BPSC (Bihar) Exam > BPSC (Bihar) Questions > A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be sepa...
Start Learning for Free
A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be separated by
- a)sublimation
- b)distillation
- c)chromatography
- d)fractional distillation
- e)None of the above / More than one of the above
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Most Upvoted Answer
A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be separated bya)sublimationb)di...
- Naphthalene is a colourless crystalline solid with a strong mothball odour.
- It is also called white tar & tar camphor.
- Melting point: 80.1 C.
- Boiling point: 218.C.
- Molecular Weight: 128.17 g/mol.
- Molecular formula: C10H8.
- Chemical structure:
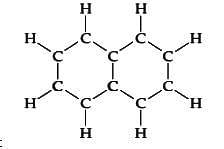
- It is obtained from either coal tar or petroleum distillation.
- It is a white, volatile, solid polycyclic hydrocarbon.
- It is almost insoluble in water.
- The solid is denser than water and thus insoluble in water.
- It is highly volatile.
- Uses:
- It is used in the dyes industry.
- It is used as a moth repellent.
- It is used as wood preservatives.
- It used as fumigant, lubricants, and to make other chemicals.
- It is used in the manufacture of polyvinyl chloride ( PVC) plastics.
- It is used in synthetic tanning, preservative, textile chemicals, emulsion breakers.
- It is used around garden and building peripheries to repel animals such as snakes and rabbits.
- Fuels such as petroleum and coal contain naphthalene.
- It is the most abundant single constituent of coal tar.
- It is commercially produced by crystallization from the intermediate fraction of condensed coal tar and from the heavier fraction of cracked petroleum.
- Negative effects:
- Excess exposure to naphthalene can cause the following issues:
- Hemolytic anaemia.
- Damage to the liver.
- Neurological system.
- Cataracts.
- It is generally accepted to be a human carcinogen.
- It may increase the risk of developing laryngeal (larynx) and colorectal (colon) cancer.
- It is a white solid that evaporates easily because of sublimation.
- Excess exposure to naphthalene can cause the following issues:
- Sublimation:
- It is the process of transition of a substance from the solid-state to the gaseous state without passing through the liquid state.
- The substance showing this phenomenon is called sublimate.
- E.g: Camphor, Naphthalene, Dry ice (solid CO2) etc.
- When naphthalene is heated, it sublimes easily because it is made up of non-polar molecules that are held together only by weak Van der Waal intermolecular forces of attraction.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be separated bya)sublimationb)di...
Separation of Sand and Naphthalene
To separate a mixture of sand and naphthalene, sublimation is the most effective method. Here’s a detailed explanation.
What is Sublimation?
- Sublimation is the process where a solid turns directly into a gas without passing through a liquid state.
- Naphthalene, being a solid at room temperature, sublimates readily when heated.
Properties of Naphthalene
- Naphthalene has a relatively low melting point (about 80 °C) and sublimates at room temperature, especially when exposed to heat.
- In contrast, sand is an inorganic solid that does not sublimate and remains as a solid throughout the process.
Separation Process
- When the mixture of sand and naphthalene is gently heated, naphthalene will sublime into vapor.
- The vapor can then be collected and cooled, allowing it to condense back into solid naphthalene.
- The remaining sand will be left behind as it does not undergo sublimation.
Why Not Other Methods?
- Distillation: This method is used for separating liquids based on boiling points, which is not applicable here.
- Chromatography: This is primarily for separating mixtures in solution, not solid mixtures.
- Fractional Distillation: Similar to distillation, it’s not suitable for solid-solid separation.
- None of the Above: Since sublimation is effective, this option is incorrect.
Conclusion
- The best method to separate a mixture of sand and naphthalene is by sublimation, making option 'A' the correct answer.
To separate a mixture of sand and naphthalene, sublimation is the most effective method. Here’s a detailed explanation.
What is Sublimation?
- Sublimation is the process where a solid turns directly into a gas without passing through a liquid state.
- Naphthalene, being a solid at room temperature, sublimates readily when heated.
Properties of Naphthalene
- Naphthalene has a relatively low melting point (about 80 °C) and sublimates at room temperature, especially when exposed to heat.
- In contrast, sand is an inorganic solid that does not sublimate and remains as a solid throughout the process.
Separation Process
- When the mixture of sand and naphthalene is gently heated, naphthalene will sublime into vapor.
- The vapor can then be collected and cooled, allowing it to condense back into solid naphthalene.
- The remaining sand will be left behind as it does not undergo sublimation.
Why Not Other Methods?
- Distillation: This method is used for separating liquids based on boiling points, which is not applicable here.
- Chromatography: This is primarily for separating mixtures in solution, not solid mixtures.
- Fractional Distillation: Similar to distillation, it’s not suitable for solid-solid separation.
- None of the Above: Since sublimation is effective, this option is incorrect.
Conclusion
- The best method to separate a mixture of sand and naphthalene is by sublimation, making option 'A' the correct answer.
Attention BPSC (Bihar) Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed BPSC (Bihar) study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in BPSC (Bihar).

|
Explore Courses for BPSC (Bihar) exam
|

|
A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be separated bya)sublimationb)distillationc)chromatographyd)fractional distillatione)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be separated bya)sublimationb)distillationc)chromatographyd)fractional distillatione)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for BPSC (Bihar) 2024 is part of BPSC (Bihar) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the BPSC (Bihar) exam syllabus. Information about A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be separated bya)sublimationb)distillationc)chromatographyd)fractional distillatione)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for BPSC (Bihar) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be separated bya)sublimationb)distillationc)chromatographyd)fractional distillatione)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be separated bya)sublimationb)distillationc)chromatographyd)fractional distillatione)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for BPSC (Bihar) 2024 is part of BPSC (Bihar) preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the BPSC (Bihar) exam syllabus. Information about A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be separated bya)sublimationb)distillationc)chromatographyd)fractional distillatione)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for BPSC (Bihar) 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be separated bya)sublimationb)distillationc)chromatographyd)fractional distillatione)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be separated bya)sublimationb)distillationc)chromatographyd)fractional distillatione)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for BPSC (Bihar).
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for BPSC (Bihar) Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be separated bya)sublimationb)distillationc)chromatographyd)fractional distillatione)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be separated bya)sublimationb)distillationc)chromatographyd)fractional distillatione)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be separated bya)sublimationb)distillationc)chromatographyd)fractional distillatione)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be separated bya)sublimationb)distillationc)chromatographyd)fractional distillatione)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A mixture of sand and naphthalene can be separated bya)sublimationb)distillationc)chromatographyd)fractional distillatione)None of the above / More than one of the aboveCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice BPSC (Bihar) tests.

|
Explore Courses for BPSC (Bihar) exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Test: Human Environment Interactions the Tropical and The Subtropical Region
Test | 15 questions
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.






















