RRB NTPC/ASM/CA/TA Exam > RRB NTPC/ASM/CA/TA Questions > Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC...
Start Learning for Free
Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved when the power factor of the load is:
- a)Unity slightly less than lagging
- b)Unity Less Than Leading
- c)1
- d)Less than 1
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved w...
The efficiency of a transmission line is defined as the ratio of the power transmitted from the receiving end to the sending end.
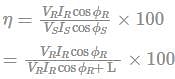
VR = Receiving end voltage
IR = Receive end current
ϕR = Receiving end power factor angle
VS = Sending end voltage
IS = End of sending a stream
ϕS = Transmit end power factor angle
L = Loss
For loads slightly less than the unity power factor leading, the transmission line's reactive power requirement is supplied by the load itself. In addition, the current flow in the line will be reduced leading to a reduction in losses, so the efficiency in the transmission of bulk AC power is increased by providing a load slightly less than the unity leading. Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved when the power factor of the load is slightly less than the unity leading.
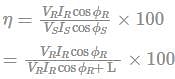
VR = Receiving end voltage
IR = Receive end current
ϕR = Receiving end power factor angle
VS = Sending end voltage
IS = End of sending a stream
ϕS = Transmit end power factor angle
L = Loss
For loads slightly less than the unity power factor leading, the transmission line's reactive power requirement is supplied by the load itself. In addition, the current flow in the line will be reduced leading to a reduction in losses, so the efficiency in the transmission of bulk AC power is increased by providing a load slightly less than the unity leading. Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved when the power factor of the load is slightly less than the unity leading.
Most Upvoted Answer
Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved w...
Introduction:
Efficiency in the transmission of bulk AC power is an important consideration in electrical systems. The power factor of the load plays a significant role in determining the efficiency of power transmission. In this case, the maximum efficiency is achieved when the power factor of the load is less than unity (less than 1) and leading.
Explanation:
1. Power Factor:
- Power factor is the ratio of real power (active power) to apparent power in an AC circuit. It represents the efficiency of power utilization.
- Power factor can be lagging (inductive load) or leading (capacitive load), or unity (resistive load).
- Lagging power factor occurs when the load has inductive components like motors and transformers, which cause the current to lag behind the voltage waveform.
- Leading power factor occurs when the load has capacitive components like capacitors, which cause the current to lead the voltage waveform.
- Unity power factor occurs when the load is purely resistive, with no reactive components. The current is in phase with the voltage waveform.
2. Power Transmission Efficiency:
- The efficiency of power transmission is defined as the ratio of real power delivered to the load to the total power transmitted.
- Real power is the power that is actually consumed by the load and performs useful work.
- Apparent power is the product of voltage and current in an AC circuit and represents the total power transmitted, including both useful and reactive power.
3. Maximum Efficiency:
- The maximum efficiency in power transmission is achieved when the power factor of the load is less than unity and leading.
- Leading power factor reduces the reactive power component in the transmission line, which reduces the losses due to reactive power flow.
- Lagging power factor increases the reactive power component, resulting in additional losses in the transmission line.
- Unity power factor results in the transmission of only real power, but it does not provide any power factor correction or reduction in losses.
Conclusion:
In summary, the maximum efficiency in the transmission of bulk AC power is achieved when the power factor of the load is less than unity and leading. This reduces the losses due to reactive power flow and improves the overall efficiency of the power transmission system.
Efficiency in the transmission of bulk AC power is an important consideration in electrical systems. The power factor of the load plays a significant role in determining the efficiency of power transmission. In this case, the maximum efficiency is achieved when the power factor of the load is less than unity (less than 1) and leading.
Explanation:
1. Power Factor:
- Power factor is the ratio of real power (active power) to apparent power in an AC circuit. It represents the efficiency of power utilization.
- Power factor can be lagging (inductive load) or leading (capacitive load), or unity (resistive load).
- Lagging power factor occurs when the load has inductive components like motors and transformers, which cause the current to lag behind the voltage waveform.
- Leading power factor occurs when the load has capacitive components like capacitors, which cause the current to lead the voltage waveform.
- Unity power factor occurs when the load is purely resistive, with no reactive components. The current is in phase with the voltage waveform.
2. Power Transmission Efficiency:
- The efficiency of power transmission is defined as the ratio of real power delivered to the load to the total power transmitted.
- Real power is the power that is actually consumed by the load and performs useful work.
- Apparent power is the product of voltage and current in an AC circuit and represents the total power transmitted, including both useful and reactive power.
3. Maximum Efficiency:
- The maximum efficiency in power transmission is achieved when the power factor of the load is less than unity and leading.
- Leading power factor reduces the reactive power component in the transmission line, which reduces the losses due to reactive power flow.
- Lagging power factor increases the reactive power component, resulting in additional losses in the transmission line.
- Unity power factor results in the transmission of only real power, but it does not provide any power factor correction or reduction in losses.
Conclusion:
In summary, the maximum efficiency in the transmission of bulk AC power is achieved when the power factor of the load is less than unity and leading. This reduces the losses due to reactive power flow and improves the overall efficiency of the power transmission system.

|
Explore Courses for RRB NTPC/ASM/CA/TA exam
|

|
Similar RRB NTPC/ASM/CA/TA Doubts
Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved when the power factor of the load is:a)Unity slightly less than laggingb)Unity Less Than Leadingc)1d)Less than 1Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved when the power factor of the load is:a)Unity slightly less than laggingb)Unity Less Than Leadingc)1d)Less than 1Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for RRB NTPC/ASM/CA/TA 2025 is part of RRB NTPC/ASM/CA/TA preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the RRB NTPC/ASM/CA/TA exam syllabus. Information about Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved when the power factor of the load is:a)Unity slightly less than laggingb)Unity Less Than Leadingc)1d)Less than 1Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for RRB NTPC/ASM/CA/TA 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved when the power factor of the load is:a)Unity slightly less than laggingb)Unity Less Than Leadingc)1d)Less than 1Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved when the power factor of the load is:a)Unity slightly less than laggingb)Unity Less Than Leadingc)1d)Less than 1Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for RRB NTPC/ASM/CA/TA 2025 is part of RRB NTPC/ASM/CA/TA preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the RRB NTPC/ASM/CA/TA exam syllabus. Information about Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved when the power factor of the load is:a)Unity slightly less than laggingb)Unity Less Than Leadingc)1d)Less than 1Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for RRB NTPC/ASM/CA/TA 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved when the power factor of the load is:a)Unity slightly less than laggingb)Unity Less Than Leadingc)1d)Less than 1Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved when the power factor of the load is:a)Unity slightly less than laggingb)Unity Less Than Leadingc)1d)Less than 1Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for RRB NTPC/ASM/CA/TA.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for RRB NTPC/ASM/CA/TA Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved when the power factor of the load is:a)Unity slightly less than laggingb)Unity Less Than Leadingc)1d)Less than 1Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved when the power factor of the load is:a)Unity slightly less than laggingb)Unity Less Than Leadingc)1d)Less than 1Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved when the power factor of the load is:a)Unity slightly less than laggingb)Unity Less Than Leadingc)1d)Less than 1Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved when the power factor of the load is:a)Unity slightly less than laggingb)Unity Less Than Leadingc)1d)Less than 1Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Maximum efficiency in transmission of bulk AC power will be achieved when the power factor of the load is:a)Unity slightly less than laggingb)Unity Less Than Leadingc)1d)Less than 1Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice RRB NTPC/ASM/CA/TA tests.

|
Explore Courses for RRB NTPC/ASM/CA/TA exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























