Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > In the geotechnical engineering lab, the pycn...
Start Learning for Free
In the geotechnical engineering lab, the pycnometer is used for the determination of
- a)Area of compaction
- b)Specific gravity
- c)Fineness of soil
- d)Void ratio
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
In the geotechnical engineering lab, the pycnometer is used for the de...
Concept:
Pycnometer method is used to determine specific gravity and water content both. This method is suitable for cohesionless soils.
Pycnometer is a glass jar of 1-liter capacity that is fitted at its top by a conical cap made of brass. It has a screw type cover and there is a small hole at its apex of 6 mm diameter.
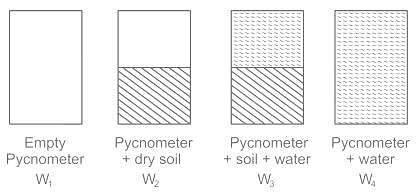
W1 = Mass of empty volume of pycnometer
W2 = Mass of pycnometer + Mass of moist sample
W3 = Mass of pycnometer + soil + water
W4 = Mass of pycnometer full of water
G, = Specific gravity of soil solids
Water content of the soil sample is given by:
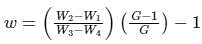
Specific gravity is usually reported at 27°C and it is given by:
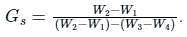
Pycnometer method is used to determine specific gravity and water content both. This method is suitable for cohesionless soils.
Pycnometer is a glass jar of 1-liter capacity that is fitted at its top by a conical cap made of brass. It has a screw type cover and there is a small hole at its apex of 6 mm diameter.

W1 = Mass of empty volume of pycnometer
W2 = Mass of pycnometer + Mass of moist sample
W3 = Mass of pycnometer + soil + water
W4 = Mass of pycnometer full of water
G, = Specific gravity of soil solids
Water content of the soil sample is given by:
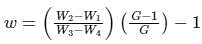
Specific gravity is usually reported at 27°C and it is given by:
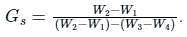
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
In the geotechnical engineering lab, the pycnometer is used for the de...
The Pycnometer in Geotechnical Engineering Lab
The pycnometer is a commonly used instrument in geotechnical engineering laboratories for the determination of specific gravity. Specific gravity is an important property of soil that helps in the characterization and classification of soils for various engineering applications.
What is Specific Gravity?
Specific gravity is defined as the ratio of the mass of a substance to the mass of an equal volume of water at a specified temperature. In the case of soils, it is the ratio of the mass of solids to the mass of an equal volume of water at a specified temperature.
Importance of Specific Gravity in Geotechnical Engineering
Specific gravity is a fundamental property of soil that provides insights into its composition, density, and behavior under different conditions. It is used in several geotechnical engineering calculations and analyses, including:
1. Soil Classification: Specific gravity is one of the parameters used in soil classification systems such as the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS) and the AASHTO soil classification system. It helps in distinguishing different soil types based on their mineral composition and density.
2. Soil Compaction: Specific gravity is used to determine the maximum dry density and optimum moisture content of a soil during compaction tests. This information is crucial for designing and constructing earthworks, embankments, and foundations.
3. Soil Mechanics: Specific gravity is used in various soil mechanics calculations, such as determining the void ratio, porosity, and degree of saturation of a soil sample. These properties are essential for understanding the behavior and strength of soils under different loading conditions.
How is Specific Gravity Determined using a Pycnometer?
The pycnometer is a small, glass container with a known volume. The specific gravity of a soil sample is determined by measuring the mass of the pycnometer filled with water and then filled with a known mass of the soil sample.
The specific gravity (G) is calculated using the following formula:
G = (W1 - W2) / (W3 - W2)
Where:
- W1 is the mass of the pycnometer filled with water
- W2 is the mass of the empty pycnometer
- W3 is the mass of the pycnometer filled with both water and soil
By knowing the specific gravity of a soil sample, engineers can make informed decisions regarding its suitability for various construction projects. It helps in determining the compaction characteristics, settlement potential, and shear strength of the soil, among other factors.
In conclusion, the pycnometer is a vital tool in geotechnical engineering labs for determining the specific gravity of soils. This property plays a crucial role in soil classification, compaction, and soil mechanics calculations, making it essential for understanding the behavior and performance of soils in engineering applications.
The pycnometer is a commonly used instrument in geotechnical engineering laboratories for the determination of specific gravity. Specific gravity is an important property of soil that helps in the characterization and classification of soils for various engineering applications.
What is Specific Gravity?
Specific gravity is defined as the ratio of the mass of a substance to the mass of an equal volume of water at a specified temperature. In the case of soils, it is the ratio of the mass of solids to the mass of an equal volume of water at a specified temperature.
Importance of Specific Gravity in Geotechnical Engineering
Specific gravity is a fundamental property of soil that provides insights into its composition, density, and behavior under different conditions. It is used in several geotechnical engineering calculations and analyses, including:
1. Soil Classification: Specific gravity is one of the parameters used in soil classification systems such as the Unified Soil Classification System (USCS) and the AASHTO soil classification system. It helps in distinguishing different soil types based on their mineral composition and density.
2. Soil Compaction: Specific gravity is used to determine the maximum dry density and optimum moisture content of a soil during compaction tests. This information is crucial for designing and constructing earthworks, embankments, and foundations.
3. Soil Mechanics: Specific gravity is used in various soil mechanics calculations, such as determining the void ratio, porosity, and degree of saturation of a soil sample. These properties are essential for understanding the behavior and strength of soils under different loading conditions.
How is Specific Gravity Determined using a Pycnometer?
The pycnometer is a small, glass container with a known volume. The specific gravity of a soil sample is determined by measuring the mass of the pycnometer filled with water and then filled with a known mass of the soil sample.
The specific gravity (G) is calculated using the following formula:
G = (W1 - W2) / (W3 - W2)
Where:
- W1 is the mass of the pycnometer filled with water
- W2 is the mass of the empty pycnometer
- W3 is the mass of the pycnometer filled with both water and soil
By knowing the specific gravity of a soil sample, engineers can make informed decisions regarding its suitability for various construction projects. It helps in determining the compaction characteristics, settlement potential, and shear strength of the soil, among other factors.
In conclusion, the pycnometer is a vital tool in geotechnical engineering labs for determining the specific gravity of soils. This property plays a crucial role in soil classification, compaction, and soil mechanics calculations, making it essential for understanding the behavior and performance of soils in engineering applications.
Attention Civil Engineering (CE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Civil Engineering (CE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Civil Engineering (CE).

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
In the geotechnical engineering lab, the pycnometer is used for the determination ofa)Area of compactionb)Specific gravityc)Fineness of soild)Void ratioCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
In the geotechnical engineering lab, the pycnometer is used for the determination ofa)Area of compactionb)Specific gravityc)Fineness of soild)Void ratioCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about In the geotechnical engineering lab, the pycnometer is used for the determination ofa)Area of compactionb)Specific gravityc)Fineness of soild)Void ratioCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In the geotechnical engineering lab, the pycnometer is used for the determination ofa)Area of compactionb)Specific gravityc)Fineness of soild)Void ratioCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
In the geotechnical engineering lab, the pycnometer is used for the determination ofa)Area of compactionb)Specific gravityc)Fineness of soild)Void ratioCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about In the geotechnical engineering lab, the pycnometer is used for the determination ofa)Area of compactionb)Specific gravityc)Fineness of soild)Void ratioCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In the geotechnical engineering lab, the pycnometer is used for the determination ofa)Area of compactionb)Specific gravityc)Fineness of soild)Void ratioCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In the geotechnical engineering lab, the pycnometer is used for the determination ofa)Area of compactionb)Specific gravityc)Fineness of soild)Void ratioCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In the geotechnical engineering lab, the pycnometer is used for the determination ofa)Area of compactionb)Specific gravityc)Fineness of soild)Void ratioCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In the geotechnical engineering lab, the pycnometer is used for the determination ofa)Area of compactionb)Specific gravityc)Fineness of soild)Void ratioCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In the geotechnical engineering lab, the pycnometer is used for the determination ofa)Area of compactionb)Specific gravityc)Fineness of soild)Void ratioCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In the geotechnical engineering lab, the pycnometer is used for the determination ofa)Area of compactionb)Specific gravityc)Fineness of soild)Void ratioCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In the geotechnical engineering lab, the pycnometer is used for the determination ofa)Area of compactionb)Specific gravityc)Fineness of soild)Void ratioCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.






















