Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Division taking place in tapetum cell is -a)M...
Start Learning for Free
Division taking place in tapetum cell is -
- a)Meiosis
- b)Amitosis
- c)Endomitosis
- d)Only mitosis
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Division taking place in tapetum cell is -a)Meiosisb)Amitosisc)Endomit...
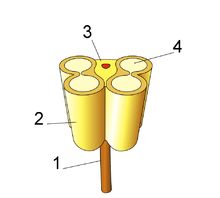
The tapetum is a specialised layer of nutritive cells found within the anther, of flowering plants, where it is located between the sporangenous tissue and the anther wall. Tapetum is important for the nutrition and development of pollen grains, as well as a source of precursors for the pollen coat.
[1]
The cells are usually bigger and normally have more than one nucleus per cell. As the sporogenous cells undergo mitosis, the nuclei of tapetal cells also divide. Sometimes, this mitosis is not normal due to which many cells of mature tapetum become multinucleate
. Sometimes polyploidy and polyteny can also be seen. The unusually large nuclear constitution of the tapetum helps it in providing nutrients and regulatory molecules to the forming pollen grains. The following processes are responsible for this:- Endomitosis
- Normal mitosis not followed by cytokinesis
- Formation of restitution nuclei
- Endoreduplication
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Division taking place in tapetum cell is -a)Meiosisb)Amitosisc)Endomit...
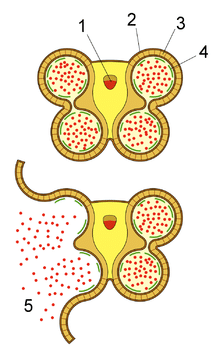
Endomitosis in Tapetum Cell Division
In tapetum cells, division occurs through a process called endomitosis. Endomitosis is a type of cell division where the nuclear division takes place without the subsequent cytokinesis, resulting in cells with multiple nuclei. This process is essential for the development and function of tapetum cells in plants.
Process of Endomitosis
- Endomitosis starts with the replication of DNA in the nucleus of the tapetum cell.
- The replicated chromosomes then undergo multiple rounds of condensation and segregation, leading to the formation of multiple sets of chromosomes within the same cell.
- Unlike in normal mitosis where the cell divides into two daughter cells, in endomitosis, the cell retains all the nuclei within a shared cytoplasm.
- This results in the formation of cells with multiple nuclei, which is a characteristic feature of tapetum cells.
Significance of Endomitosis in Tapetum Cells
- The process of endomitosis in tapetum cells allows for the accumulation of nutrients, proteins, and other essential molecules required for pollen development.
- The presence of multiple nuclei in tapetum cells facilitates the synthesis and secretion of various compounds that are essential for pollen wall formation and pollen maturation.
- Endomitosis also plays a crucial role in providing mechanical and structural support to the developing pollen grains.
Conclusion
Endomitosis in tapetum cells is a unique process of cell division that is crucial for the development and function of tapetum cells in plants. By undergoing endomitosis, tapetum cells are able to support the growth and maturation of pollen grains through the synthesis and secretion of essential compounds.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Division taking place in tapetum cell is -a)Meiosisb)Amitosisc)Endomitosisd)Only mitosisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Division taking place in tapetum cell is -a)Meiosisb)Amitosisc)Endomitosisd)Only mitosisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Division taking place in tapetum cell is -a)Meiosisb)Amitosisc)Endomitosisd)Only mitosisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Division taking place in tapetum cell is -a)Meiosisb)Amitosisc)Endomitosisd)Only mitosisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Division taking place in tapetum cell is -a)Meiosisb)Amitosisc)Endomitosisd)Only mitosisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Division taking place in tapetum cell is -a)Meiosisb)Amitosisc)Endomitosisd)Only mitosisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Division taking place in tapetum cell is -a)Meiosisb)Amitosisc)Endomitosisd)Only mitosisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Division taking place in tapetum cell is -a)Meiosisb)Amitosisc)Endomitosisd)Only mitosisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Division taking place in tapetum cell is -a)Meiosisb)Amitosisc)Endomitosisd)Only mitosisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Division taking place in tapetum cell is -a)Meiosisb)Amitosisc)Endomitosisd)Only mitosisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Division taking place in tapetum cell is -a)Meiosisb)Amitosisc)Endomitosisd)Only mitosisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Division taking place in tapetum cell is -a)Meiosisb)Amitosisc)Endomitosisd)Only mitosisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Division taking place in tapetum cell is -a)Meiosisb)Amitosisc)Endomitosisd)Only mitosisCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.