Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is ...
Start Learning for Free
The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is higher than that of simple Rankine cycle because
- a)The enthalpy of main steam is higher for superheat cycle
- b)The mean temperature of heat addition is higher for superheat cycle
- c)The temperature of steam in the condenser is high
- d)The quality of stem in the condenser is low
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is higher than that of simpl...
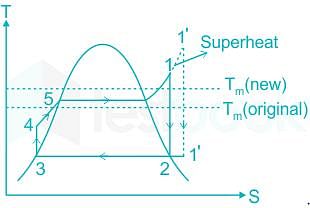 Rankine cycle with superheating is shown in the figure.
Rankine cycle with superheating is shown in the figure.- Increased heat addition and rejection
- Due to increase heat addition, mean temperature of heat addition increases
- The increase in mean temperature of heat addition increases the efficiency
∴ In the superheat Rankine cycle the mean temperature of heat addition increases and hence the efficiency increases.
Most Upvoted Answer
The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is higher than that of simpl...
Explanation:
The efficiency of a Rankine cycle is determined by the mean temperature of heat addition, which is the average temperature at which heat is added to the working fluid. The superheat Rankine cycle has a higher efficiency than the simple Rankine cycle because of the following reasons:
Mean temperature of heat addition is higher for superheat cycle:
- In the simple Rankine cycle, the working fluid is vaporized and then expanded in the turbine. The steam is then condensed and pumped back to the boiler.
- In the superheat Rankine cycle, the steam is generated at a higher temperature and then heated further to a higher temperature by the superheater before entering the turbine.
- This results in a higher mean temperature of heat addition in the superheat Rankine cycle, which leads to a higher thermal efficiency.
Enthalpy of main steam is higher for superheat cycle:
- The enthalpy of the main steam is the energy content of the steam at the inlet to the turbine.
- In the superheat Rankine cycle, the steam is heated to a higher temperature, which results in a higher enthalpy of the main steam.
- This higher energy content of the steam results in a higher power output from the turbine and higher efficiency.
Temperature of steam in the condenser is high:
- The temperature of the steam in the condenser is a function of the cooling medium used to condense the steam.
- In the superheat Rankine cycle, the higher temperature of the steam entering the condenser results in a higher temperature of the cooling medium required to condense the steam.
- This higher temperature of the cooling medium results in a lower efficiency due to the higher temperature difference between the working fluid and the cooling medium.
Quality of steam in the condenser is low:
- The quality of the steam in the condenser is the ratio of the mass of vapor to the total mass of the working fluid at the condenser outlet.
- In the superheat Rankine cycle, the higher temperature of the steam entering the condenser results in a lower quality of the steam at the condenser outlet.
- This lower quality of the steam results in a lower efficiency due to the higher moisture content of the working fluid at the turbine inlet.
Conclusion:
The superheat Rankine cycle has a higher efficiency than the simple Rankine cycle because of the higher mean temperature of heat addition, which is a result of the higher temperature of the steam entering the turbine.
The efficiency of a Rankine cycle is determined by the mean temperature of heat addition, which is the average temperature at which heat is added to the working fluid. The superheat Rankine cycle has a higher efficiency than the simple Rankine cycle because of the following reasons:
Mean temperature of heat addition is higher for superheat cycle:
- In the simple Rankine cycle, the working fluid is vaporized and then expanded in the turbine. The steam is then condensed and pumped back to the boiler.
- In the superheat Rankine cycle, the steam is generated at a higher temperature and then heated further to a higher temperature by the superheater before entering the turbine.
- This results in a higher mean temperature of heat addition in the superheat Rankine cycle, which leads to a higher thermal efficiency.
Enthalpy of main steam is higher for superheat cycle:
- The enthalpy of the main steam is the energy content of the steam at the inlet to the turbine.
- In the superheat Rankine cycle, the steam is heated to a higher temperature, which results in a higher enthalpy of the main steam.
- This higher energy content of the steam results in a higher power output from the turbine and higher efficiency.
Temperature of steam in the condenser is high:
- The temperature of the steam in the condenser is a function of the cooling medium used to condense the steam.
- In the superheat Rankine cycle, the higher temperature of the steam entering the condenser results in a higher temperature of the cooling medium required to condense the steam.
- This higher temperature of the cooling medium results in a lower efficiency due to the higher temperature difference between the working fluid and the cooling medium.
Quality of steam in the condenser is low:
- The quality of the steam in the condenser is the ratio of the mass of vapor to the total mass of the working fluid at the condenser outlet.
- In the superheat Rankine cycle, the higher temperature of the steam entering the condenser results in a lower quality of the steam at the condenser outlet.
- This lower quality of the steam results in a lower efficiency due to the higher moisture content of the working fluid at the turbine inlet.
Conclusion:
The superheat Rankine cycle has a higher efficiency than the simple Rankine cycle because of the higher mean temperature of heat addition, which is a result of the higher temperature of the steam entering the turbine.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is higher than that of simpl...
It's simple. superheater is heated the steam then the stream is get more efficient due to use the component supper heater. but simple Rankine cycle is not used superheater.so superheater rankine cycle is more efficiency.
Attention Mechanical Engineering Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Mechanical Engineering study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Mechanical Engineering.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Mechanical Engineering Doubts
The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is higher than that of simple Rankine cycle becausea)The enthalpy of main steam is higher for superheat cycle b)The mean temperature of heat addition is higher for superheat cyclec)The temperature of steam in the condenser is highd)The quality of stem in the condenser is lowCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is higher than that of simple Rankine cycle becausea)The enthalpy of main steam is higher for superheat cycle b)The mean temperature of heat addition is higher for superheat cyclec)The temperature of steam in the condenser is highd)The quality of stem in the condenser is lowCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is higher than that of simple Rankine cycle becausea)The enthalpy of main steam is higher for superheat cycle b)The mean temperature of heat addition is higher for superheat cyclec)The temperature of steam in the condenser is highd)The quality of stem in the condenser is lowCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is higher than that of simple Rankine cycle becausea)The enthalpy of main steam is higher for superheat cycle b)The mean temperature of heat addition is higher for superheat cyclec)The temperature of steam in the condenser is highd)The quality of stem in the condenser is lowCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is higher than that of simple Rankine cycle becausea)The enthalpy of main steam is higher for superheat cycle b)The mean temperature of heat addition is higher for superheat cyclec)The temperature of steam in the condenser is highd)The quality of stem in the condenser is lowCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is higher than that of simple Rankine cycle becausea)The enthalpy of main steam is higher for superheat cycle b)The mean temperature of heat addition is higher for superheat cyclec)The temperature of steam in the condenser is highd)The quality of stem in the condenser is lowCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is higher than that of simple Rankine cycle becausea)The enthalpy of main steam is higher for superheat cycle b)The mean temperature of heat addition is higher for superheat cyclec)The temperature of steam in the condenser is highd)The quality of stem in the condenser is lowCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is higher than that of simple Rankine cycle becausea)The enthalpy of main steam is higher for superheat cycle b)The mean temperature of heat addition is higher for superheat cyclec)The temperature of steam in the condenser is highd)The quality of stem in the condenser is lowCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is higher than that of simple Rankine cycle becausea)The enthalpy of main steam is higher for superheat cycle b)The mean temperature of heat addition is higher for superheat cyclec)The temperature of steam in the condenser is highd)The quality of stem in the condenser is lowCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is higher than that of simple Rankine cycle becausea)The enthalpy of main steam is higher for superheat cycle b)The mean temperature of heat addition is higher for superheat cyclec)The temperature of steam in the condenser is highd)The quality of stem in the condenser is lowCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is higher than that of simple Rankine cycle becausea)The enthalpy of main steam is higher for superheat cycle b)The mean temperature of heat addition is higher for superheat cyclec)The temperature of steam in the condenser is highd)The quality of stem in the condenser is lowCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is higher than that of simple Rankine cycle becausea)The enthalpy of main steam is higher for superheat cycle b)The mean temperature of heat addition is higher for superheat cyclec)The temperature of steam in the condenser is highd)The quality of stem in the condenser is lowCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The efficiency of superheat Rankine cycle is higher than that of simple Rankine cycle becausea)The enthalpy of main steam is higher for superheat cycle b)The mean temperature of heat addition is higher for superheat cyclec)The temperature of steam in the condenser is highd)The quality of stem in the condenser is lowCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























