Class 6 Exam > Class 6 Questions > Name the different layers of atmosphere.?
Start Learning for Free
Name the different layers of atmosphere.?
Verified Answer
Name the different layers of atmosphere.?
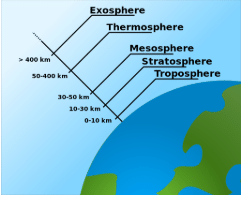
Layers of the atmosphere
The atmosphere is comprised of layers based on temperature. These layers are the troposphere, stratosphere, mesosphere and thermosphere. A further region at about 500 km above the Earth's surface is called the exosphere.
The atmosphere can be divided into layers based on its temperature, as shown in the figure below. These layers are the troposphere, the stratosphere, the mesosphere and the thermosphere. A further region, beginning about 500 km above the Earth's surface, is called the exosphere.
The Troposphere
This is the lowest part of the atmosphere - the part we live in. It contains most of our weather - clouds, rain, snow. In this part of the atmosphere the temperature gets colder as the distance above the earth increases, by about 6.5deg C per kilometre. The actual change of temperature with height varies from day to day, depending on the weather.
The Stratosphere
This extends upwards from the tropopause to about 50 km. It contains much of the ozone in the atmosphere. The increase in temperature with height occurs because of absorption of ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the sun by this ozone. Temperatures in the stratosphere are highest over the summer pole, and lowest over the winter pole.
The Mesosphere
The region above the stratosphere is called the mesosphere. Here the temperature again decreases with height, reaching a minimum of about -90 deg C at the "mesopause".
The Thermosphere and Ionosphere
The thermosphere lies above the mesopause, and is a region in which temperatures again increase with height. This temperature increase is caused by the absorption of energetic ultraviolet and X-Ray radiation from the sun.
The Exosphere
The region above about 500 km is called the exosphere. It contains mainly oxygen and hydrogen atoms, but there are so few of them that they rarely collide - they follow "ballistic" trajectories under the influence of gravity, and some of them escape right out into space.
The Magnetosphere
The earth behaves like a huge magnet. It traps electrons (negative charge) and protons (positive), concentrating them in two bands about 3,000 and 16,000 km above the globe - the Van Allen "radiation" belts. This outer region surrounding the earth, where charged particles spiral along the magnetic field lines, is called the magnetosphere.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 6 courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all Class 6 courses
Most Upvoted Answer
Name the different layers of atmosphere.?
Layers of the Atmosphere
The Earth's atmosphere is composed of several distinct layers, each with its own unique characteristics. These layers are classified based on their temperature changes with increasing altitude. From the surface of the Earth to the outer space, the layers of the atmosphere are as follows:
Troposphere:
- The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere, extending from the Earth's surface up to an average altitude of about 12 kilometers.
- It is the layer where weather phenomena, such as cloud formation, precipitation, and storms occur.
- The temperature decreases with increasing altitude in the troposphere.
Stratosphere:
- The stratosphere lies above the troposphere and extends from approximately 12 kilometers to 50 kilometers above the Earth's surface.
- It contains the ozone layer, which absorbs harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun.
- The temperature remains relatively constant or slightly increases with altitude in the stratosphere.
Mesosphere:
- Above the stratosphere, the mesosphere extends from about 50 kilometers to 85 kilometers.
- It is the layer where meteors burn up upon entering the Earth's atmosphere.
- The temperature decreases with altitude in the mesosphere, reaching extremely low levels.
Thermosphere:
- The thermosphere lies above the mesosphere and extends from approximately 85 kilometers to 600 kilometers above the Earth's surface.
- It is the layer where the International Space Station (ISS) orbits the Earth.
- The temperature in the thermosphere can reach thousands of degrees Celsius due to the absorption of high-energy solar radiation.
Exosphere:
- The exosphere is the outermost layer of the atmosphere, extending from the upper limit of the thermosphere to the edge of space.
- It gradually transitions into the vacuum of outer space.
- The exosphere is sparsely populated with gas molecules, and the temperature can vary greatly depending on solar activity.
Overall, the Earth's atmosphere is divided into these distinct layers that play crucial roles in weather patterns, climate regulation, and protection against harmful radiation. Each layer has its own unique characteristics and properties, which vary in terms of temperature, altitude, and composition. Understanding these layers helps us comprehend the complex dynamics of our atmosphere and how it interacts with the Earth's surface and space.
The Earth's atmosphere is composed of several distinct layers, each with its own unique characteristics. These layers are classified based on their temperature changes with increasing altitude. From the surface of the Earth to the outer space, the layers of the atmosphere are as follows:
Troposphere:
- The troposphere is the lowest layer of the atmosphere, extending from the Earth's surface up to an average altitude of about 12 kilometers.
- It is the layer where weather phenomena, such as cloud formation, precipitation, and storms occur.
- The temperature decreases with increasing altitude in the troposphere.
Stratosphere:
- The stratosphere lies above the troposphere and extends from approximately 12 kilometers to 50 kilometers above the Earth's surface.
- It contains the ozone layer, which absorbs harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation from the Sun.
- The temperature remains relatively constant or slightly increases with altitude in the stratosphere.
Mesosphere:
- Above the stratosphere, the mesosphere extends from about 50 kilometers to 85 kilometers.
- It is the layer where meteors burn up upon entering the Earth's atmosphere.
- The temperature decreases with altitude in the mesosphere, reaching extremely low levels.
Thermosphere:
- The thermosphere lies above the mesosphere and extends from approximately 85 kilometers to 600 kilometers above the Earth's surface.
- It is the layer where the International Space Station (ISS) orbits the Earth.
- The temperature in the thermosphere can reach thousands of degrees Celsius due to the absorption of high-energy solar radiation.
Exosphere:
- The exosphere is the outermost layer of the atmosphere, extending from the upper limit of the thermosphere to the edge of space.
- It gradually transitions into the vacuum of outer space.
- The exosphere is sparsely populated with gas molecules, and the temperature can vary greatly depending on solar activity.
Overall, the Earth's atmosphere is divided into these distinct layers that play crucial roles in weather patterns, climate regulation, and protection against harmful radiation. Each layer has its own unique characteristics and properties, which vary in terms of temperature, altitude, and composition. Understanding these layers helps us comprehend the complex dynamics of our atmosphere and how it interacts with the Earth's surface and space.
Community Answer
Name the different layers of atmosphere.?
Troposphere
Attention Class 6 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 6 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 6.

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|
Similar Class 6 Doubts
Name the different layers of atmosphere.?
Question Description
Name the different layers of atmosphere.? for Class 6 2024 is part of Class 6 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 6 exam syllabus. Information about Name the different layers of atmosphere.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 6 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Name the different layers of atmosphere.?.
Name the different layers of atmosphere.? for Class 6 2024 is part of Class 6 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 6 exam syllabus. Information about Name the different layers of atmosphere.? covers all topics & solutions for Class 6 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Name the different layers of atmosphere.?.
Solutions for Name the different layers of atmosphere.? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 6.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 6 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Name the different layers of atmosphere.? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Name the different layers of atmosphere.?, a detailed solution for Name the different layers of atmosphere.? has been provided alongside types of Name the different layers of atmosphere.? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Name the different layers of atmosphere.? tests, examples and also practice Class 6 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 6 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.

























