Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydro...
Start Learning for Free
HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to give
a) CH
3
CHO and CH
3
Br
b) BrCH
2
CHO and CH
3
OH
c) BrCH
2
– CH
2
– OCH
3
d) H
3
C – CHBr – OCH
3
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room tem...
The correct answer is d.
Methyl vinyl ether is a very reactive gas. It is hydrolysed rapidly by dilute acids at room temperature to give methanol and aldehyde. However, under anhydrous conditions at room temperature, it undergoes many addition reactions at the double bond.
Methyl vinyl ether is a very reactive gas. It is hydrolysed rapidly by dilute acids at room temperature to give methanol and aldehyde. However, under anhydrous conditions at room temperature, it undergoes many addition reactions at the double bond.
Electrophilic addition reaction more favourable.

Most Upvoted Answer
HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room tem...
Reactants and Conditions:
- HBr (Hydrogen bromide)
- CH2 = CH – OCH3 (Methyl vinyl ether)
- Anhydrous conditions (without water)
- Room temperature
Reaction:
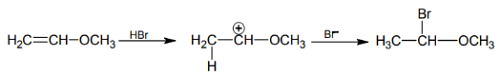
The reaction between HBr and CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature leads to the formation of BrCH2– CH2– OCH3.
Explanation:
1. Electrophilic Addition Reaction:
The reaction between HBr and CH2 = CH – OCH3 involves an electrophilic addition reaction mechanism. HBr acts as an electrophile due to the presence of a polar covalent bond between hydrogen and bromine. The double bond in CH2 = CH – OCH3 acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic hydrogen in HBr.
2. Formation of Carbocation:
The attack of the double bond on HBr leads to the formation of a carbocation intermediate. The oxygen atom in CH2 = CH – OCH3 donates electron density towards the carbon-carbon double bond, making it more susceptible to attack by the electrophilic hydrogen in HBr. As a result, the hydrogen atom in HBr gets attached to one of the carbon atoms, while the bromine atom gains a positive charge.
3. Nucleophilic Attack:
The bromide ion (Br-) acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation intermediate. The bromide ion, being negatively charged, is attracted towards the positively charged carbon atom. The bromide ion donates its lone pair of electrons to form a bond with the positively charged carbon atom.
4. Formation of Product:
The final product is BrCH2– CH2– OCH3, where the bromine atom is attached to one of the carbon atoms in the double bond, and the oxygen atom remains attached to the other carbon atom. The reaction proceeds via an electrophilic addition mechanism, where the double bond in CH2 = CH – OCH3 is broken, and the bromine atom is added to the carbon atoms.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'C' - BrCH2– CH2– OCH3. This is the product formed when HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature.
- HBr (Hydrogen bromide)
- CH2 = CH – OCH3 (Methyl vinyl ether)
- Anhydrous conditions (without water)
- Room temperature
Reaction:
The reaction between HBr and CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature leads to the formation of BrCH2– CH2– OCH3.
Explanation:
1. Electrophilic Addition Reaction:
The reaction between HBr and CH2 = CH – OCH3 involves an electrophilic addition reaction mechanism. HBr acts as an electrophile due to the presence of a polar covalent bond between hydrogen and bromine. The double bond in CH2 = CH – OCH3 acts as a nucleophile and attacks the electrophilic hydrogen in HBr.
2. Formation of Carbocation:
The attack of the double bond on HBr leads to the formation of a carbocation intermediate. The oxygen atom in CH2 = CH – OCH3 donates electron density towards the carbon-carbon double bond, making it more susceptible to attack by the electrophilic hydrogen in HBr. As a result, the hydrogen atom in HBr gets attached to one of the carbon atoms, while the bromine atom gains a positive charge.
3. Nucleophilic Attack:
The bromide ion (Br-) acts as a nucleophile and attacks the carbocation intermediate. The bromide ion, being negatively charged, is attracted towards the positively charged carbon atom. The bromide ion donates its lone pair of electrons to form a bond with the positively charged carbon atom.
4. Formation of Product:
The final product is BrCH2– CH2– OCH3, where the bromine atom is attached to one of the carbon atoms in the double bond, and the oxygen atom remains attached to the other carbon atom. The reaction proceeds via an electrophilic addition mechanism, where the double bond in CH2 = CH – OCH3 is broken, and the bromine atom is added to the carbon atoms.
In conclusion, the correct answer is option 'C' - BrCH2– CH2– OCH3. This is the product formed when HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature.
Attention Class 11 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 11 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 11.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Similar Class 11 Doubts
HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to givea) CH3CHO and CH3Brb) BrCH2CHO and CH3OHc) BrCH2– CH2– OCH3d) H3C – CHBr – OCH3Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to givea) CH3CHO and CH3Brb) BrCH2CHO and CH3OHc) BrCH2– CH2– OCH3d) H3C – CHBr – OCH3Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to givea) CH3CHO and CH3Brb) BrCH2CHO and CH3OHc) BrCH2– CH2– OCH3d) H3C – CHBr – OCH3Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to givea) CH3CHO and CH3Brb) BrCH2CHO and CH3OHc) BrCH2– CH2– OCH3d) H3C – CHBr – OCH3Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to givea) CH3CHO and CH3Brb) BrCH2CHO and CH3OHc) BrCH2– CH2– OCH3d) H3C – CHBr – OCH3Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to givea) CH3CHO and CH3Brb) BrCH2CHO and CH3OHc) BrCH2– CH2– OCH3d) H3C – CHBr – OCH3Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to givea) CH3CHO and CH3Brb) BrCH2CHO and CH3OHc) BrCH2– CH2– OCH3d) H3C – CHBr – OCH3Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to givea) CH3CHO and CH3Brb) BrCH2CHO and CH3OHc) BrCH2– CH2– OCH3d) H3C – CHBr – OCH3Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to givea) CH3CHO and CH3Brb) BrCH2CHO and CH3OHc) BrCH2– CH2– OCH3d) H3C – CHBr – OCH3Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to givea) CH3CHO and CH3Brb) BrCH2CHO and CH3OHc) BrCH2– CH2– OCH3d) H3C – CHBr – OCH3Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to givea) CH3CHO and CH3Brb) BrCH2CHO and CH3OHc) BrCH2– CH2– OCH3d) H3C – CHBr – OCH3Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to givea) CH3CHO and CH3Brb) BrCH2CHO and CH3OHc) BrCH2– CH2– OCH3d) H3C – CHBr – OCH3Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice HBr reacts with CH2 = CH – OCH3 under anhydrous conditions at room temperature to givea) CH3CHO and CH3Brb) BrCH2CHO and CH3OHc) BrCH2– CH2– OCH3d) H3C – CHBr – OCH3Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























