literacy rate of 94%, followed by Lakshadweep and Mizoram with a literacy rate of 91.8% and 91.3% respectively. 14 states have a literacy rate higher than 80%, while only 8 states have a literacy rate below 70%, with Bihar having the lowest literacy rate of 61.8%. The highest male and the female literacy rate of 96.1% and 92.1% respectively is also reported from the state of Kerala.Q. By how much percentage has the gender gap in the literacy rate declined from 2001 to 2011?a)13.6%b)16.2%c)21.7%d)23.1%e)27.9%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Banking Exams 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Direction: The given caselet shows the statistics of India’s literacy rate according to the 2011 census. Study the caselet and answer the questions that follow.The literacy rate is the basic and an important measure to indicate the development in a developing nation like India. It indicates the quality of life and the level of skill and awareness in the people of the nation. Higher level of literacy leads to awareness and improves the social and economic conditions of the country. The effective literacy rate in India is computed relating the population with 7 years of age and above, that can read and write with understanding, while the crude literacy rate is computed relating the total population of the country. According to the 2011 census of India, India’s literacy rate is reported as 74.04%, in which the female literacy rate is 65.46% and the male literacy rate is 82.14%. The adult literacy rate (above the age of 15 years) for males is 78.8%, while that of females is 59.3%. From the year 2001, the female literacy rate has increased by 22% and that of male has increased by 9%, indicating the narrowing of gender gap, thereby, providing an increment of 14% in the total literacy rate. Out of 35 states and union territories, only 3 states have a literacy rate higher than 90%, in which Kerala has the highest literacy rate of 94%, followed by Lakshadweep and Mizoram with a literacy rate of 91.8% and 91.3% respectively. 14 states have a literacy rate higher than 80%, while only 8 states have a literacy rate below 70%, with Bihar having the lowest literacy rate of 61.8%. The highest male and the female literacy rate of 96.1% and 92.1% respectively is also reported from the state of Kerala.Q. By how much percentage has the gender gap in the literacy rate declined from 2001 to 2011?a)13.6%b)16.2%c)21.7%d)23.1%e)27.9%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Direction: The given caselet shows the statistics of India’s literacy rate according to the 2011 census. Study the caselet and answer the questions that follow.The literacy rate is the basic and an important measure to indicate the development in a developing nation like India. It indicates the quality of life and the level of skill and awareness in the people of the nation. Higher level of literacy leads to awareness and improves the social and economic conditions of the country. The effective literacy rate in India is computed relating the population with 7 years of age and above, that can read and write with understanding, while the crude literacy rate is computed relating the total population of the country. According to the 2011 census of India, India’s literacy rate is reported as 74.04%, in which the female literacy rate is 65.46% and the male literacy rate is 82.14%. The adult literacy rate (above the age of 15 years) for males is 78.8%, while that of females is 59.3%. From the year 2001, the female literacy rate has increased by 22% and that of male has increased by 9%, indicating the narrowing of gender gap, thereby, providing an increment of 14% in the total literacy rate. Out of 35 states and union territories, only 3 states have a literacy rate higher than 90%, in which Kerala has the highest literacy rate of 94%, followed by Lakshadweep and Mizoram with a literacy rate of 91.8% and 91.3% respectively. 14 states have a literacy rate higher than 80%, while only 8 states have a literacy rate below 70%, with Bihar having the lowest literacy rate of 61.8%. The highest male and the female literacy rate of 96.1% and 92.1% respectively is also reported from the state of Kerala.Q. By how much percentage has the gender gap in the literacy rate declined from 2001 to 2011?a)13.6%b)16.2%c)21.7%d)23.1%e)27.9%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Banking Exams.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Banking Exams Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Direction: The given caselet shows the statistics of India’s literacy rate according to the 2011 census. Study the caselet and answer the questions that follow.The literacy rate is the basic and an important measure to indicate the development in a developing nation like India. It indicates the quality of life and the level of skill and awareness in the people of the nation. Higher level of literacy leads to awareness and improves the social and economic conditions of the country. The effective literacy rate in India is computed relating the population with 7 years of age and above, that can read and write with understanding, while the crude literacy rate is computed relating the total population of the country. According to the 2011 census of India, India’s literacy rate is reported as 74.04%, in which the female literacy rate is 65.46% and the male literacy rate is 82.14%. The adult literacy rate (above the age of 15 years) for males is 78.8%, while that of females is 59.3%. From the year 2001, the female literacy rate has increased by 22% and that of male has increased by 9%, indicating the narrowing of gender gap, thereby, providing an increment of 14% in the total literacy rate. Out of 35 states and union territories, only 3 states have a literacy rate higher than 90%, in which Kerala has the highest literacy rate of 94%, followed by Lakshadweep and Mizoram with a literacy rate of 91.8% and 91.3% respectively. 14 states have a literacy rate higher than 80%, while only 8 states have a literacy rate below 70%, with Bihar having the lowest literacy rate of 61.8%. The highest male and the female literacy rate of 96.1% and 92.1% respectively is also reported from the state of Kerala.Q. By how much percentage has the gender gap in the literacy rate declined from 2001 to 2011?a)13.6%b)16.2%c)21.7%d)23.1%e)27.9%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Direction: The given caselet shows the statistics of India’s literacy rate according to the 2011 census. Study the caselet and answer the questions that follow.The literacy rate is the basic and an important measure to indicate the development in a developing nation like India. It indicates the quality of life and the level of skill and awareness in the people of the nation. Higher level of literacy leads to awareness and improves the social and economic conditions of the country. The effective literacy rate in India is computed relating the population with 7 years of age and above, that can read and write with understanding, while the crude literacy rate is computed relating the total population of the country. According to the 2011 census of India, India’s literacy rate is reported as 74.04%, in which the female literacy rate is 65.46% and the male literacy rate is 82.14%. The adult literacy rate (above the age of 15 years) for males is 78.8%, while that of females is 59.3%. From the year 2001, the female literacy rate has increased by 22% and that of male has increased by 9%, indicating the narrowing of gender gap, thereby, providing an increment of 14% in the total literacy rate. Out of 35 states and union territories, only 3 states have a literacy rate higher than 90%, in which Kerala has the highest literacy rate of 94%, followed by Lakshadweep and Mizoram with a literacy rate of 91.8% and 91.3% respectively. 14 states have a literacy rate higher than 80%, while only 8 states have a literacy rate below 70%, with Bihar having the lowest literacy rate of 61.8%. The highest male and the female literacy rate of 96.1% and 92.1% respectively is also reported from the state of Kerala.Q. By how much percentage has the gender gap in the literacy rate declined from 2001 to 2011?a)13.6%b)16.2%c)21.7%d)23.1%e)27.9%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Direction: The given caselet shows the statistics of India’s literacy rate according to the 2011 census. Study the caselet and answer the questions that follow.The literacy rate is the basic and an important measure to indicate the development in a developing nation like India. It indicates the quality of life and the level of skill and awareness in the people of the nation. Higher level of literacy leads to awareness and improves the social and economic conditions of the country. The effective literacy rate in India is computed relating the population with 7 years of age and above, that can read and write with understanding, while the crude literacy rate is computed relating the total population of the country. According to the 2011 census of India, India’s literacy rate is reported as 74.04%, in which the female literacy rate is 65.46% and the male literacy rate is 82.14%. The adult literacy rate (above the age of 15 years) for males is 78.8%, while that of females is 59.3%. From the year 2001, the female literacy rate has increased by 22% and that of male has increased by 9%, indicating the narrowing of gender gap, thereby, providing an increment of 14% in the total literacy rate. Out of 35 states and union territories, only 3 states have a literacy rate higher than 90%, in which Kerala has the highest literacy rate of 94%, followed by Lakshadweep and Mizoram with a literacy rate of 91.8% and 91.3% respectively. 14 states have a literacy rate higher than 80%, while only 8 states have a literacy rate below 70%, with Bihar having the lowest literacy rate of 61.8%. The highest male and the female literacy rate of 96.1% and 92.1% respectively is also reported from the state of Kerala.Q. By how much percentage has the gender gap in the literacy rate declined from 2001 to 2011?a)13.6%b)16.2%c)21.7%d)23.1%e)27.9%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Direction: The given caselet shows the statistics of India’s literacy rate according to the 2011 census. Study the caselet and answer the questions that follow.The literacy rate is the basic and an important measure to indicate the development in a developing nation like India. It indicates the quality of life and the level of skill and awareness in the people of the nation. Higher level of literacy leads to awareness and improves the social and economic conditions of the country. The effective literacy rate in India is computed relating the population with 7 years of age and above, that can read and write with understanding, while the crude literacy rate is computed relating the total population of the country. According to the 2011 census of India, India’s literacy rate is reported as 74.04%, in which the female literacy rate is 65.46% and the male literacy rate is 82.14%. The adult literacy rate (above the age of 15 years) for males is 78.8%, while that of females is 59.3%. From the year 2001, the female literacy rate has increased by 22% and that of male has increased by 9%, indicating the narrowing of gender gap, thereby, providing an increment of 14% in the total literacy rate. Out of 35 states and union territories, only 3 states have a literacy rate higher than 90%, in which Kerala has the highest literacy rate of 94%, followed by Lakshadweep and Mizoram with a literacy rate of 91.8% and 91.3% respectively. 14 states have a literacy rate higher than 80%, while only 8 states have a literacy rate below 70%, with Bihar having the lowest literacy rate of 61.8%. The highest male and the female literacy rate of 96.1% and 92.1% respectively is also reported from the state of Kerala.Q. By how much percentage has the gender gap in the literacy rate declined from 2001 to 2011?a)13.6%b)16.2%c)21.7%d)23.1%e)27.9%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Direction: The given caselet shows the statistics of India’s literacy rate according to the 2011 census. Study the caselet and answer the questions that follow.The literacy rate is the basic and an important measure to indicate the development in a developing nation like India. It indicates the quality of life and the level of skill and awareness in the people of the nation. Higher level of literacy leads to awareness and improves the social and economic conditions of the country. The effective literacy rate in India is computed relating the population with 7 years of age and above, that can read and write with understanding, while the crude literacy rate is computed relating the total population of the country. According to the 2011 census of India, India’s literacy rate is reported as 74.04%, in which the female literacy rate is 65.46% and the male literacy rate is 82.14%. The adult literacy rate (above the age of 15 years) for males is 78.8%, while that of females is 59.3%. From the year 2001, the female literacy rate has increased by 22% and that of male has increased by 9%, indicating the narrowing of gender gap, thereby, providing an increment of 14% in the total literacy rate. Out of 35 states and union territories, only 3 states have a literacy rate higher than 90%, in which Kerala has the highest literacy rate of 94%, followed by Lakshadweep and Mizoram with a literacy rate of 91.8% and 91.3% respectively. 14 states have a literacy rate higher than 80%, while only 8 states have a literacy rate below 70%, with Bihar having the lowest literacy rate of 61.8%. The highest male and the female literacy rate of 96.1% and 92.1% respectively is also reported from the state of Kerala.Q. By how much percentage has the gender gap in the literacy rate declined from 2001 to 2011?a)13.6%b)16.2%c)21.7%d)23.1%e)27.9%Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Banking Exams tests.

|
Explore Courses for Banking Exams exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























