JEE Exam > JEE Questions > Consider two point charges of equal magnitude...
Start Learning for Free
Consider two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign separated by a certain distance .the neutral point Between them?
Verified Answer
Consider two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign separa...
These two charges form an electric dipole, mid- point of which is called neutral point.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all JEE courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all JEE courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Consider two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign separa...
Neutral Point Between Two Point Charges
When two point charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign are separated by a certain distance, there exists a neutral point between them. This neutral point is the location where the electric field due to one charge cancels out the electric field due to the other charge, resulting in a net electric field of zero.
1. Electric Field
The electric field is a vector quantity that describes the force experienced by a positive test charge placed in the vicinity of an electric charge. The electric field produced by a point charge is given by Coulomb's law, which states that the magnitude of the electric field at a point is directly proportional to the magnitude of the charge and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the charges.
2. Superposition Principle
According to the superposition principle, the total electric field at any point in space due to multiple charges is the vector sum of the electric fields produced by each individual charge. This principle allows us to analyze the electric fields produced by the two point charges separately and then combine them to determine the net electric field at any given point.
3. Electric Field of Individual Charges
Let's consider two point charges, q1 and q2, separated by a distance d. If q1 and q2 have equal magnitude but opposite sign, their electric fields will also have equal magnitudes but opposite directions. The electric field produced by q1 at any point is radially outward, while the electric field produced by q2 is radially inward.
4. Neutral Point
Between the two charges, there exists a point where the electric field due to q1 cancels out the electric field due to q2. This neutral point is the location where the net electric field is zero. At this point, the magnitudes of the electric fields produced by q1 and q2 are equal, but their directions are opposite.
5. Calculation of Neutral Point Position
To find the position of the neutral point, we can equate the magnitudes of the electric fields due to q1 and q2. By using Coulomb's law and the distance between the charges, we can solve for the position where the net electric field is zero.
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, when two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign are separated by a certain distance, a neutral point exists between them. At this neutral point, the electric field due to one charge cancels out the electric field due to the other charge, resulting in a net electric field of zero. By calculating the position of this neutral point, we can determine where the electric fields of the two charges cancel each other out.
When two point charges of equal magnitude but opposite sign are separated by a certain distance, there exists a neutral point between them. This neutral point is the location where the electric field due to one charge cancels out the electric field due to the other charge, resulting in a net electric field of zero.
1. Electric Field
The electric field is a vector quantity that describes the force experienced by a positive test charge placed in the vicinity of an electric charge. The electric field produced by a point charge is given by Coulomb's law, which states that the magnitude of the electric field at a point is directly proportional to the magnitude of the charge and inversely proportional to the square of the distance between the charges.
2. Superposition Principle
According to the superposition principle, the total electric field at any point in space due to multiple charges is the vector sum of the electric fields produced by each individual charge. This principle allows us to analyze the electric fields produced by the two point charges separately and then combine them to determine the net electric field at any given point.
3. Electric Field of Individual Charges
Let's consider two point charges, q1 and q2, separated by a distance d. If q1 and q2 have equal magnitude but opposite sign, their electric fields will also have equal magnitudes but opposite directions. The electric field produced by q1 at any point is radially outward, while the electric field produced by q2 is radially inward.
4. Neutral Point
Between the two charges, there exists a point where the electric field due to q1 cancels out the electric field due to q2. This neutral point is the location where the net electric field is zero. At this point, the magnitudes of the electric fields produced by q1 and q2 are equal, but their directions are opposite.
5. Calculation of Neutral Point Position
To find the position of the neutral point, we can equate the magnitudes of the electric fields due to q1 and q2. By using Coulomb's law and the distance between the charges, we can solve for the position where the net electric field is zero.
6. Conclusion
In conclusion, when two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign are separated by a certain distance, a neutral point exists between them. At this neutral point, the electric field due to one charge cancels out the electric field due to the other charge, resulting in a net electric field of zero. By calculating the position of this neutral point, we can determine where the electric fields of the two charges cancel each other out.
Community Answer
Consider two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign separa...
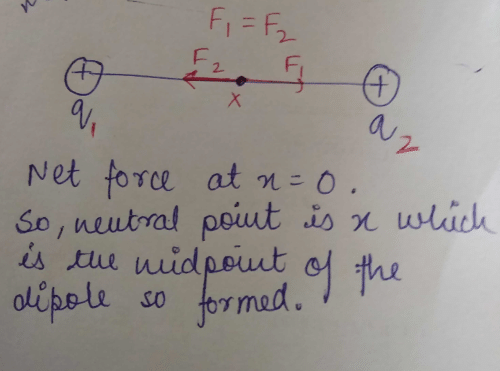
Attention JEE Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed JEE study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in JEE.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Similar JEE Doubts
Consider two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign separated by a certain distance .the neutral point Between them?
Question Description
Consider two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign separated by a certain distance .the neutral point Between them? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Consider two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign separated by a certain distance .the neutral point Between them? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign separated by a certain distance .the neutral point Between them?.
Consider two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign separated by a certain distance .the neutral point Between them? for JEE 2024 is part of JEE preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the JEE exam syllabus. Information about Consider two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign separated by a certain distance .the neutral point Between them? covers all topics & solutions for JEE 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign separated by a certain distance .the neutral point Between them?.
Solutions for Consider two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign separated by a certain distance .the neutral point Between them? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for JEE.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for JEE Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Consider two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign separated by a certain distance .the neutral point Between them? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Consider two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign separated by a certain distance .the neutral point Between them?, a detailed solution for Consider two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign separated by a certain distance .the neutral point Between them? has been provided alongside types of Consider two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign separated by a certain distance .the neutral point Between them? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Consider two point charges of equal magnitude and opposite sign separated by a certain distance .the neutral point Between them? tests, examples and also practice JEE tests.

|
Explore Courses for JEE exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























