Mechanical Engineering Exam > Mechanical Engineering Questions > Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pur...
Start Learning for Free
Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the principal planes through that point making an angle of 45° with plane of shearing stress carries principal stresses whose magnitude is equal to that of shearing stress.
Reason (R): Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.
- a)Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of A
- b)Both A and R are individually true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
- c)A is true but R is false
- d)A is false but R is true
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the princip...
Answer : 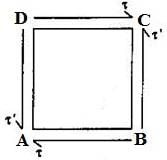
View all questions of this test
- b)Both A and R are individually true but R is NOT the correct explanation of A
Principle of complementary shear stresses
Let us consider a rectangular block ABCD as displayed in following figure. Let us assume that a set of shear stresses (τ) of opposite direction, as displayed in following figure, is applied over the opposite surfaces of rectangular block i.e. AB and CD.

Now if we consider the effect of this set of shear stresses (τ) of opposite direction, we can easily say that there will be zero net force acting over the rectangular block but there will be one couple acting over the rectangular block in clockwise direction.
In order to balance the rectangular block, there must be one more couple of similar intensity acting over the rectangular block in opposite direction i.e. in anti clockwise direction. Therefore, there will be one more set of shear stresses (τ’) of same intensity acting over the rest two opposite surfaces of rectangular block and this set of shear stresses will be termed as complementary shear stress.
Therefore we can say that according to principle of complementary shear stresses,
“A set of shear stresses acting across a plane will always be accompanied by a set of balancing shear stresses of similar intensity across the plane and acting normal to it”
Most Upvoted Answer
Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the princip...
Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the principal planes through that point making an angle of 45° with the plane of shearing stress carries principal stresses whose magnitude is equal to that of shearing stress.
Reason (R): Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.
Explanation:
Pure Shear:
- Pure shear is a state of deformation in which one face of an object is displaced parallel to a plane while the opposite face is fixed.
- In pure shear, there is no change in volume, only a distortion or shape change occurs.
Principal Stresses and Planes:
- Principal stresses are the maximum and minimum normal stresses that act on the principal planes of an object.
- Principal planes are the planes where the shear stress is zero, and only normal stresses act.
Angle of Principal Planes:
- The principal planes through a point in a state of pure shear make an angle of 45° with the plane of shearing stress.
- This means that the principal planes are inclined at 45° to the plane where the shearing stress is acting.
Magnitude of Principal Stresses:
- In the case of pure shear, the magnitude of the principal stresses is equal to the magnitude of the shearing stress.
- This is because the principal stresses are equal and opposite in direction, resulting in a balanced state of stress.
Complementary Shear Stresses:
- Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.
- In pure shear, the shearing stress acts on the plane of shearing stress and its complementary shear stress acts on the principal planes.
- The complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude to the shearing stress and have opposite directions.
Conclusion:
- Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are individually true.
- The Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A) because the complementary shear stresses being equal in magnitude but opposite in direction result in the principal planes carrying principal stresses of equal magnitude as the shearing stress.
Reason (R): Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.
Explanation:
Pure Shear:
- Pure shear is a state of deformation in which one face of an object is displaced parallel to a plane while the opposite face is fixed.
- In pure shear, there is no change in volume, only a distortion or shape change occurs.
Principal Stresses and Planes:
- Principal stresses are the maximum and minimum normal stresses that act on the principal planes of an object.
- Principal planes are the planes where the shear stress is zero, and only normal stresses act.
Angle of Principal Planes:
- The principal planes through a point in a state of pure shear make an angle of 45° with the plane of shearing stress.
- This means that the principal planes are inclined at 45° to the plane where the shearing stress is acting.
Magnitude of Principal Stresses:
- In the case of pure shear, the magnitude of the principal stresses is equal to the magnitude of the shearing stress.
- This is because the principal stresses are equal and opposite in direction, resulting in a balanced state of stress.
Complementary Shear Stresses:
- Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude but opposite in direction.
- In pure shear, the shearing stress acts on the plane of shearing stress and its complementary shear stress acts on the principal planes.
- The complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude to the shearing stress and have opposite directions.
Conclusion:
- Both Assertion (A) and Reason (R) are individually true.
- The Reason (R) is the correct explanation of Assertion (A) because the complementary shear stresses being equal in magnitude but opposite in direction result in the principal planes carrying principal stresses of equal magnitude as the shearing stress.
Attention Mechanical Engineering Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Mechanical Engineering study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Mechanical Engineering.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Similar Mechanical Engineering Doubts
Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the principal planes through that point making an angle of 45° with plane of shearing stress carries principal stresses whose magnitude is equal to that of shearing stress.Reason (R): Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.a)Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)Both A and R are individually true but R is NOT the correct explanation of Ac)A is true but R is falsed)A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the principal planes through that point making an angle of 45° with plane of shearing stress carries principal stresses whose magnitude is equal to that of shearing stress.Reason (R): Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.a)Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)Both A and R are individually true but R is NOT the correct explanation of Ac)A is true but R is falsed)A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the principal planes through that point making an angle of 45° with plane of shearing stress carries principal stresses whose magnitude is equal to that of shearing stress.Reason (R): Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.a)Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)Both A and R are individually true but R is NOT the correct explanation of Ac)A is true but R is falsed)A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the principal planes through that point making an angle of 45° with plane of shearing stress carries principal stresses whose magnitude is equal to that of shearing stress.Reason (R): Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.a)Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)Both A and R are individually true but R is NOT the correct explanation of Ac)A is true but R is falsed)A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the principal planes through that point making an angle of 45° with plane of shearing stress carries principal stresses whose magnitude is equal to that of shearing stress.Reason (R): Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.a)Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)Both A and R are individually true but R is NOT the correct explanation of Ac)A is true but R is falsed)A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Mechanical Engineering 2024 is part of Mechanical Engineering preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Mechanical Engineering exam syllabus. Information about Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the principal planes through that point making an angle of 45° with plane of shearing stress carries principal stresses whose magnitude is equal to that of shearing stress.Reason (R): Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.a)Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)Both A and R are individually true but R is NOT the correct explanation of Ac)A is true but R is falsed)A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Mechanical Engineering 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the principal planes through that point making an angle of 45° with plane of shearing stress carries principal stresses whose magnitude is equal to that of shearing stress.Reason (R): Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.a)Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)Both A and R are individually true but R is NOT the correct explanation of Ac)A is true but R is falsed)A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the principal planes through that point making an angle of 45° with plane of shearing stress carries principal stresses whose magnitude is equal to that of shearing stress.Reason (R): Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.a)Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)Both A and R are individually true but R is NOT the correct explanation of Ac)A is true but R is falsed)A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Mechanical Engineering.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Mechanical Engineering Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the principal planes through that point making an angle of 45° with plane of shearing stress carries principal stresses whose magnitude is equal to that of shearing stress.Reason (R): Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.a)Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)Both A and R are individually true but R is NOT the correct explanation of Ac)A is true but R is falsed)A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the principal planes through that point making an angle of 45° with plane of shearing stress carries principal stresses whose magnitude is equal to that of shearing stress.Reason (R): Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.a)Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)Both A and R are individually true but R is NOT the correct explanation of Ac)A is true but R is falsed)A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the principal planes through that point making an angle of 45° with plane of shearing stress carries principal stresses whose magnitude is equal to that of shearing stress.Reason (R): Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.a)Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)Both A and R are individually true but R is NOT the correct explanation of Ac)A is true but R is falsed)A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the principal planes through that point making an angle of 45° with plane of shearing stress carries principal stresses whose magnitude is equal to that of shearing stress.Reason (R): Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.a)Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)Both A and R are individually true but R is NOT the correct explanation of Ac)A is true but R is falsed)A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Assertion (A): If the state at a point is pure shear, then the principal planes through that point making an angle of 45° with plane of shearing stress carries principal stresses whose magnitude is equal to that of shearing stress.Reason (R): Complementary shear stresses are equal in magnitude, but opposite in direction.a)Both A and R are individually true and R is the correct explanation of Ab)Both A and R are individually true but R is NOT the correct explanation of Ac)A is true but R is falsed)A is false but R is trueCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Mechanical Engineering tests.

|
Explore Courses for Mechanical Engineering exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























