Software Development Exam > Software Development Questions > In a lake ecosystem, bottom-up effects (B) re...
Start Learning for Free
In a lake ecosystem, bottom-up effects (B) refer to control of a lower trophic level by the higher trophic levels and top-down effects (T) refer to the opposite. In a lake with three trophic levels-Phytoplankton (P), Zooplankton (Z) and primary Carnivore (C), what kind of effect can be observed in this ecosystem:
- a)P and C are controlled by B, and Z is controlled by T.
- b)P, Z and C are all controlled by T.
- c)P is controlled by B, Z is controlled by T and C is controlled by B.
- d)P is controlled by T, Z is controlled by B and C is controlled by T.
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Verified Answer
In a lake ecosystem, bottom-up effects (B) refer to control of a lower...
Concept:
- Bottom-up effects are important in limiting population densities of herbivores and carnivores.
- First, there is a progressive lessening of available energy passing from plants through herbivores to carnivores and to the carnivores that eat carnivores.
- This line of evidence, based on the thermodynamic properties of energy transfer, suggests that plants should regulate the population densities of all other species that rely on them.
Explanation:
Fig 1: Bottom-up and top-down control
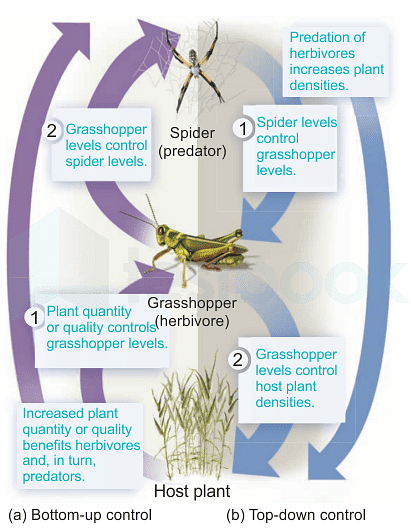
(a) Bottom-up control proposes that host plant quantity or quality limits the density of herbivores, which in turn sets limits on the abundance of predators.
- Taken together, this means that high levels of host plants would result in increased numbers of predators because of higher densities of the herbivores on which they prey.
(b) Top-down control proposes that plant densities are limited by herbivores and that herbivores are limited by predators.
- Taken together, this means that high levels of predation would result in high densities of host plants because there would be fewer herbivores
- In the given query we have a lake with three trophic levels-Phytoplankton (P), Zooplankton (Z) and primary Carnivore (C) so it is clear that number of Carnivore controls Zooplankton and zooplanktons control the phyto planktons.
- thus we have top down control.
hence the correct answer is option 2
Most Upvoted Answer
In a lake ecosystem, bottom-up effects (B) refer to control of a lower...
Explanation:
Top-Down Effects in a Lake Ecosystem:
- In a lake ecosystem, top-down effects (T) occur when higher trophic levels control the abundance or behavior of lower trophic levels.
- In this scenario, all trophic levels are controlled by T, meaning that the primary Carnivore (C) controls Zooplankton (Z), which in turn controls Phytoplankton (P).
Why Option B is the Correct Answer:
- The correct answer is option B because it states that all trophic levels (P, Z, C) are controlled by top-down effects (T).
- This means that the primary Carnivore (C) controls Zooplankton (Z), and Zooplankton (Z) controls Phytoplankton (P) in this lake ecosystem.
Conclusion:
- In this lake ecosystem with three trophic levels, top-down effects play a crucial role in controlling the abundance and dynamics of the different trophic levels.
- Understanding these top-down effects is essential for managing and conserving the balance of the ecosystem.
Top-Down Effects in a Lake Ecosystem:
- In a lake ecosystem, top-down effects (T) occur when higher trophic levels control the abundance or behavior of lower trophic levels.
- In this scenario, all trophic levels are controlled by T, meaning that the primary Carnivore (C) controls Zooplankton (Z), which in turn controls Phytoplankton (P).
Why Option B is the Correct Answer:
- The correct answer is option B because it states that all trophic levels (P, Z, C) are controlled by top-down effects (T).
- This means that the primary Carnivore (C) controls Zooplankton (Z), and Zooplankton (Z) controls Phytoplankton (P) in this lake ecosystem.
Conclusion:
- In this lake ecosystem with three trophic levels, top-down effects play a crucial role in controlling the abundance and dynamics of the different trophic levels.
- Understanding these top-down effects is essential for managing and conserving the balance of the ecosystem.

|
Explore Courses for Software Development exam
|

|
Similar Software Development Doubts
In a lake ecosystem, bottom-up effects (B) refer to control of a lower trophic level by the higher trophic levels and top-down effects (T) refer to the opposite. In a lake with three trophic levels-Phytoplankton (P), Zooplankton (Z) and primary Carnivore (C), what kind of effect can be observed in this ecosystem:a)P and C are controlled by B, and Z is controlled by T.b)P, Z and C are all controlled by T.c)P is controlled by B, Z is controlled by T and C is controlled by B.d)P is controlled by T, Z is controlled by B and C is controlled by T.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
In a lake ecosystem, bottom-up effects (B) refer to control of a lower trophic level by the higher trophic levels and top-down effects (T) refer to the opposite. In a lake with three trophic levels-Phytoplankton (P), Zooplankton (Z) and primary Carnivore (C), what kind of effect can be observed in this ecosystem:a)P and C are controlled by B, and Z is controlled by T.b)P, Z and C are all controlled by T.c)P is controlled by B, Z is controlled by T and C is controlled by B.d)P is controlled by T, Z is controlled by B and C is controlled by T.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Software Development exam syllabus. Information about In a lake ecosystem, bottom-up effects (B) refer to control of a lower trophic level by the higher trophic levels and top-down effects (T) refer to the opposite. In a lake with three trophic levels-Phytoplankton (P), Zooplankton (Z) and primary Carnivore (C), what kind of effect can be observed in this ecosystem:a)P and C are controlled by B, and Z is controlled by T.b)P, Z and C are all controlled by T.c)P is controlled by B, Z is controlled by T and C is controlled by B.d)P is controlled by T, Z is controlled by B and C is controlled by T.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Software Development 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a lake ecosystem, bottom-up effects (B) refer to control of a lower trophic level by the higher trophic levels and top-down effects (T) refer to the opposite. In a lake with three trophic levels-Phytoplankton (P), Zooplankton (Z) and primary Carnivore (C), what kind of effect can be observed in this ecosystem:a)P and C are controlled by B, and Z is controlled by T.b)P, Z and C are all controlled by T.c)P is controlled by B, Z is controlled by T and C is controlled by B.d)P is controlled by T, Z is controlled by B and C is controlled by T.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
In a lake ecosystem, bottom-up effects (B) refer to control of a lower trophic level by the higher trophic levels and top-down effects (T) refer to the opposite. In a lake with three trophic levels-Phytoplankton (P), Zooplankton (Z) and primary Carnivore (C), what kind of effect can be observed in this ecosystem:a)P and C are controlled by B, and Z is controlled by T.b)P, Z and C are all controlled by T.c)P is controlled by B, Z is controlled by T and C is controlled by B.d)P is controlled by T, Z is controlled by B and C is controlled by T.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Software Development 2025 is part of Software Development preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Software Development exam syllabus. Information about In a lake ecosystem, bottom-up effects (B) refer to control of a lower trophic level by the higher trophic levels and top-down effects (T) refer to the opposite. In a lake with three trophic levels-Phytoplankton (P), Zooplankton (Z) and primary Carnivore (C), what kind of effect can be observed in this ecosystem:a)P and C are controlled by B, and Z is controlled by T.b)P, Z and C are all controlled by T.c)P is controlled by B, Z is controlled by T and C is controlled by B.d)P is controlled by T, Z is controlled by B and C is controlled by T.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Software Development 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for In a lake ecosystem, bottom-up effects (B) refer to control of a lower trophic level by the higher trophic levels and top-down effects (T) refer to the opposite. In a lake with three trophic levels-Phytoplankton (P), Zooplankton (Z) and primary Carnivore (C), what kind of effect can be observed in this ecosystem:a)P and C are controlled by B, and Z is controlled by T.b)P, Z and C are all controlled by T.c)P is controlled by B, Z is controlled by T and C is controlled by B.d)P is controlled by T, Z is controlled by B and C is controlled by T.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for In a lake ecosystem, bottom-up effects (B) refer to control of a lower trophic level by the higher trophic levels and top-down effects (T) refer to the opposite. In a lake with three trophic levels-Phytoplankton (P), Zooplankton (Z) and primary Carnivore (C), what kind of effect can be observed in this ecosystem:a)P and C are controlled by B, and Z is controlled by T.b)P, Z and C are all controlled by T.c)P is controlled by B, Z is controlled by T and C is controlled by B.d)P is controlled by T, Z is controlled by B and C is controlled by T.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Software Development.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Software Development Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of In a lake ecosystem, bottom-up effects (B) refer to control of a lower trophic level by the higher trophic levels and top-down effects (T) refer to the opposite. In a lake with three trophic levels-Phytoplankton (P), Zooplankton (Z) and primary Carnivore (C), what kind of effect can be observed in this ecosystem:a)P and C are controlled by B, and Z is controlled by T.b)P, Z and C are all controlled by T.c)P is controlled by B, Z is controlled by T and C is controlled by B.d)P is controlled by T, Z is controlled by B and C is controlled by T.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
In a lake ecosystem, bottom-up effects (B) refer to control of a lower trophic level by the higher trophic levels and top-down effects (T) refer to the opposite. In a lake with three trophic levels-Phytoplankton (P), Zooplankton (Z) and primary Carnivore (C), what kind of effect can be observed in this ecosystem:a)P and C are controlled by B, and Z is controlled by T.b)P, Z and C are all controlled by T.c)P is controlled by B, Z is controlled by T and C is controlled by B.d)P is controlled by T, Z is controlled by B and C is controlled by T.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for In a lake ecosystem, bottom-up effects (B) refer to control of a lower trophic level by the higher trophic levels and top-down effects (T) refer to the opposite. In a lake with three trophic levels-Phytoplankton (P), Zooplankton (Z) and primary Carnivore (C), what kind of effect can be observed in this ecosystem:a)P and C are controlled by B, and Z is controlled by T.b)P, Z and C are all controlled by T.c)P is controlled by B, Z is controlled by T and C is controlled by B.d)P is controlled by T, Z is controlled by B and C is controlled by T.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of In a lake ecosystem, bottom-up effects (B) refer to control of a lower trophic level by the higher trophic levels and top-down effects (T) refer to the opposite. In a lake with three trophic levels-Phytoplankton (P), Zooplankton (Z) and primary Carnivore (C), what kind of effect can be observed in this ecosystem:a)P and C are controlled by B, and Z is controlled by T.b)P, Z and C are all controlled by T.c)P is controlled by B, Z is controlled by T and C is controlled by B.d)P is controlled by T, Z is controlled by B and C is controlled by T.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice In a lake ecosystem, bottom-up effects (B) refer to control of a lower trophic level by the higher trophic levels and top-down effects (T) refer to the opposite. In a lake with three trophic levels-Phytoplankton (P), Zooplankton (Z) and primary Carnivore (C), what kind of effect can be observed in this ecosystem:a)P and C are controlled by B, and Z is controlled by T.b)P, Z and C are all controlled by T.c)P is controlled by B, Z is controlled by T and C is controlled by B.d)P is controlled by T, Z is controlled by B and C is controlled by T.Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Software Development tests.

|
Explore Courses for Software Development exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























