Class 8 Exam > Class 8 Questions > what is direct and indirect speech
Start Learning for Free
what is direct and indirect speech
Verified Answer
what is direct and indirect speech
When using indirect or reported speech, the form changes. Usually indirect speech is introduced by the verb said, as in I said, Bill said, or they said. Using the verb say in this tense, indicates that something was said in the past. In these cases, the main verb in the reported sentence is put in the past. If the main verb is already in a past tense, then the tense changes to another past tense; it can almost be seen as moving even further into the past.
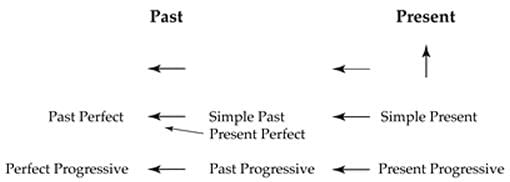
Verb tense changes also characterize other situations using indirect speech. Note the changes shown in the chart and see the table below for examples. With indirect speech, the use of that is optional.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 8 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 8 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
what is direct and indirect speech
Direct and Indirect Speech: An Explanation
Direct and indirect speech are two ways of reporting what someone has said. Direct speech is when we use the exact words spoken by a person, while indirect speech is when we report what someone has said without using their exact words. In both cases, the main goal is to convey the information accurately and maintain the meaning of the original statement.
Direct Speech:
Direct speech involves quoting the exact words spoken by an individual. It is usually enclosed within quotation marks and often includes the use of reporting verbs such as "said," "asked," "shouted," or "whispered." For example:
- Sarah said, "I am going to the park."
In this example, the exact words spoken by Sarah are reported within quotation marks.
Indirect Speech:
Indirect speech, also known as reported speech, involves reporting what someone has said without using their exact words. The reported speech is usually introduced by a reporting verb, which is often changed to match the tense of the reported statement. The pronouns, time expressions, and verb tenses may also be adjusted to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. For example:
- Sarah said that she was going to the park.
In this example, the reporting verb "said" is used to introduce the reported speech, and the tense of the verb "am" changes to "was" to match the past tense.
Differences between Direct and Indirect Speech:
There are several key differences between direct and indirect speech, including:
1. Punctuation: Direct speech is enclosed within quotation marks, while indirect speech does not require them.
2. Pronoun Changes: In indirect speech, pronouns may change to reflect the perspective of the reporter rather than the original speaker.
3. Verb Tense Changes: Verb tenses may change in indirect speech to reflect the time shift from the original statement.
4. Reporting Verb: Direct speech often uses reporting verbs such as "say," "ask," or "shout," while indirect speech usually begins with a reporting verb that reflects the context or tone of the original statement.
It is important to note that when converting direct speech to indirect speech, we must pay attention to these changes to ensure accurate reporting of the original message.
Conclusion:
Direct and indirect speech are two ways of reporting what someone has said. Direct speech involves using the exact words spoken, enclosed in quotation marks, while indirect speech reports the speech without using the exact words. Indirect speech requires adjustments in reporting verbs, pronouns, time expressions, and verb tenses to accurately convey the original message. Understanding and being able to use both direct and indirect speech is essential for effective communication and accurate reporting of conversations or statements.
Direct and indirect speech are two ways of reporting what someone has said. Direct speech is when we use the exact words spoken by a person, while indirect speech is when we report what someone has said without using their exact words. In both cases, the main goal is to convey the information accurately and maintain the meaning of the original statement.
Direct Speech:
Direct speech involves quoting the exact words spoken by an individual. It is usually enclosed within quotation marks and often includes the use of reporting verbs such as "said," "asked," "shouted," or "whispered." For example:
- Sarah said, "I am going to the park."
In this example, the exact words spoken by Sarah are reported within quotation marks.
Indirect Speech:
Indirect speech, also known as reported speech, involves reporting what someone has said without using their exact words. The reported speech is usually introduced by a reporting verb, which is often changed to match the tense of the reported statement. The pronouns, time expressions, and verb tenses may also be adjusted to reflect the change from direct to indirect speech. For example:
- Sarah said that she was going to the park.
In this example, the reporting verb "said" is used to introduce the reported speech, and the tense of the verb "am" changes to "was" to match the past tense.
Differences between Direct and Indirect Speech:
There are several key differences between direct and indirect speech, including:
1. Punctuation: Direct speech is enclosed within quotation marks, while indirect speech does not require them.
2. Pronoun Changes: In indirect speech, pronouns may change to reflect the perspective of the reporter rather than the original speaker.
3. Verb Tense Changes: Verb tenses may change in indirect speech to reflect the time shift from the original statement.
4. Reporting Verb: Direct speech often uses reporting verbs such as "say," "ask," or "shout," while indirect speech usually begins with a reporting verb that reflects the context or tone of the original statement.
It is important to note that when converting direct speech to indirect speech, we must pay attention to these changes to ensure accurate reporting of the original message.
Conclusion:
Direct and indirect speech are two ways of reporting what someone has said. Direct speech involves using the exact words spoken, enclosed in quotation marks, while indirect speech reports the speech without using the exact words. Indirect speech requires adjustments in reporting verbs, pronouns, time expressions, and verb tenses to accurately convey the original message. Understanding and being able to use both direct and indirect speech is essential for effective communication and accurate reporting of conversations or statements.
Community Answer
what is direct and indirect speech
Https://edurev.page.link/ez8gT6c5zFDbp1ho9
Attention Class 8 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 8 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 8.

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|
Similar Class 8 Doubts
what is direct and indirect speech
Question Description
what is direct and indirect speech for Class 8 2024 is part of Class 8 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 8 exam syllabus. Information about what is direct and indirect speech covers all topics & solutions for Class 8 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is direct and indirect speech.
what is direct and indirect speech for Class 8 2024 is part of Class 8 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 8 exam syllabus. Information about what is direct and indirect speech covers all topics & solutions for Class 8 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for what is direct and indirect speech.
Solutions for what is direct and indirect speech in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 8.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 8 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of what is direct and indirect speech defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
what is direct and indirect speech, a detailed solution for what is direct and indirect speech has been provided alongside types of what is direct and indirect speech theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice what is direct and indirect speech tests, examples and also practice Class 8 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 8 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























