Civil Engineering (CE) Exam > Civil Engineering (CE) Questions > The vertical angle between the longitudinal a...
Start Learning for Free
The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnetic needle and the horizontal line is referred as:
- a)Azimuth
- b)Declination
- c)Dip
- d)Bearing
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnet...
Explanation:
Dip:
- The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnetic needle and the horizontal line is referred to as "dip".
- It is an important parameter in compass surveying and navigation.
Azimuth, Declination, and Bearing:
- Azimuth refers to the angle measured clockwise from the north direction.
- Declination is the angle between the magnetic north and true north.
- Bearing is the direction or angle of a line measured in degrees from the north or south, east or west.
Significance of Dip:
- Dip is crucial in determining the accuracy of magnetic compass readings.
- It helps in accounting for the inclination of the magnetic field at a specific location.
- By considering dip, corrections can be made to ensure precise navigation and surveying.
Practical Applications:
- In compass surveying, dip correction is applied to ensure accurate measurements.
- Navigational instruments like gyrocompasses use dip correction to provide correct heading information.
- Understanding dip is essential for mining operations, where accurate compass readings are necessary for tunneling and exploration.
In conclusion, dip plays a significant role in compass-related activities by accounting for the vertical angle of a magnetic needle relative to the horizontal line. It is essential for ensuring accurate readings and navigation in various fields.
Dip:
- The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnetic needle and the horizontal line is referred to as "dip".
- It is an important parameter in compass surveying and navigation.
Azimuth, Declination, and Bearing:
- Azimuth refers to the angle measured clockwise from the north direction.
- Declination is the angle between the magnetic north and true north.
- Bearing is the direction or angle of a line measured in degrees from the north or south, east or west.
Significance of Dip:
- Dip is crucial in determining the accuracy of magnetic compass readings.
- It helps in accounting for the inclination of the magnetic field at a specific location.
- By considering dip, corrections can be made to ensure precise navigation and surveying.
Practical Applications:
- In compass surveying, dip correction is applied to ensure accurate measurements.
- Navigational instruments like gyrocompasses use dip correction to provide correct heading information.
- Understanding dip is essential for mining operations, where accurate compass readings are necessary for tunneling and exploration.
In conclusion, dip plays a significant role in compass-related activities by accounting for the vertical angle of a magnetic needle relative to the horizontal line. It is essential for ensuring accurate readings and navigation in various fields.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnet...
Dip
- It is the inclination of the magnetic needle with the horizontal. The dip is zero at the equator and the needle will remain horizontal.
- At a place near 70° north latitude and 96° west longitude, the dip will be 90°. This area is called the magnetic north pole. Similarly, near the south magnetic pole, the dip is 90°.
Declination
- It is the angle between the magnetic and geographic meridians or the angle in the horizontal plane between magnetic north and true north.
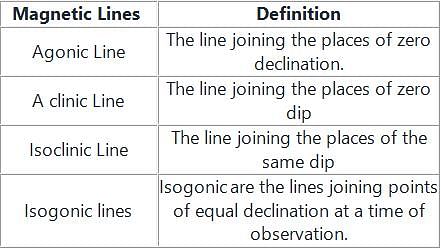
Different magnetic lines are as follows
Important Points
Isobar or pressure bulb
It is a stress contour or a line that connects all points below the ground surface at which the vertical pressure is the same.
Attention Civil Engineering (CE) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Civil Engineering (CE) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Civil Engineering (CE).

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Similar Civil Engineering (CE) Doubts
The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnetic needle and the horizontal line is referred as:a)Azimuthb)Declinationc)Dipd)BearingCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnetic needle and the horizontal line is referred as:a)Azimuthb)Declinationc)Dipd)BearingCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnetic needle and the horizontal line is referred as:a)Azimuthb)Declinationc)Dipd)BearingCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnetic needle and the horizontal line is referred as:a)Azimuthb)Declinationc)Dipd)BearingCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnetic needle and the horizontal line is referred as:a)Azimuthb)Declinationc)Dipd)BearingCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 is part of Civil Engineering (CE) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Civil Engineering (CE) exam syllabus. Information about The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnetic needle and the horizontal line is referred as:a)Azimuthb)Declinationc)Dipd)BearingCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Civil Engineering (CE) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnetic needle and the horizontal line is referred as:a)Azimuthb)Declinationc)Dipd)BearingCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnetic needle and the horizontal line is referred as:a)Azimuthb)Declinationc)Dipd)BearingCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Civil Engineering (CE).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Civil Engineering (CE) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnetic needle and the horizontal line is referred as:a)Azimuthb)Declinationc)Dipd)BearingCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnetic needle and the horizontal line is referred as:a)Azimuthb)Declinationc)Dipd)BearingCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnetic needle and the horizontal line is referred as:a)Azimuthb)Declinationc)Dipd)BearingCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnetic needle and the horizontal line is referred as:a)Azimuthb)Declinationc)Dipd)BearingCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The vertical angle between the longitudinal axis of a suspended magnetic needle and the horizontal line is referred as:a)Azimuthb)Declinationc)Dipd)BearingCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Civil Engineering (CE) tests.

|
Explore Courses for Civil Engineering (CE) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























