Class 9 Exam > Class 9 Questions > What was the Fluid mosaic model of biomembran...
Start Learning for Free
What was the Fluid mosaic model of biomembrane by Singer and Nicolson ?
Most Upvoted Answer
What was the Fluid mosaic model of biomembrane by Singer and Nicolson ...
The Fluid Mosaic Model of Biomembrane by Singer and Nicolson
The Fluid Mosaic Model of biomembrane was proposed by S.J. Singer and G.L. Nicolson in 1972. It is a widely accepted model that describes the structure and properties of cell membranes. According to this model, the cell membrane is a dynamic and fluid structure composed of various molecules that are organized in a mosaic-like pattern.
Fluidity of the Membrane
The term "fluid" in the Fluid Mosaic Model refers to the ability of the membrane to move and change its shape. The lipid bilayer, which forms the main structure of the membrane, is composed of phospholipids with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails. These lipids are free to move laterally within the bilayer, giving the membrane its fluid nature. Additionally, the presence of cholesterol molecules helps to maintain the fluidity of the membrane by preventing the phospholipids from packing too closely together.
Mosaic of Molecules
The term "mosaic" in the Fluid Mosaic Model refers to the diverse array of molecules present in the membrane. In addition to phospholipids, the membrane also contains proteins, carbohydrates, and other lipids. The proteins are embedded within the lipid bilayer and are responsible for various functions such as transport of molecules, enzymatic activity, and cell signaling. Carbohydrates are often attached to proteins or lipids on the outer surface of the membrane, forming glycoproteins or glycolipids that are involved in cell recognition and communication.
Membrane Structure
According to the Fluid Mosaic Model, the membrane is a lipid bilayer with proteins embedded within it. The lipid bilayer provides a barrier to the movement of hydrophilic molecules while allowing the passage of small hydrophobic molecules. The proteins are classified into two categories: integral proteins that span the entire width of the membrane and peripheral proteins that are attached to the surface of the membrane. The distribution and arrangement of proteins within the membrane are not fixed but can vary depending on the specific cell type and its functions.
Role in Cell Function
The Fluid Mosaic Model is crucial for understanding the functions of cell membranes. The fluidity of the membrane allows for the movement of molecules and ions across the membrane, which is essential for various cellular processes such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and cell signaling. The mosaic nature of the membrane enables the recognition and interaction of cells with their environment, facilitating cell adhesion, immune response, and cell communication.
In conclusion, the Fluid Mosaic Model proposed by Singer and Nicolson describes the dynamic and heterogeneous nature of cell membranes. It provides a framework for understanding the structure and functions of biomembranes, emphasizing the fluidity of the lipid bilayer and the diversity of molecules present in the membrane.
The Fluid Mosaic Model of biomembrane was proposed by S.J. Singer and G.L. Nicolson in 1972. It is a widely accepted model that describes the structure and properties of cell membranes. According to this model, the cell membrane is a dynamic and fluid structure composed of various molecules that are organized in a mosaic-like pattern.
Fluidity of the Membrane
The term "fluid" in the Fluid Mosaic Model refers to the ability of the membrane to move and change its shape. The lipid bilayer, which forms the main structure of the membrane, is composed of phospholipids with hydrophilic heads and hydrophobic tails. These lipids are free to move laterally within the bilayer, giving the membrane its fluid nature. Additionally, the presence of cholesterol molecules helps to maintain the fluidity of the membrane by preventing the phospholipids from packing too closely together.
Mosaic of Molecules
The term "mosaic" in the Fluid Mosaic Model refers to the diverse array of molecules present in the membrane. In addition to phospholipids, the membrane also contains proteins, carbohydrates, and other lipids. The proteins are embedded within the lipid bilayer and are responsible for various functions such as transport of molecules, enzymatic activity, and cell signaling. Carbohydrates are often attached to proteins or lipids on the outer surface of the membrane, forming glycoproteins or glycolipids that are involved in cell recognition and communication.
Membrane Structure
According to the Fluid Mosaic Model, the membrane is a lipid bilayer with proteins embedded within it. The lipid bilayer provides a barrier to the movement of hydrophilic molecules while allowing the passage of small hydrophobic molecules. The proteins are classified into two categories: integral proteins that span the entire width of the membrane and peripheral proteins that are attached to the surface of the membrane. The distribution and arrangement of proteins within the membrane are not fixed but can vary depending on the specific cell type and its functions.
Role in Cell Function
The Fluid Mosaic Model is crucial for understanding the functions of cell membranes. The fluidity of the membrane allows for the movement of molecules and ions across the membrane, which is essential for various cellular processes such as nutrient uptake, waste removal, and cell signaling. The mosaic nature of the membrane enables the recognition and interaction of cells with their environment, facilitating cell adhesion, immune response, and cell communication.
In conclusion, the Fluid Mosaic Model proposed by Singer and Nicolson describes the dynamic and heterogeneous nature of cell membranes. It provides a framework for understanding the structure and functions of biomembranes, emphasizing the fluidity of the lipid bilayer and the diversity of molecules present in the membrane.
Community Answer
What was the Fluid mosaic model of biomembrane by Singer and Nicolson ...
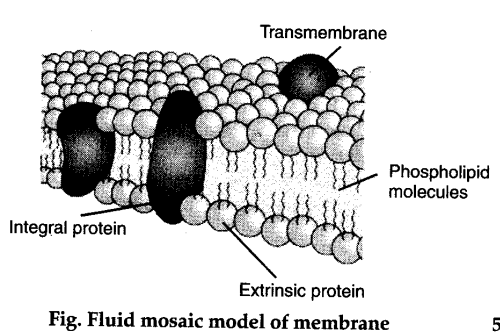
Fluid mosaic model:
Fluid mosaic model was proposed by Singer and Nicholson.
According to this model, there is a central bilipid
layer of phospholipids with their polar head group towards the outside and the non-polar tails pointing inwards. ,
Some proteins which are embedded in the lipid layer are called integral or intrinsic proteins and they cannot be separated from the membrane.
There are large globular integral proteins which project beyond the lipid layer on both the sides are believed to have channels through which water- soluble materials can pass across.
Superficially attached proteins are called extrinsic or peripheral proteins and can be easily removed.
Some membrane lipids and integral proteins remains bound to oligosaccharides which project into the extracellular fluid and influence the manner in which cells interact with one another.
There are certain specific proteins called membrane receptors, which mediate the flow of materials and information into the cell.


|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Similar Class 9 Doubts
What was the Fluid mosaic model of biomembrane by Singer and Nicolson ?
Question Description
What was the Fluid mosaic model of biomembrane by Singer and Nicolson ? for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about What was the Fluid mosaic model of biomembrane by Singer and Nicolson ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What was the Fluid mosaic model of biomembrane by Singer and Nicolson ?.
What was the Fluid mosaic model of biomembrane by Singer and Nicolson ? for Class 9 2025 is part of Class 9 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 9 exam syllabus. Information about What was the Fluid mosaic model of biomembrane by Singer and Nicolson ? covers all topics & solutions for Class 9 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What was the Fluid mosaic model of biomembrane by Singer and Nicolson ?.
Solutions for What was the Fluid mosaic model of biomembrane by Singer and Nicolson ? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 9.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 9 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What was the Fluid mosaic model of biomembrane by Singer and Nicolson ? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What was the Fluid mosaic model of biomembrane by Singer and Nicolson ?, a detailed solution for What was the Fluid mosaic model of biomembrane by Singer and Nicolson ? has been provided alongside types of What was the Fluid mosaic model of biomembrane by Singer and Nicolson ? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What was the Fluid mosaic model of biomembrane by Singer and Nicolson ? tests, examples and also practice Class 9 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 9 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























