Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > A shaft AC rotating at a constant speed carri...
Start Learning for Free
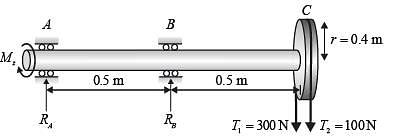
A shaft AC rotating at a constant speed carries a thin pulley of radius r = 0.4 m at the end C which drives a belt. A motor is coupled at the end A of the shaft such that it applies a torque M z about the shaft axis without causing any bending moment. The shaft is mounted on narrow frictionless bearings at A and B where AB = BC = L = 0.5 m. The taut and slack side tensions of the belt are T1 = 300 N and T2 = 100 N, respectively. The allowable shear stress for the shaft material is 80 MPa. The self-weights of the pulley and the shaft are negligible. Use the value of p available in the on-screen virtual calculator. Neglecting shock and fatigue loading and assuming maximum shear stress theory, the minimum required shaft diameter is _______ mm (round off to 2 decimal places).
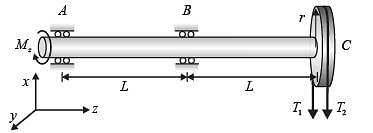

Correct answer is between '23.60,24.20'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
A shaft AC rotating at a constant speed carries a thin pulley of radiu...
Twisting moment is given by,
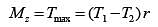
= (300 -100) x 0.4
= 80 Nm = 80 x 103 N.mm
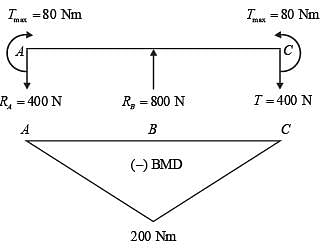
Taking moment about point A
∑MA = 0
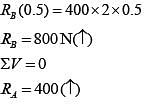
According to maximum shear stress theory,
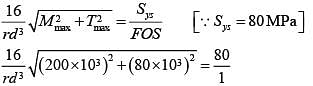
d = 23.9357 mm
Hence, the minimum required shaft diameter is 23.9357 mm.
Attention Mechanical Engineering Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Mechanical Engineering study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Mechanical Engineering.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Mechanical Engineering Doubts
A shaft AC rotating at a constant speed carries a thin pulley of radius r = 0.4 m at the end C which drives a belt. A motor is coupled at the end A of the shaft such that it applies a torque M z about the shaft axis without causing any bending moment. The shaft is mounted on narrow frictionless bearings at A and B where AB = BC = L = 0.5 m. The taut and slack side tensions of the belt are T1 = 300 N and T2 = 100 N, respectively. The allowable shear stress for the shaft material is 80 MPa. The self-weights of the pulley and the shaft are negligible. Use the value of p available in the on-screen virtual calculator. Neglecting shock and fatigue loading and assuming maximum shear stress theory, the minimum required shaft diameter is _______ mm (round off to 2 decimal places).Correct answer is between '23.60,24.20'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A shaft AC rotating at a constant speed carries a thin pulley of radius r = 0.4 m at the end C which drives a belt. A motor is coupled at the end A of the shaft such that it applies a torque M z about the shaft axis without causing any bending moment. The shaft is mounted on narrow frictionless bearings at A and B where AB = BC = L = 0.5 m. The taut and slack side tensions of the belt are T1 = 300 N and T2 = 100 N, respectively. The allowable shear stress for the shaft material is 80 MPa. The self-weights of the pulley and the shaft are negligible. Use the value of p available in the on-screen virtual calculator. Neglecting shock and fatigue loading and assuming maximum shear stress theory, the minimum required shaft diameter is _______ mm (round off to 2 decimal places).Correct answer is between '23.60,24.20'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A shaft AC rotating at a constant speed carries a thin pulley of radius r = 0.4 m at the end C which drives a belt. A motor is coupled at the end A of the shaft such that it applies a torque M z about the shaft axis without causing any bending moment. The shaft is mounted on narrow frictionless bearings at A and B where AB = BC = L = 0.5 m. The taut and slack side tensions of the belt are T1 = 300 N and T2 = 100 N, respectively. The allowable shear stress for the shaft material is 80 MPa. The self-weights of the pulley and the shaft are negligible. Use the value of p available in the on-screen virtual calculator. Neglecting shock and fatigue loading and assuming maximum shear stress theory, the minimum required shaft diameter is _______ mm (round off to 2 decimal places).Correct answer is between '23.60,24.20'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A shaft AC rotating at a constant speed carries a thin pulley of radius r = 0.4 m at the end C which drives a belt. A motor is coupled at the end A of the shaft such that it applies a torque M z about the shaft axis without causing any bending moment. The shaft is mounted on narrow frictionless bearings at A and B where AB = BC = L = 0.5 m. The taut and slack side tensions of the belt are T1 = 300 N and T2 = 100 N, respectively. The allowable shear stress for the shaft material is 80 MPa. The self-weights of the pulley and the shaft are negligible. Use the value of p available in the on-screen virtual calculator. Neglecting shock and fatigue loading and assuming maximum shear stress theory, the minimum required shaft diameter is _______ mm (round off to 2 decimal places).Correct answer is between '23.60,24.20'. Can you explain this answer?.
A shaft AC rotating at a constant speed carries a thin pulley of radius r = 0.4 m at the end C which drives a belt. A motor is coupled at the end A of the shaft such that it applies a torque M z about the shaft axis without causing any bending moment. The shaft is mounted on narrow frictionless bearings at A and B where AB = BC = L = 0.5 m. The taut and slack side tensions of the belt are T1 = 300 N and T2 = 100 N, respectively. The allowable shear stress for the shaft material is 80 MPa. The self-weights of the pulley and the shaft are negligible. Use the value of p available in the on-screen virtual calculator. Neglecting shock and fatigue loading and assuming maximum shear stress theory, the minimum required shaft diameter is _______ mm (round off to 2 decimal places).Correct answer is between '23.60,24.20'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about A shaft AC rotating at a constant speed carries a thin pulley of radius r = 0.4 m at the end C which drives a belt. A motor is coupled at the end A of the shaft such that it applies a torque M z about the shaft axis without causing any bending moment. The shaft is mounted on narrow frictionless bearings at A and B where AB = BC = L = 0.5 m. The taut and slack side tensions of the belt are T1 = 300 N and T2 = 100 N, respectively. The allowable shear stress for the shaft material is 80 MPa. The self-weights of the pulley and the shaft are negligible. Use the value of p available in the on-screen virtual calculator. Neglecting shock and fatigue loading and assuming maximum shear stress theory, the minimum required shaft diameter is _______ mm (round off to 2 decimal places).Correct answer is between '23.60,24.20'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A shaft AC rotating at a constant speed carries a thin pulley of radius r = 0.4 m at the end C which drives a belt. A motor is coupled at the end A of the shaft such that it applies a torque M z about the shaft axis without causing any bending moment. The shaft is mounted on narrow frictionless bearings at A and B where AB = BC = L = 0.5 m. The taut and slack side tensions of the belt are T1 = 300 N and T2 = 100 N, respectively. The allowable shear stress for the shaft material is 80 MPa. The self-weights of the pulley and the shaft are negligible. Use the value of p available in the on-screen virtual calculator. Neglecting shock and fatigue loading and assuming maximum shear stress theory, the minimum required shaft diameter is _______ mm (round off to 2 decimal places).Correct answer is between '23.60,24.20'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A shaft AC rotating at a constant speed carries a thin pulley of radius r = 0.4 m at the end C which drives a belt. A motor is coupled at the end A of the shaft such that it applies a torque M z about the shaft axis without causing any bending moment. The shaft is mounted on narrow frictionless bearings at A and B where AB = BC = L = 0.5 m. The taut and slack side tensions of the belt are T1 = 300 N and T2 = 100 N, respectively. The allowable shear stress for the shaft material is 80 MPa. The self-weights of the pulley and the shaft are negligible. Use the value of p available in the on-screen virtual calculator. Neglecting shock and fatigue loading and assuming maximum shear stress theory, the minimum required shaft diameter is _______ mm (round off to 2 decimal places).Correct answer is between '23.60,24.20'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A shaft AC rotating at a constant speed carries a thin pulley of radius r = 0.4 m at the end C which drives a belt. A motor is coupled at the end A of the shaft such that it applies a torque M z about the shaft axis without causing any bending moment. The shaft is mounted on narrow frictionless bearings at A and B where AB = BC = L = 0.5 m. The taut and slack side tensions of the belt are T1 = 300 N and T2 = 100 N, respectively. The allowable shear stress for the shaft material is 80 MPa. The self-weights of the pulley and the shaft are negligible. Use the value of p available in the on-screen virtual calculator. Neglecting shock and fatigue loading and assuming maximum shear stress theory, the minimum required shaft diameter is _______ mm (round off to 2 decimal places).Correct answer is between '23.60,24.20'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A shaft AC rotating at a constant speed carries a thin pulley of radius r = 0.4 m at the end C which drives a belt. A motor is coupled at the end A of the shaft such that it applies a torque M z about the shaft axis without causing any bending moment. The shaft is mounted on narrow frictionless bearings at A and B where AB = BC = L = 0.5 m. The taut and slack side tensions of the belt are T1 = 300 N and T2 = 100 N, respectively. The allowable shear stress for the shaft material is 80 MPa. The self-weights of the pulley and the shaft are negligible. Use the value of p available in the on-screen virtual calculator. Neglecting shock and fatigue loading and assuming maximum shear stress theory, the minimum required shaft diameter is _______ mm (round off to 2 decimal places).Correct answer is between '23.60,24.20'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A shaft AC rotating at a constant speed carries a thin pulley of radius r = 0.4 m at the end C which drives a belt. A motor is coupled at the end A of the shaft such that it applies a torque M z about the shaft axis without causing any bending moment. The shaft is mounted on narrow frictionless bearings at A and B where AB = BC = L = 0.5 m. The taut and slack side tensions of the belt are T1 = 300 N and T2 = 100 N, respectively. The allowable shear stress for the shaft material is 80 MPa. The self-weights of the pulley and the shaft are negligible. Use the value of p available in the on-screen virtual calculator. Neglecting shock and fatigue loading and assuming maximum shear stress theory, the minimum required shaft diameter is _______ mm (round off to 2 decimal places).Correct answer is between '23.60,24.20'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A shaft AC rotating at a constant speed carries a thin pulley of radius r = 0.4 m at the end C which drives a belt. A motor is coupled at the end A of the shaft such that it applies a torque M z about the shaft axis without causing any bending moment. The shaft is mounted on narrow frictionless bearings at A and B where AB = BC = L = 0.5 m. The taut and slack side tensions of the belt are T1 = 300 N and T2 = 100 N, respectively. The allowable shear stress for the shaft material is 80 MPa. The self-weights of the pulley and the shaft are negligible. Use the value of p available in the on-screen virtual calculator. Neglecting shock and fatigue loading and assuming maximum shear stress theory, the minimum required shaft diameter is _______ mm (round off to 2 decimal places).Correct answer is between '23.60,24.20'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A shaft AC rotating at a constant speed carries a thin pulley of radius r = 0.4 m at the end C which drives a belt. A motor is coupled at the end A of the shaft such that it applies a torque M z about the shaft axis without causing any bending moment. The shaft is mounted on narrow frictionless bearings at A and B where AB = BC = L = 0.5 m. The taut and slack side tensions of the belt are T1 = 300 N and T2 = 100 N, respectively. The allowable shear stress for the shaft material is 80 MPa. The self-weights of the pulley and the shaft are negligible. Use the value of p available in the on-screen virtual calculator. Neglecting shock and fatigue loading and assuming maximum shear stress theory, the minimum required shaft diameter is _______ mm (round off to 2 decimal places).Correct answer is between '23.60,24.20'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























