MCAT Exam > MCAT Questions > A cell membrane defines the limits of the cel...
Start Learning for Free
A cell membrane defines the limits of the cell and serves as the boundary between the cell and its surroundings. It is made of a double layer of lipids that blocks the passage of polar substances. The image below shows a typical cell membrane:
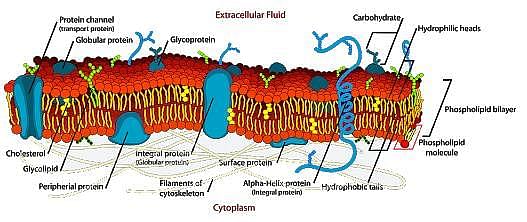

One important concept related to cell membranes is membrane fluidity. Cells need to keep a certain level of flexibility in order to maintain their stability. Increasing temperature, cholesterol content, and unsaturation of the fatty acid tail of the phospholipids in the bilayer increases the membrane fluidity.
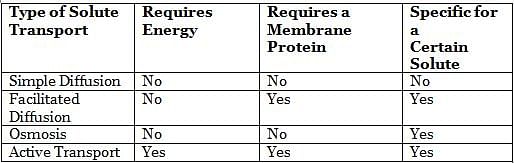
Substances pass through the cell membrane by a process called “transport”. Transport can be passive if no energy is consumed or active if energy is required to transport substances across the membrane. The movement of an uncharged solute across a membrane depends on its concentration gradient, while the movement of an ion depends both on its concentration gradient and the electric potential of the membrane. Membranes are said to be polarized if the resting membrane potential is different than zero, depolarized if the membrane potential is higher than the resting membrane potential, and hyperpolarized if the membrane potential is lower than the resting membrane potential.
The following table shows the characteristics of the different types of solute transport across a membrane:

Q. To maintain the concentration gradients of Na+ and K+, a special protein commonly known as the sodium-potassium pump is used. For every ATP molecule that is broken down by this protein, 2 K+ ions are moved from the outside to the inside of the cell, and 3 Na+ ions are moved from the inside to the outside of the cell. If there’s a certain condition that prevents the sodium-potassium pump from functioning properly, what will happen to the membrane? (You may consult the attachment.)
- a)The membrane will be depolarized.
- b)The membrane would be hyperpolarized.
- c)The membrane would be at its resting membrane potential.
- d)The membrane would be polarized.
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
A cell membrane defines the limits of the cell and serves as the bound...
The sodium-potassium pump polarizes the membrane by creating a difference in the number of charged particles in the outside and the inside of the cell. When it is functioning properly this potential is negative, as there would be fewer positive ions in the inside of the cell. However, if the sodium-potassium pump stops working, the concentration gradient would gradually dissipate and become more positive, depolarizing the cell membrane.
Attention MCAT Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed MCAT study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in MCAT.

|
Explore Courses for MCAT exam
|

|
A cell membrane defines the limits of the cell and serves as the boundary between the cell and its surroundings. It is made of a double layer of lipids that blocks the passage of polar substances. The image below shows a typical cell membrane:One important concept related to cell membranes is membrane fluidity. Cells need to keep a certain level of flexibility in order to maintain their stability. Increasing temperature, cholesterol content, and unsaturation of the fatty acid tail of the phospholipids in the bilayer increases the membrane fluidity.Substances pass through the cell membrane by a process called “transport”. Transport can be passive if no energy is consumed or active if energy is required to transport substances across the membrane. The movement of an uncharged solute across a membrane depends on its concentration gradient, while the movement of an ion depends both on its concentration gradient and the electric potential of the membrane. Membranes are said to be polarized if the resting membrane potential is different than zero, depolarized if the membrane potential is higher than the resting membrane potential, and hyperpolarized if the membrane potential is lower than the resting membrane potential.The following table shows the characteristics of the different types of solute transport across a membrane:Q.To maintain the concentration gradients of Na+and K+, a special protein commonly known as the sodium-potassium pump is used. For every ATP molecule that is broken down by this protein, 2 K+ions are moved from the outside to the inside of the cell, and 3 Na+ions are moved from the inside to the outside of the cell. If there’s a certain condition that prevents the sodium-potassium pump from functioning properly, what will happen to the membrane? (You may consult the attachment.)a)The membrane will be depolarized.b)The membrane would be hyperpolarized.c)The membrane would be at its resting membrane potential.d)The membrane would be polarized.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A cell membrane defines the limits of the cell and serves as the boundary between the cell and its surroundings. It is made of a double layer of lipids that blocks the passage of polar substances. The image below shows a typical cell membrane:One important concept related to cell membranes is membrane fluidity. Cells need to keep a certain level of flexibility in order to maintain their stability. Increasing temperature, cholesterol content, and unsaturation of the fatty acid tail of the phospholipids in the bilayer increases the membrane fluidity.Substances pass through the cell membrane by a process called “transport”. Transport can be passive if no energy is consumed or active if energy is required to transport substances across the membrane. The movement of an uncharged solute across a membrane depends on its concentration gradient, while the movement of an ion depends both on its concentration gradient and the electric potential of the membrane. Membranes are said to be polarized if the resting membrane potential is different than zero, depolarized if the membrane potential is higher than the resting membrane potential, and hyperpolarized if the membrane potential is lower than the resting membrane potential.The following table shows the characteristics of the different types of solute transport across a membrane:Q.To maintain the concentration gradients of Na+and K+, a special protein commonly known as the sodium-potassium pump is used. For every ATP molecule that is broken down by this protein, 2 K+ions are moved from the outside to the inside of the cell, and 3 Na+ions are moved from the inside to the outside of the cell. If there’s a certain condition that prevents the sodium-potassium pump from functioning properly, what will happen to the membrane? (You may consult the attachment.)a)The membrane will be depolarized.b)The membrane would be hyperpolarized.c)The membrane would be at its resting membrane potential.d)The membrane would be polarized.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for MCAT 2024 is part of MCAT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. Information about A cell membrane defines the limits of the cell and serves as the boundary between the cell and its surroundings. It is made of a double layer of lipids that blocks the passage of polar substances. The image below shows a typical cell membrane:One important concept related to cell membranes is membrane fluidity. Cells need to keep a certain level of flexibility in order to maintain their stability. Increasing temperature, cholesterol content, and unsaturation of the fatty acid tail of the phospholipids in the bilayer increases the membrane fluidity.Substances pass through the cell membrane by a process called “transport”. Transport can be passive if no energy is consumed or active if energy is required to transport substances across the membrane. The movement of an uncharged solute across a membrane depends on its concentration gradient, while the movement of an ion depends both on its concentration gradient and the electric potential of the membrane. Membranes are said to be polarized if the resting membrane potential is different than zero, depolarized if the membrane potential is higher than the resting membrane potential, and hyperpolarized if the membrane potential is lower than the resting membrane potential.The following table shows the characteristics of the different types of solute transport across a membrane:Q.To maintain the concentration gradients of Na+and K+, a special protein commonly known as the sodium-potassium pump is used. For every ATP molecule that is broken down by this protein, 2 K+ions are moved from the outside to the inside of the cell, and 3 Na+ions are moved from the inside to the outside of the cell. If there’s a certain condition that prevents the sodium-potassium pump from functioning properly, what will happen to the membrane? (You may consult the attachment.)a)The membrane will be depolarized.b)The membrane would be hyperpolarized.c)The membrane would be at its resting membrane potential.d)The membrane would be polarized.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for MCAT 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A cell membrane defines the limits of the cell and serves as the boundary between the cell and its surroundings. It is made of a double layer of lipids that blocks the passage of polar substances. The image below shows a typical cell membrane:One important concept related to cell membranes is membrane fluidity. Cells need to keep a certain level of flexibility in order to maintain their stability. Increasing temperature, cholesterol content, and unsaturation of the fatty acid tail of the phospholipids in the bilayer increases the membrane fluidity.Substances pass through the cell membrane by a process called “transport”. Transport can be passive if no energy is consumed or active if energy is required to transport substances across the membrane. The movement of an uncharged solute across a membrane depends on its concentration gradient, while the movement of an ion depends both on its concentration gradient and the electric potential of the membrane. Membranes are said to be polarized if the resting membrane potential is different than zero, depolarized if the membrane potential is higher than the resting membrane potential, and hyperpolarized if the membrane potential is lower than the resting membrane potential.The following table shows the characteristics of the different types of solute transport across a membrane:Q.To maintain the concentration gradients of Na+and K+, a special protein commonly known as the sodium-potassium pump is used. For every ATP molecule that is broken down by this protein, 2 K+ions are moved from the outside to the inside of the cell, and 3 Na+ions are moved from the inside to the outside of the cell. If there’s a certain condition that prevents the sodium-potassium pump from functioning properly, what will happen to the membrane? (You may consult the attachment.)a)The membrane will be depolarized.b)The membrane would be hyperpolarized.c)The membrane would be at its resting membrane potential.d)The membrane would be polarized.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
A cell membrane defines the limits of the cell and serves as the boundary between the cell and its surroundings. It is made of a double layer of lipids that blocks the passage of polar substances. The image below shows a typical cell membrane:One important concept related to cell membranes is membrane fluidity. Cells need to keep a certain level of flexibility in order to maintain their stability. Increasing temperature, cholesterol content, and unsaturation of the fatty acid tail of the phospholipids in the bilayer increases the membrane fluidity.Substances pass through the cell membrane by a process called “transport”. Transport can be passive if no energy is consumed or active if energy is required to transport substances across the membrane. The movement of an uncharged solute across a membrane depends on its concentration gradient, while the movement of an ion depends both on its concentration gradient and the electric potential of the membrane. Membranes are said to be polarized if the resting membrane potential is different than zero, depolarized if the membrane potential is higher than the resting membrane potential, and hyperpolarized if the membrane potential is lower than the resting membrane potential.The following table shows the characteristics of the different types of solute transport across a membrane:Q.To maintain the concentration gradients of Na+and K+, a special protein commonly known as the sodium-potassium pump is used. For every ATP molecule that is broken down by this protein, 2 K+ions are moved from the outside to the inside of the cell, and 3 Na+ions are moved from the inside to the outside of the cell. If there’s a certain condition that prevents the sodium-potassium pump from functioning properly, what will happen to the membrane? (You may consult the attachment.)a)The membrane will be depolarized.b)The membrane would be hyperpolarized.c)The membrane would be at its resting membrane potential.d)The membrane would be polarized.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for MCAT 2024 is part of MCAT preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the MCAT exam syllabus. Information about A cell membrane defines the limits of the cell and serves as the boundary between the cell and its surroundings. It is made of a double layer of lipids that blocks the passage of polar substances. The image below shows a typical cell membrane:One important concept related to cell membranes is membrane fluidity. Cells need to keep a certain level of flexibility in order to maintain their stability. Increasing temperature, cholesterol content, and unsaturation of the fatty acid tail of the phospholipids in the bilayer increases the membrane fluidity.Substances pass through the cell membrane by a process called “transport”. Transport can be passive if no energy is consumed or active if energy is required to transport substances across the membrane. The movement of an uncharged solute across a membrane depends on its concentration gradient, while the movement of an ion depends both on its concentration gradient and the electric potential of the membrane. Membranes are said to be polarized if the resting membrane potential is different than zero, depolarized if the membrane potential is higher than the resting membrane potential, and hyperpolarized if the membrane potential is lower than the resting membrane potential.The following table shows the characteristics of the different types of solute transport across a membrane:Q.To maintain the concentration gradients of Na+and K+, a special protein commonly known as the sodium-potassium pump is used. For every ATP molecule that is broken down by this protein, 2 K+ions are moved from the outside to the inside of the cell, and 3 Na+ions are moved from the inside to the outside of the cell. If there’s a certain condition that prevents the sodium-potassium pump from functioning properly, what will happen to the membrane? (You may consult the attachment.)a)The membrane will be depolarized.b)The membrane would be hyperpolarized.c)The membrane would be at its resting membrane potential.d)The membrane would be polarized.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for MCAT 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A cell membrane defines the limits of the cell and serves as the boundary between the cell and its surroundings. It is made of a double layer of lipids that blocks the passage of polar substances. The image below shows a typical cell membrane:One important concept related to cell membranes is membrane fluidity. Cells need to keep a certain level of flexibility in order to maintain their stability. Increasing temperature, cholesterol content, and unsaturation of the fatty acid tail of the phospholipids in the bilayer increases the membrane fluidity.Substances pass through the cell membrane by a process called “transport”. Transport can be passive if no energy is consumed or active if energy is required to transport substances across the membrane. The movement of an uncharged solute across a membrane depends on its concentration gradient, while the movement of an ion depends both on its concentration gradient and the electric potential of the membrane. Membranes are said to be polarized if the resting membrane potential is different than zero, depolarized if the membrane potential is higher than the resting membrane potential, and hyperpolarized if the membrane potential is lower than the resting membrane potential.The following table shows the characteristics of the different types of solute transport across a membrane:Q.To maintain the concentration gradients of Na+and K+, a special protein commonly known as the sodium-potassium pump is used. For every ATP molecule that is broken down by this protein, 2 K+ions are moved from the outside to the inside of the cell, and 3 Na+ions are moved from the inside to the outside of the cell. If there’s a certain condition that prevents the sodium-potassium pump from functioning properly, what will happen to the membrane? (You may consult the attachment.)a)The membrane will be depolarized.b)The membrane would be hyperpolarized.c)The membrane would be at its resting membrane potential.d)The membrane would be polarized.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A cell membrane defines the limits of the cell and serves as the boundary between the cell and its surroundings. It is made of a double layer of lipids that blocks the passage of polar substances. The image below shows a typical cell membrane:One important concept related to cell membranes is membrane fluidity. Cells need to keep a certain level of flexibility in order to maintain their stability. Increasing temperature, cholesterol content, and unsaturation of the fatty acid tail of the phospholipids in the bilayer increases the membrane fluidity.Substances pass through the cell membrane by a process called “transport”. Transport can be passive if no energy is consumed or active if energy is required to transport substances across the membrane. The movement of an uncharged solute across a membrane depends on its concentration gradient, while the movement of an ion depends both on its concentration gradient and the electric potential of the membrane. Membranes are said to be polarized if the resting membrane potential is different than zero, depolarized if the membrane potential is higher than the resting membrane potential, and hyperpolarized if the membrane potential is lower than the resting membrane potential.The following table shows the characteristics of the different types of solute transport across a membrane:Q.To maintain the concentration gradients of Na+and K+, a special protein commonly known as the sodium-potassium pump is used. For every ATP molecule that is broken down by this protein, 2 K+ions are moved from the outside to the inside of the cell, and 3 Na+ions are moved from the inside to the outside of the cell. If there’s a certain condition that prevents the sodium-potassium pump from functioning properly, what will happen to the membrane? (You may consult the attachment.)a)The membrane will be depolarized.b)The membrane would be hyperpolarized.c)The membrane would be at its resting membrane potential.d)The membrane would be polarized.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for MCAT.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for MCAT Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A cell membrane defines the limits of the cell and serves as the boundary between the cell and its surroundings. It is made of a double layer of lipids that blocks the passage of polar substances. The image below shows a typical cell membrane:One important concept related to cell membranes is membrane fluidity. Cells need to keep a certain level of flexibility in order to maintain their stability. Increasing temperature, cholesterol content, and unsaturation of the fatty acid tail of the phospholipids in the bilayer increases the membrane fluidity.Substances pass through the cell membrane by a process called “transport”. Transport can be passive if no energy is consumed or active if energy is required to transport substances across the membrane. The movement of an uncharged solute across a membrane depends on its concentration gradient, while the movement of an ion depends both on its concentration gradient and the electric potential of the membrane. Membranes are said to be polarized if the resting membrane potential is different than zero, depolarized if the membrane potential is higher than the resting membrane potential, and hyperpolarized if the membrane potential is lower than the resting membrane potential.The following table shows the characteristics of the different types of solute transport across a membrane:Q.To maintain the concentration gradients of Na+and K+, a special protein commonly known as the sodium-potassium pump is used. For every ATP molecule that is broken down by this protein, 2 K+ions are moved from the outside to the inside of the cell, and 3 Na+ions are moved from the inside to the outside of the cell. If there’s a certain condition that prevents the sodium-potassium pump from functioning properly, what will happen to the membrane? (You may consult the attachment.)a)The membrane will be depolarized.b)The membrane would be hyperpolarized.c)The membrane would be at its resting membrane potential.d)The membrane would be polarized.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A cell membrane defines the limits of the cell and serves as the boundary between the cell and its surroundings. It is made of a double layer of lipids that blocks the passage of polar substances. The image below shows a typical cell membrane:One important concept related to cell membranes is membrane fluidity. Cells need to keep a certain level of flexibility in order to maintain their stability. Increasing temperature, cholesterol content, and unsaturation of the fatty acid tail of the phospholipids in the bilayer increases the membrane fluidity.Substances pass through the cell membrane by a process called “transport”. Transport can be passive if no energy is consumed or active if energy is required to transport substances across the membrane. The movement of an uncharged solute across a membrane depends on its concentration gradient, while the movement of an ion depends both on its concentration gradient and the electric potential of the membrane. Membranes are said to be polarized if the resting membrane potential is different than zero, depolarized if the membrane potential is higher than the resting membrane potential, and hyperpolarized if the membrane potential is lower than the resting membrane potential.The following table shows the characteristics of the different types of solute transport across a membrane:Q.To maintain the concentration gradients of Na+and K+, a special protein commonly known as the sodium-potassium pump is used. For every ATP molecule that is broken down by this protein, 2 K+ions are moved from the outside to the inside of the cell, and 3 Na+ions are moved from the inside to the outside of the cell. If there’s a certain condition that prevents the sodium-potassium pump from functioning properly, what will happen to the membrane? (You may consult the attachment.)a)The membrane will be depolarized.b)The membrane would be hyperpolarized.c)The membrane would be at its resting membrane potential.d)The membrane would be polarized.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A cell membrane defines the limits of the cell and serves as the boundary between the cell and its surroundings. It is made of a double layer of lipids that blocks the passage of polar substances. The image below shows a typical cell membrane:One important concept related to cell membranes is membrane fluidity. Cells need to keep a certain level of flexibility in order to maintain their stability. Increasing temperature, cholesterol content, and unsaturation of the fatty acid tail of the phospholipids in the bilayer increases the membrane fluidity.Substances pass through the cell membrane by a process called “transport”. Transport can be passive if no energy is consumed or active if energy is required to transport substances across the membrane. The movement of an uncharged solute across a membrane depends on its concentration gradient, while the movement of an ion depends both on its concentration gradient and the electric potential of the membrane. Membranes are said to be polarized if the resting membrane potential is different than zero, depolarized if the membrane potential is higher than the resting membrane potential, and hyperpolarized if the membrane potential is lower than the resting membrane potential.The following table shows the characteristics of the different types of solute transport across a membrane:Q.To maintain the concentration gradients of Na+and K+, a special protein commonly known as the sodium-potassium pump is used. For every ATP molecule that is broken down by this protein, 2 K+ions are moved from the outside to the inside of the cell, and 3 Na+ions are moved from the inside to the outside of the cell. If there’s a certain condition that prevents the sodium-potassium pump from functioning properly, what will happen to the membrane? (You may consult the attachment.)a)The membrane will be depolarized.b)The membrane would be hyperpolarized.c)The membrane would be at its resting membrane potential.d)The membrane would be polarized.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A cell membrane defines the limits of the cell and serves as the boundary between the cell and its surroundings. It is made of a double layer of lipids that blocks the passage of polar substances. The image below shows a typical cell membrane:One important concept related to cell membranes is membrane fluidity. Cells need to keep a certain level of flexibility in order to maintain their stability. Increasing temperature, cholesterol content, and unsaturation of the fatty acid tail of the phospholipids in the bilayer increases the membrane fluidity.Substances pass through the cell membrane by a process called “transport”. Transport can be passive if no energy is consumed or active if energy is required to transport substances across the membrane. The movement of an uncharged solute across a membrane depends on its concentration gradient, while the movement of an ion depends both on its concentration gradient and the electric potential of the membrane. Membranes are said to be polarized if the resting membrane potential is different than zero, depolarized if the membrane potential is higher than the resting membrane potential, and hyperpolarized if the membrane potential is lower than the resting membrane potential.The following table shows the characteristics of the different types of solute transport across a membrane:Q.To maintain the concentration gradients of Na+and K+, a special protein commonly known as the sodium-potassium pump is used. For every ATP molecule that is broken down by this protein, 2 K+ions are moved from the outside to the inside of the cell, and 3 Na+ions are moved from the inside to the outside of the cell. If there’s a certain condition that prevents the sodium-potassium pump from functioning properly, what will happen to the membrane? (You may consult the attachment.)a)The membrane will be depolarized.b)The membrane would be hyperpolarized.c)The membrane would be at its resting membrane potential.d)The membrane would be polarized.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A cell membrane defines the limits of the cell and serves as the boundary between the cell and its surroundings. It is made of a double layer of lipids that blocks the passage of polar substances. The image below shows a typical cell membrane:One important concept related to cell membranes is membrane fluidity. Cells need to keep a certain level of flexibility in order to maintain their stability. Increasing temperature, cholesterol content, and unsaturation of the fatty acid tail of the phospholipids in the bilayer increases the membrane fluidity.Substances pass through the cell membrane by a process called “transport”. Transport can be passive if no energy is consumed or active if energy is required to transport substances across the membrane. The movement of an uncharged solute across a membrane depends on its concentration gradient, while the movement of an ion depends both on its concentration gradient and the electric potential of the membrane. Membranes are said to be polarized if the resting membrane potential is different than zero, depolarized if the membrane potential is higher than the resting membrane potential, and hyperpolarized if the membrane potential is lower than the resting membrane potential.The following table shows the characteristics of the different types of solute transport across a membrane:Q.To maintain the concentration gradients of Na+and K+, a special protein commonly known as the sodium-potassium pump is used. For every ATP molecule that is broken down by this protein, 2 K+ions are moved from the outside to the inside of the cell, and 3 Na+ions are moved from the inside to the outside of the cell. If there’s a certain condition that prevents the sodium-potassium pump from functioning properly, what will happen to the membrane? (You may consult the attachment.)a)The membrane will be depolarized.b)The membrane would be hyperpolarized.c)The membrane would be at its resting membrane potential.d)The membrane would be polarized.Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice MCAT tests.

|
Explore Courses for MCAT exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.