JEE Exam > JEE Questions > According to the valence bond theory, the hyb...
Start Learning for Free
According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of central metal atom is dsp2 for which of the following compounds?
- a)Na2[NiCl4]
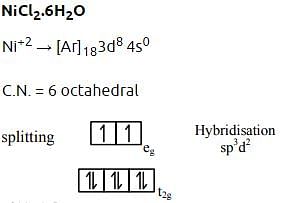
- b)NiCl2.6H2O
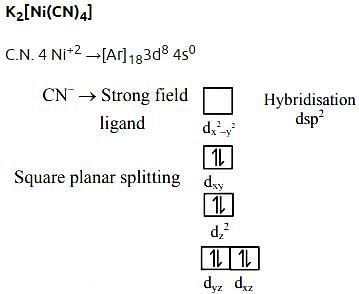
- c)K2[Ni(CN)4]
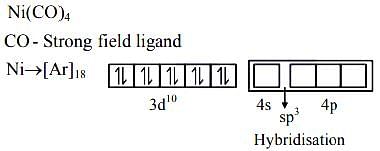
- d)[Ni(CO)4]
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of central met...
Valence Bond Theory and Hybridization
The valence bond theory is a model used to explain the formation of chemical bonds in terms of overlapping atomic orbitals. According to this theory, atoms form bonds by overlapping their valence orbitals, which results in the sharing of electron pairs. The concept of hybridization arises from the need to explain the observed geometries of molecules.
Hybridization in Coordination Compounds
Coordination compounds are formed when a central metal atom or ion is surrounded by ligands. The ligands are Lewis bases that donate electron pairs to the metal atom, forming coordinate covalent bonds. In coordination compounds, the central metal atom/ion often undergoes hybridization to explain its geometry.
Hybridization in K2[Ni(CN)4]
In K2[Ni(CN)4], the central metal atom is nickel (Ni). To determine the hybridization of the central atom, we need to consider the electronic configuration and geometry of the compound.
- The electronic configuration of Ni is [Ar] 3d8 4s2.
- The compound has a square planar geometry.
- In a square planar geometry, the central atom is bonded to four ligands in a plane, with bond angles of 90°.
Application of Valence Bond Theory
According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of the central metal atom is determined by the number and type of ligands attached to it. The hybridization of the central atom in K2[Ni(CN)4] can be determined as follows:
- The compound has four ligands (CN-) attached to the central Ni atom.
- Each CN- ligand donates a lone pair of electrons to form a coordinate covalent bond with Ni.
- The four ligands form sigma bonds with the Ni atom by overlapping their atomic orbitals.
- To accommodate the bonding and achieve the observed square planar geometry, the 3d, 4s, and 4p orbitals of Ni undergo hybridization.
Explanation of dsp2 Hybridization
In dsp2 hybridization, the central atom's 3d, 4s, and 4p orbitals combine to form five hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals are directed towards the corners of a trigonal bipyramidal geometry, with three orbitals lying in the xy-plane and the other two perpendicular to it.
In the case of K2[Ni(CN)4]:
- The 3d and 4s orbitals of Ni combine to form three hybrid orbitals.
- The 4p orbitals of Ni remain unhybridized.
- The three hybrid orbitals form sigma bonds with three CN- ligands, resulting in trigonal planar geometry.
- The remaining two 4p orbitals of Ni form pi bonds with the remaining two CN- ligands, resulting in a square planar geometry.
Therefore, the hybridization of the central atom (Ni) in K2[Ni(CN)4] is dsp2.
The valence bond theory is a model used to explain the formation of chemical bonds in terms of overlapping atomic orbitals. According to this theory, atoms form bonds by overlapping their valence orbitals, which results in the sharing of electron pairs. The concept of hybridization arises from the need to explain the observed geometries of molecules.
Hybridization in Coordination Compounds
Coordination compounds are formed when a central metal atom or ion is surrounded by ligands. The ligands are Lewis bases that donate electron pairs to the metal atom, forming coordinate covalent bonds. In coordination compounds, the central metal atom/ion often undergoes hybridization to explain its geometry.
Hybridization in K2[Ni(CN)4]
In K2[Ni(CN)4], the central metal atom is nickel (Ni). To determine the hybridization of the central atom, we need to consider the electronic configuration and geometry of the compound.
- The electronic configuration of Ni is [Ar] 3d8 4s2.
- The compound has a square planar geometry.
- In a square planar geometry, the central atom is bonded to four ligands in a plane, with bond angles of 90°.
Application of Valence Bond Theory
According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of the central metal atom is determined by the number and type of ligands attached to it. The hybridization of the central atom in K2[Ni(CN)4] can be determined as follows:
- The compound has four ligands (CN-) attached to the central Ni atom.
- Each CN- ligand donates a lone pair of electrons to form a coordinate covalent bond with Ni.
- The four ligands form sigma bonds with the Ni atom by overlapping their atomic orbitals.
- To accommodate the bonding and achieve the observed square planar geometry, the 3d, 4s, and 4p orbitals of Ni undergo hybridization.
Explanation of dsp2 Hybridization
In dsp2 hybridization, the central atom's 3d, 4s, and 4p orbitals combine to form five hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals are directed towards the corners of a trigonal bipyramidal geometry, with three orbitals lying in the xy-plane and the other two perpendicular to it.
In the case of K2[Ni(CN)4]:
- The 3d and 4s orbitals of Ni combine to form three hybrid orbitals.
- The 4p orbitals of Ni remain unhybridized.
- The three hybrid orbitals form sigma bonds with three CN- ligands, resulting in trigonal planar geometry.
- The remaining two 4p orbitals of Ni form pi bonds with the remaining two CN- ligands, resulting in a square planar geometry.
Therefore, the hybridization of the central atom (Ni) in K2[Ni(CN)4] is dsp2.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of central met...


|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of central metal atom is dsp2for which of the following compounds?a)Na2[NiCl4]b)NiCl2.6H2Oc)K2[Ni(CN)4]d)[Ni(CO)4]Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of central metal atom is dsp2for which of the following compounds?a)Na2[NiCl4]b)NiCl2.6H2Oc)K2[Ni(CN)4]d)[Ni(CO)4]Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of central metal atom is dsp2for which of the following compounds?a)Na2[NiCl4]b)NiCl2.6H2Oc)K2[Ni(CN)4]d)[Ni(CO)4]Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of central metal atom is dsp2for which of the following compounds?a)Na2[NiCl4]b)NiCl2.6H2Oc)K2[Ni(CN)4]d)[Ni(CO)4]Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of central metal atom is dsp2for which of the following compounds?a)Na2[NiCl4]b)NiCl2.6H2Oc)K2[Ni(CN)4]d)[Ni(CO)4]Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2025 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of central metal atom is dsp2for which of the following compounds?a)Na2[NiCl4]b)NiCl2.6H2Oc)K2[Ni(CN)4]d)[Ni(CO)4]Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of central metal atom is dsp2for which of the following compounds?a)Na2[NiCl4]b)NiCl2.6H2Oc)K2[Ni(CN)4]d)[Ni(CO)4]Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of central metal atom is dsp2for which of the following compounds?a)Na2[NiCl4]b)NiCl2.6H2Oc)K2[Ni(CN)4]d)[Ni(CO)4]Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of central metal atom is dsp2for which of the following compounds?a)Na2[NiCl4]b)NiCl2.6H2Oc)K2[Ni(CN)4]d)[Ni(CO)4]Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of central metal atom is dsp2for which of the following compounds?a)Na2[NiCl4]b)NiCl2.6H2Oc)K2[Ni(CN)4]d)[Ni(CO)4]Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of central metal atom is dsp2for which of the following compounds?a)Na2[NiCl4]b)NiCl2.6H2Oc)K2[Ni(CN)4]d)[Ni(CO)4]Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of central metal atom is dsp2for which of the following compounds?a)Na2[NiCl4]b)NiCl2.6H2Oc)K2[Ni(CN)4]d)[Ni(CO)4]Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice According to the valence bond theory, the hybridization of central metal atom is dsp2for which of the following compounds?a)Na2[NiCl4]b)NiCl2.6H2Oc)K2[Ni(CN)4]d)[Ni(CO)4]Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























