JEE Exam > JEE Questions > Homolytic fission of C - C bond in ethane giv...
Start Learning for Free
Homolytic fission of C - C bond in ethane gives an intermediate in which carbon is
- a)sp3-hybridised
- b)sp2-hybridised
- c)sp -hybridised
- d)sp2d-hybridised
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
Homolytic fission of C - C bond in ethane gives an intermediate in whi...
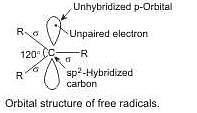
Homolytic fission of C — C bond gives free radicals in which carbon is sp2 hybridised.

Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Homolytic fission of C - C bond in ethane gives an intermediate in whi...
Homolytic fission of C-C bond in ethane results in the formation of two free radicals. In order to understand why the carbon in the intermediate is sp2-hybridized, we need to consider the electronic configuration and bonding in ethane.
1. Electronic Configuration of Ethane:
Ethane (C2H6) consists of two carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. Each carbon atom has four valence electrons, while each hydrogen atom has one valence electron. The electronic configuration of carbon is 1s2 2s2 2p2.
2. Bonding in Ethane:
In ethane, the two carbon atoms are bonded together by a sigma (σ) bond formed by overlap of sp3 hybrid orbitals. Each carbon atom in ethane undergoes sp3 hybridization, where one s orbital and three p orbitals combine to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals are arranged in a tetrahedral geometry around each carbon atom, with the four sigma bonds formed by overlapping these hybrid orbitals with the s orbitals of hydrogen atoms.
3. Homolytic Fission of C-C Bond:
During homolytic fission of the C-C bond in ethane, the bond breaks symmetrically, and each carbon atom retains one of the shared electrons, resulting in the formation of two free radicals. In this process, each carbon atom gains an unpaired electron in its p orbital.
4. Hybridization of Carbon in the Intermediate:
After the homolytic fission, the carbon atom in the intermediate has three sigma bonds and one unpaired electron in its p orbital. This arrangement is characteristic of sp2 hybridization, where one s orbital and two p orbitals combine to form three sp2 hybrid orbitals. These sp2 hybrid orbitals are involved in forming the sigma bonds with the remaining hydrogen atoms and the other carbon atom.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - the carbon in the intermediate is sp2-hybridized.
In summary, during homolytic fission of the C-C bond in ethane, the carbon atoms in the intermediate are sp2-hybridized. This is because the carbon atom in the intermediate forms three sigma bonds and has one unpaired electron in its p orbital, which is consistent with sp2 hybridization.
1. Electronic Configuration of Ethane:
Ethane (C2H6) consists of two carbon atoms and six hydrogen atoms. Each carbon atom has four valence electrons, while each hydrogen atom has one valence electron. The electronic configuration of carbon is 1s2 2s2 2p2.
2. Bonding in Ethane:
In ethane, the two carbon atoms are bonded together by a sigma (σ) bond formed by overlap of sp3 hybrid orbitals. Each carbon atom in ethane undergoes sp3 hybridization, where one s orbital and three p orbitals combine to form four sp3 hybrid orbitals. These hybrid orbitals are arranged in a tetrahedral geometry around each carbon atom, with the four sigma bonds formed by overlapping these hybrid orbitals with the s orbitals of hydrogen atoms.
3. Homolytic Fission of C-C Bond:
During homolytic fission of the C-C bond in ethane, the bond breaks symmetrically, and each carbon atom retains one of the shared electrons, resulting in the formation of two free radicals. In this process, each carbon atom gains an unpaired electron in its p orbital.
4. Hybridization of Carbon in the Intermediate:
After the homolytic fission, the carbon atom in the intermediate has three sigma bonds and one unpaired electron in its p orbital. This arrangement is characteristic of sp2 hybridization, where one s orbital and two p orbitals combine to form three sp2 hybrid orbitals. These sp2 hybrid orbitals are involved in forming the sigma bonds with the remaining hydrogen atoms and the other carbon atom.
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'B' - the carbon in the intermediate is sp2-hybridized.
In summary, during homolytic fission of the C-C bond in ethane, the carbon atoms in the intermediate are sp2-hybridized. This is because the carbon atom in the intermediate forms three sigma bonds and has one unpaired electron in its p orbital, which is consistent with sp2 hybridization.
Attention JEE Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed JEE study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in JEE.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
Homolytic fission of C - C bond in ethane gives an intermediate in which carbon isa)sp3-hybridisedb)sp2-hybridisedc)sp -hybridisedd)sp2d-hybridisedCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Homolytic fission of C - C bond in ethane gives an intermediate in which carbon isa)sp3-hybridisedb)sp2-hybridisedc)sp -hybridisedd)sp2d-hybridisedCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Homolytic fission of C - C bond in ethane gives an intermediate in which carbon isa)sp3-hybridisedb)sp2-hybridisedc)sp -hybridisedd)sp2d-hybridisedCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Homolytic fission of C - C bond in ethane gives an intermediate in which carbon isa)sp3-hybridisedb)sp2-hybridisedc)sp -hybridisedd)sp2d-hybridisedCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Homolytic fission of C - C bond in ethane gives an intermediate in which carbon isa)sp3-hybridisedb)sp2-hybridisedc)sp -hybridisedd)sp2d-hybridisedCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Homolytic fission of C - C bond in ethane gives an intermediate in which carbon isa)sp3-hybridisedb)sp2-hybridisedc)sp -hybridisedd)sp2d-hybridisedCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Homolytic fission of C - C bond in ethane gives an intermediate in which carbon isa)sp3-hybridisedb)sp2-hybridisedc)sp -hybridisedd)sp2d-hybridisedCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Homolytic fission of C - C bond in ethane gives an intermediate in which carbon isa)sp3-hybridisedb)sp2-hybridisedc)sp -hybridisedd)sp2d-hybridisedCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Homolytic fission of C - C bond in ethane gives an intermediate in which carbon isa)sp3-hybridisedb)sp2-hybridisedc)sp -hybridisedd)sp2d-hybridisedCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Homolytic fission of C - C bond in ethane gives an intermediate in which carbon isa)sp3-hybridisedb)sp2-hybridisedc)sp -hybridisedd)sp2d-hybridisedCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Homolytic fission of C - C bond in ethane gives an intermediate in which carbon isa)sp3-hybridisedb)sp2-hybridisedc)sp -hybridisedd)sp2d-hybridisedCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Homolytic fission of C - C bond in ethane gives an intermediate in which carbon isa)sp3-hybridisedb)sp2-hybridisedc)sp -hybridisedd)sp2d-hybridisedCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Homolytic fission of C - C bond in ethane gives an intermediate in which carbon isa)sp3-hybridisedb)sp2-hybridisedc)sp -hybridisedd)sp2d-hybridisedCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























