Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a serie...
Start Learning for Free
A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipated over a cycle. Under what condition is (i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit, (ii) maximum power dissipated in the circuit ?
Verified Answer
A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the...
Ans.
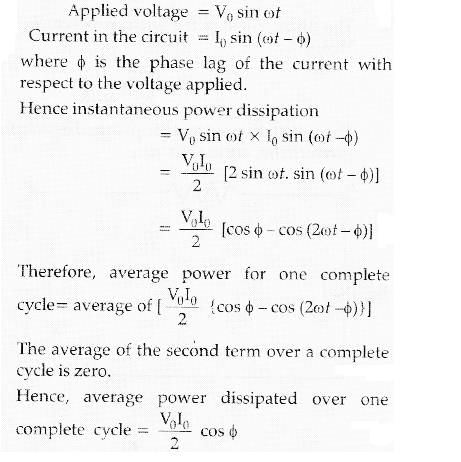

 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 12 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 12 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the...
Derivation of Average Power Dissipated in a Series LCR Circuit:
In a series LCR circuit, a voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied. The circuit consists of an inductor (L), a capacitor (C), and a resistor (R). We need to derive the expression for the average power dissipated over a cycle.
1. Instantaneous Power Dissipation:
The instantaneous power dissipated in the series LCR circuit can be calculated using the formula:
P(t) = V(t) * I(t)
where P(t) is the instantaneous power, V(t) is the voltage across the circuit, and I(t) is the current flowing through the circuit.
Since the voltage across the LCR circuit is given as V(t) = V0 sin ωt, and the current can be represented as I(t) = I0 sin (ωt + φ), where I0 is the maximum current and φ is the phase difference between the voltage and current, we can rewrite the equation for instantaneous power as:
P(t) = V0 sin ωt * I0 sin (ωt + φ)
2. Average Power Dissipation:
The average power dissipated over a cycle can be determined by integrating the instantaneous power over one complete cycle and then dividing it by the period of the waveform.
3. Integration of the Instantaneous Power:
Integrating the product of sin functions can be simplified by using the trigonometric identity:
sin α sin β = 1/2 [cos(α - β) - cos(α + β)]
Applying this identity to the equation for instantaneous power, we get:
P(t) = (V0 * I0 / 2) [cos φ - cos (2ωt + φ)]
4. Average Power Dissipation:
To find the average power dissipated, we need to integrate the instantaneous power over one complete cycle and divide by the period T.
Integrating over one complete cycle (0 to T), we get:
∫[0 to T] P(t) dt = (V0 * I0 / 2) [∫[0 to T] cos φ dt - ∫[0 to T] cos (2ωt + φ) dt]
The first integral on the right-hand side gives us:
∫[0 to T] cos φ dt = φT
The second integral on the right-hand side gives us:
∫[0 to T] cos (2ωt + φ) dt = 0
Since the integral of cos (2ωt + φ) over one complete cycle is zero, the average power dissipated over a cycle becomes:
P_avg = (V0 * I0 / 2) * φT / T = (V0 * I0 / 2) φ
Conditions for Power Dissipation:
(i) No Power Dissipated:
No power is dissipated when the phase difference between voltage and current is such that cos φ = 1. This occurs when the circuit is purely resistive (R) and there is no reactance from the inductor (L) or capacitor (C). In this case, the current is in phase with the voltage, and power is not dissipated.
(ii) Maximum Power Dissipated:
Maximum power
In a series LCR circuit, a voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied. The circuit consists of an inductor (L), a capacitor (C), and a resistor (R). We need to derive the expression for the average power dissipated over a cycle.
1. Instantaneous Power Dissipation:
The instantaneous power dissipated in the series LCR circuit can be calculated using the formula:
P(t) = V(t) * I(t)
where P(t) is the instantaneous power, V(t) is the voltage across the circuit, and I(t) is the current flowing through the circuit.
Since the voltage across the LCR circuit is given as V(t) = V0 sin ωt, and the current can be represented as I(t) = I0 sin (ωt + φ), where I0 is the maximum current and φ is the phase difference between the voltage and current, we can rewrite the equation for instantaneous power as:
P(t) = V0 sin ωt * I0 sin (ωt + φ)
2. Average Power Dissipation:
The average power dissipated over a cycle can be determined by integrating the instantaneous power over one complete cycle and then dividing it by the period of the waveform.
3. Integration of the Instantaneous Power:
Integrating the product of sin functions can be simplified by using the trigonometric identity:
sin α sin β = 1/2 [cos(α - β) - cos(α + β)]
Applying this identity to the equation for instantaneous power, we get:
P(t) = (V0 * I0 / 2) [cos φ - cos (2ωt + φ)]
4. Average Power Dissipation:
To find the average power dissipated, we need to integrate the instantaneous power over one complete cycle and divide by the period T.
Integrating over one complete cycle (0 to T), we get:
∫[0 to T] P(t) dt = (V0 * I0 / 2) [∫[0 to T] cos φ dt - ∫[0 to T] cos (2ωt + φ) dt]
The first integral on the right-hand side gives us:
∫[0 to T] cos φ dt = φT
The second integral on the right-hand side gives us:
∫[0 to T] cos (2ωt + φ) dt = 0
Since the integral of cos (2ωt + φ) over one complete cycle is zero, the average power dissipated over a cycle becomes:
P_avg = (V0 * I0 / 2) * φT / T = (V0 * I0 / 2) φ
Conditions for Power Dissipation:
(i) No Power Dissipated:
No power is dissipated when the phase difference between voltage and current is such that cos φ = 1. This occurs when the circuit is purely resistive (R) and there is no reactance from the inductor (L) or capacitor (C). In this case, the current is in phase with the voltage, and power is not dissipated.
(ii) Maximum Power Dissipated:
Maximum power

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipated over a cycle. Under what condition is (i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit, (ii) maximum power dissipated in the circuit ?
Question Description
A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipated over a cycle. Under what condition is (i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit, (ii) maximum power dissipated in the circuit ? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipated over a cycle. Under what condition is (i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit, (ii) maximum power dissipated in the circuit ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipated over a cycle. Under what condition is (i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit, (ii) maximum power dissipated in the circuit ?.
A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipated over a cycle. Under what condition is (i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit, (ii) maximum power dissipated in the circuit ? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipated over a cycle. Under what condition is (i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit, (ii) maximum power dissipated in the circuit ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipated over a cycle. Under what condition is (i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit, (ii) maximum power dissipated in the circuit ?.
Solutions for A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipated over a cycle. Under what condition is (i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit, (ii) maximum power dissipated in the circuit ? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipated over a cycle. Under what condition is (i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit, (ii) maximum power dissipated in the circuit ? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipated over a cycle. Under what condition is (i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit, (ii) maximum power dissipated in the circuit ?, a detailed solution for A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipated over a cycle. Under what condition is (i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit, (ii) maximum power dissipated in the circuit ? has been provided alongside types of A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipated over a cycle. Under what condition is (i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit, (ii) maximum power dissipated in the circuit ? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A voltage V = V0 sin ωt is applied to a series LCR circuit. Derive the expression for the average power dissipated over a cycle. Under what condition is (i) no power dissipated even though the current flows through the circuit, (ii) maximum power dissipated in the circuit ? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















