Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > A small Steel of mass M is tied to a string o...
Start Learning for Free
A small Steel of mass M is tied to a string of length R whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity 2w. the string is suddenly pulled so that radius of the circle is half. The new angular velocity will be?
Verified Answer
A small Steel of mass M is tied to a string of length R whirled in a h...
Mass of sphere = m
Initial radius of path r1 = r
Final radius of path r2 = r/2
The initial M.I. of a particle of mass m rotating in a horizontal circle is given by:
m(r1)^2 = m(r^2)
Similarly, the final M.L of a particle rotating in a circle is:
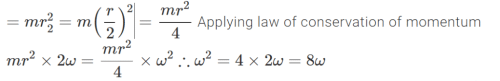
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 12 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 12 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
A small Steel of mass M is tied to a string of length R whirled in a h...
Introduction:
When a small steel mass is whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity, and the string is suddenly pulled so that the radius of the circle is halved, the new angular velocity of the steel mass will change. To understand this change, we need to consider the conservation of angular momentum.
Conservation of Angular Momentum:
Angular momentum is conserved when no external torque acts on a system. The angular momentum (L) of an object is given by the product of its moment of inertia (I) and its angular velocity (ω): L = Iω.
Initial Situation:
In the initial situation, the small steel mass is whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity of 2ω. The moment of inertia (I) of the steel mass remains constant.
Change in Radius:
When the string is suddenly pulled so that the radius of the circle is halved, the moment of inertia (I) of the steel mass changes. The moment of inertia of a point mass about an axis passing through its center of mass is given by the formula: I = MR², where M is the mass of the steel and R is the initial radius.
Final Situation:
In the final situation, the radius of the circle is halved, which means the new radius (R') is equal to R/2. Therefore, the new moment of inertia (I') of the steel mass is given by: I' = M(R/2)² = (1/4)MR².
Conservation of Angular Momentum Equation:
According to the conservation of angular momentum, the initial angular momentum (L) of the steel mass should be equal to the final angular momentum (L') after the change in radius.
Initial Angular Momentum: L = Iω = MR²(2ω) = 2MωR²
Final Angular Momentum: L' = I'ω' = (1/4)MR²ω'
Since the angular momentum is conserved, we can equate the initial and final angular momenta to find the new angular velocity (ω'):
2MωR² = (1/4)MR²ω'
Calculation of New Angular Velocity:
Simplifying the equation, we get:
ω' = 8ω
Therefore, the new angular velocity (ω') is 8 times the initial angular velocity (ω).
Conclusion:
When the radius of the circle is halved, the new angular velocity of the steel mass becomes 8 times the initial angular velocity. This change in angular velocity is a result of the conservation of angular momentum, where the moment of inertia decreases with the decrease in radius, leading to an increase in angular velocity to maintain the angular momentum.
When a small steel mass is whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity, and the string is suddenly pulled so that the radius of the circle is halved, the new angular velocity of the steel mass will change. To understand this change, we need to consider the conservation of angular momentum.
Conservation of Angular Momentum:
Angular momentum is conserved when no external torque acts on a system. The angular momentum (L) of an object is given by the product of its moment of inertia (I) and its angular velocity (ω): L = Iω.
Initial Situation:
In the initial situation, the small steel mass is whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity of 2ω. The moment of inertia (I) of the steel mass remains constant.
Change in Radius:
When the string is suddenly pulled so that the radius of the circle is halved, the moment of inertia (I) of the steel mass changes. The moment of inertia of a point mass about an axis passing through its center of mass is given by the formula: I = MR², where M is the mass of the steel and R is the initial radius.
Final Situation:
In the final situation, the radius of the circle is halved, which means the new radius (R') is equal to R/2. Therefore, the new moment of inertia (I') of the steel mass is given by: I' = M(R/2)² = (1/4)MR².
Conservation of Angular Momentum Equation:
According to the conservation of angular momentum, the initial angular momentum (L) of the steel mass should be equal to the final angular momentum (L') after the change in radius.
Initial Angular Momentum: L = Iω = MR²(2ω) = 2MωR²
Final Angular Momentum: L' = I'ω' = (1/4)MR²ω'
Since the angular momentum is conserved, we can equate the initial and final angular momenta to find the new angular velocity (ω'):
2MωR² = (1/4)MR²ω'
Calculation of New Angular Velocity:
Simplifying the equation, we get:
ω' = 8ω
Therefore, the new angular velocity (ω') is 8 times the initial angular velocity (ω).
Conclusion:
When the radius of the circle is halved, the new angular velocity of the steel mass becomes 8 times the initial angular velocity. This change in angular velocity is a result of the conservation of angular momentum, where the moment of inertia decreases with the decrease in radius, leading to an increase in angular velocity to maintain the angular momentum.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
A small Steel of mass M is tied to a string of length R whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity 2w. the string is suddenly pulled so that radius of the circle is half. The new angular velocity will be?
Question Description
A small Steel of mass M is tied to a string of length R whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity 2w. the string is suddenly pulled so that radius of the circle is half. The new angular velocity will be? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about A small Steel of mass M is tied to a string of length R whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity 2w. the string is suddenly pulled so that radius of the circle is half. The new angular velocity will be? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A small Steel of mass M is tied to a string of length R whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity 2w. the string is suddenly pulled so that radius of the circle is half. The new angular velocity will be?.
A small Steel of mass M is tied to a string of length R whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity 2w. the string is suddenly pulled so that radius of the circle is half. The new angular velocity will be? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about A small Steel of mass M is tied to a string of length R whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity 2w. the string is suddenly pulled so that radius of the circle is half. The new angular velocity will be? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for A small Steel of mass M is tied to a string of length R whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity 2w. the string is suddenly pulled so that radius of the circle is half. The new angular velocity will be?.
Solutions for A small Steel of mass M is tied to a string of length R whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity 2w. the string is suddenly pulled so that radius of the circle is half. The new angular velocity will be? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of A small Steel of mass M is tied to a string of length R whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity 2w. the string is suddenly pulled so that radius of the circle is half. The new angular velocity will be? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
A small Steel of mass M is tied to a string of length R whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity 2w. the string is suddenly pulled so that radius of the circle is half. The new angular velocity will be?, a detailed solution for A small Steel of mass M is tied to a string of length R whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity 2w. the string is suddenly pulled so that radius of the circle is half. The new angular velocity will be? has been provided alongside types of A small Steel of mass M is tied to a string of length R whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity 2w. the string is suddenly pulled so that radius of the circle is half. The new angular velocity will be? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice A small Steel of mass M is tied to a string of length R whirled in a horizontal circle with a uniform angular velocity 2w. the string is suddenly pulled so that radius of the circle is half. The new angular velocity will be? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















