UGC NET Exam > UGC NET Questions > In the base (OH–) hydrolysis of a trans...
Start Learning for Free
In the base (OH–) hydrolysis of a transition metal complex [ML6]z+, the slope between log (k/k0) and √I is found to be -2.1. The charge on the complex is:
- a)+1
- b)+2
- c)+3
- d)+4
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
In the base (OH–) hydrolysis of a transition metal complex [ML6]...
Primary Kinetic Salt Effect:
- The effect of electrolyte concentration on the rate constants of a number of reactions involving ions in aqueous solutions can be explained in terms of transition state theory and the Debye-Hückel theory.
- The primary kinetic salt effect is the study of the effect of adding an inner electrolyte to an ionic reacting system.
- It is the modification of the transition state theory for ionic reactions.
- For the chemical reaction,
AzA + BzB → Products
If we look at the reaction above and reconsider it in terms of the formation of an activated complex,
AzA + BzB → X‡ → Products
Then, according to the transition theory, the equilibrium constant for the above reaction will be,
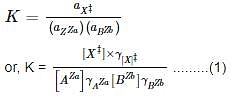
[As, Activity (a)= Concentration(c) × activity coefficient]
in which X‡ is the activated complex that is formed in the transition state, γ’s are the activity coefficients.
If we look at the reaction above and reconsider it in terms of the formation of an activated complex,
AzA + BzB → X‡ → Products
Then, according to the transition theory, the equilibrium constant for the above reaction will be,
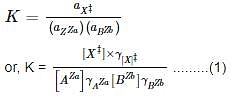
[As, Activity (a)= Concentration(c) × activity coefficient]
in which X‡ is the activated complex that is formed in the transition state, γ’s are the activity coefficients.
- From the above equation, using transition state theory the activity coefficient terms can be estimated from the DebyeHückel theory in dilute solutions. At 298 K

- This is known as the Brønsted equation and it predicts that the plot of log(k) versus the square root of ionic strength I should be a straight line.
- For an aqueous solution, the slope is nearly equal to ZAZB, the product of the ionic charges. Three special cases could occur:
- If ZA and ZB have the same sign, then ZAZB is positive, and the rate constant increases with ionic strength.
- If ZA and ZB have different signs, ZAZB is negative and the rate constant decreases with ionic strength.
- If one of the reactants is uncharged, ZAZB is zero and the rate constant is independent of the ionic strength.
the slope between log (k/k0) and √I is found to be -2.1.
From above equation no 2
slope = 2AZaZb
The value of A is 0.509
−2.1=2∗0.509ZaZb also value of Zb is -1
−2.1=2∗0.509(−1)Za
Za =+2.06
or nearly equal to +2.
Hence, If the charge of one ion is -1, the charge of other ion is close to +2
From above equation no 2
slope = 2AZaZb
The value of A is 0.509
−2.1=2∗0.509ZaZb also value of Zb is -1
−2.1=2∗0.509(−1)Za
Za =+2.06
or nearly equal to +2.
Hence, If the charge of one ion is -1, the charge of other ion is close to +2

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|
In the base (OH–) hydrolysis of a transition metal complex [ML6]z+, the slope between log (k/k0) and √I is found to be -2.1. The charge on the complex is:a)+1b)+2c)+3d)+4Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
In the base (OH–) hydrolysis of a transition metal complex [ML6]z+, the slope between log (k/k0) and √I is found to be -2.1. The charge on the complex is:a)+1b)+2c)+3d)+4Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for UGC NET 2025 is part of UGC NET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UGC NET exam syllabus. Information about In the base (OH–) hydrolysis of a transition metal complex [ML6]z+, the slope between log (k/k0) and √I is found to be -2.1. The charge on the complex is:a)+1b)+2c)+3d)+4Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UGC NET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In the base (OH–) hydrolysis of a transition metal complex [ML6]z+, the slope between log (k/k0) and √I is found to be -2.1. The charge on the complex is:a)+1b)+2c)+3d)+4Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
In the base (OH–) hydrolysis of a transition metal complex [ML6]z+, the slope between log (k/k0) and √I is found to be -2.1. The charge on the complex is:a)+1b)+2c)+3d)+4Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for UGC NET 2025 is part of UGC NET preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the UGC NET exam syllabus. Information about In the base (OH–) hydrolysis of a transition metal complex [ML6]z+, the slope between log (k/k0) and √I is found to be -2.1. The charge on the complex is:a)+1b)+2c)+3d)+4Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for UGC NET 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In the base (OH–) hydrolysis of a transition metal complex [ML6]z+, the slope between log (k/k0) and √I is found to be -2.1. The charge on the complex is:a)+1b)+2c)+3d)+4Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In the base (OH–) hydrolysis of a transition metal complex [ML6]z+, the slope between log (k/k0) and √I is found to be -2.1. The charge on the complex is:a)+1b)+2c)+3d)+4Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for UGC NET.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for UGC NET Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In the base (OH–) hydrolysis of a transition metal complex [ML6]z+, the slope between log (k/k0) and √I is found to be -2.1. The charge on the complex is:a)+1b)+2c)+3d)+4Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In the base (OH–) hydrolysis of a transition metal complex [ML6]z+, the slope between log (k/k0) and √I is found to be -2.1. The charge on the complex is:a)+1b)+2c)+3d)+4Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In the base (OH–) hydrolysis of a transition metal complex [ML6]z+, the slope between log (k/k0) and √I is found to be -2.1. The charge on the complex is:a)+1b)+2c)+3d)+4Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In the base (OH–) hydrolysis of a transition metal complex [ML6]z+, the slope between log (k/k0) and √I is found to be -2.1. The charge on the complex is:a)+1b)+2c)+3d)+4Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In the base (OH–) hydrolysis of a transition metal complex [ML6]z+, the slope between log (k/k0) and √I is found to be -2.1. The charge on the complex is:a)+1b)+2c)+3d)+4Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice UGC NET tests.

|
Explore Courses for UGC NET exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.






















