IIT JAM Exam > IIT JAM Questions > What is Adsorption Hysteresis Related: Intro...
Start Learning for Free
What is Adsorption Hysteresis
Verified Answer
What is Adsorption Hysteresis Related: Introduction to Adsorption - A...
The hysteresis between the adsorption isotherm and desorption isotherm is thought to be caused by the gradual desorption mechanism (percolation theory) due to the different size pores being combined. This percolation theory suggests that the pore size distribution obtained from the desorption isotherm is problematic to be used. It is commonly said that the pore size distribution obtained from the adsorption isotherm has less problems and is closer to the true value.
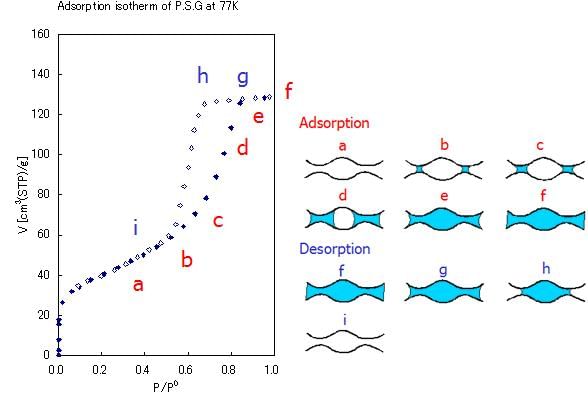
Additionally, there is a phenomenon that the desorption isotherm is closed to the adsorption isotherm side at the same equilibrium pressure even if the pore size is changed (without the special case of low pressure hysteresis). This phenomenon shows that the reason of desorption isotherm to be closed is not related to the pore size and is due to the adsorptive physical property at the adsorption temperature. This behavior is caused by the cavitations of adsorption phase in the pores. The pore size distribution analysis obtained from the desorption isotherm always has the peak of 3.4 nm pore due to the pressure of cavitations. This pore needs to be ignored when using the desorption of N2 isotherm at 77 K because this is not related to the pore condensation on the material.
 This question is part of UPSC exam. View all IIT JAM courses
This question is part of UPSC exam. View all IIT JAM courses
Most Upvoted Answer
What is Adsorption Hysteresis Related: Introduction to Adsorption - A...
Adsorption Hysteresis
Adsorption hysteresis is a phenomenon that occurs during the process of adsorption, which is the accumulation of molecules on the surface of a solid or liquid. It refers to the difference in the amount of adsorbate (the substance being adsorbed) adsorbed during increasing and decreasing pressures or temperatures. In other words, the amount of adsorbate taken up by the adsorbent is different when the pressure or temperature is raised compared to when it is lowered.
Explanation
Adsorption hysteresis is a result of the interactions between the adsorbate and the adsorbent, as well as the structure and properties of the adsorbent material itself. It can occur in various systems, including gas-solid, liquid-solid, and vapor-solid interfaces.
The hysteresis loop observed in adsorption is due to the differences in the adsorption and desorption mechanisms. During the adsorption process, the adsorbate molecules accumulate on the surface of the adsorbent due to attractive forces such as van der Waals interactions or chemical bonding. As the pressure or temperature increases, more adsorbate molecules can be adsorbed because the adsorbent becomes more accessible or the attractive forces become stronger.
However, when the pressure or temperature is reduced, the adsorbate molecules do not easily detach from the adsorbent surface. This is because the desorption process is influenced by factors such as the strength of the adsorbate-adsorbent interactions, the presence of capillary condensation, or the presence of multilayer adsorption. These factors can create energy barriers that prevent the adsorbate from readily leaving the surface, leading to a higher amount of adsorbate remaining on the adsorbent than would be expected based on the decreasing pressure or temperature alone.
Significance
The presence of adsorption hysteresis has important implications for various applications and processes. It can affect the efficiency and performance of adsorption-based separation processes, such as gas purification or liquid chromatography. Understanding and controlling adsorption hysteresis is crucial for optimizing these processes and achieving desired separation outcomes.
Moreover, adsorption hysteresis can provide insights into the properties and behavior of adsorbent materials. By studying the shape and extent of the hysteresis loop, scientists can gain information about the pore structure, surface chemistry, and surface energy of the adsorbent. This knowledge can be used to design and develop improved adsorbents with enhanced adsorption capacities and selectivities.
Conclusion
In summary, adsorption hysteresis is a phenomenon that occurs during adsorption, where the amount of adsorbate adsorbed during increasing and decreasing pressures or temperatures is different. It is influenced by the interactions between the adsorbate and adsorbent, as well as the structure and properties of the adsorbent material. Understanding and controlling adsorption hysteresis is important for various applications and can provide insights into the properties of adsorbent materials.
Adsorption hysteresis is a phenomenon that occurs during the process of adsorption, which is the accumulation of molecules on the surface of a solid or liquid. It refers to the difference in the amount of adsorbate (the substance being adsorbed) adsorbed during increasing and decreasing pressures or temperatures. In other words, the amount of adsorbate taken up by the adsorbent is different when the pressure or temperature is raised compared to when it is lowered.
Explanation
Adsorption hysteresis is a result of the interactions between the adsorbate and the adsorbent, as well as the structure and properties of the adsorbent material itself. It can occur in various systems, including gas-solid, liquid-solid, and vapor-solid interfaces.
The hysteresis loop observed in adsorption is due to the differences in the adsorption and desorption mechanisms. During the adsorption process, the adsorbate molecules accumulate on the surface of the adsorbent due to attractive forces such as van der Waals interactions or chemical bonding. As the pressure or temperature increases, more adsorbate molecules can be adsorbed because the adsorbent becomes more accessible or the attractive forces become stronger.
However, when the pressure or temperature is reduced, the adsorbate molecules do not easily detach from the adsorbent surface. This is because the desorption process is influenced by factors such as the strength of the adsorbate-adsorbent interactions, the presence of capillary condensation, or the presence of multilayer adsorption. These factors can create energy barriers that prevent the adsorbate from readily leaving the surface, leading to a higher amount of adsorbate remaining on the adsorbent than would be expected based on the decreasing pressure or temperature alone.
Significance
The presence of adsorption hysteresis has important implications for various applications and processes. It can affect the efficiency and performance of adsorption-based separation processes, such as gas purification or liquid chromatography. Understanding and controlling adsorption hysteresis is crucial for optimizing these processes and achieving desired separation outcomes.
Moreover, adsorption hysteresis can provide insights into the properties and behavior of adsorbent materials. By studying the shape and extent of the hysteresis loop, scientists can gain information about the pore structure, surface chemistry, and surface energy of the adsorbent. This knowledge can be used to design and develop improved adsorbents with enhanced adsorption capacities and selectivities.
Conclusion
In summary, adsorption hysteresis is a phenomenon that occurs during adsorption, where the amount of adsorbate adsorbed during increasing and decreasing pressures or temperatures is different. It is influenced by the interactions between the adsorbate and adsorbent, as well as the structure and properties of the adsorbent material. Understanding and controlling adsorption hysteresis is important for various applications and can provide insights into the properties of adsorbent materials.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Similar IIT JAM Doubts
What is Adsorption Hysteresis Related: Introduction to Adsorption - Adsorption, Physical Chemistry
Question Description
What is Adsorption Hysteresis Related: Introduction to Adsorption - Adsorption, Physical Chemistry for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about What is Adsorption Hysteresis Related: Introduction to Adsorption - Adsorption, Physical Chemistry covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is Adsorption Hysteresis Related: Introduction to Adsorption - Adsorption, Physical Chemistry.
What is Adsorption Hysteresis Related: Introduction to Adsorption - Adsorption, Physical Chemistry for IIT JAM 2024 is part of IIT JAM preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the IIT JAM exam syllabus. Information about What is Adsorption Hysteresis Related: Introduction to Adsorption - Adsorption, Physical Chemistry covers all topics & solutions for IIT JAM 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for What is Adsorption Hysteresis Related: Introduction to Adsorption - Adsorption, Physical Chemistry.
Solutions for What is Adsorption Hysteresis Related: Introduction to Adsorption - Adsorption, Physical Chemistry in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for IIT JAM.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for IIT JAM Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of What is Adsorption Hysteresis Related: Introduction to Adsorption - Adsorption, Physical Chemistry defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
What is Adsorption Hysteresis Related: Introduction to Adsorption - Adsorption, Physical Chemistry, a detailed solution for What is Adsorption Hysteresis Related: Introduction to Adsorption - Adsorption, Physical Chemistry has been provided alongside types of What is Adsorption Hysteresis Related: Introduction to Adsorption - Adsorption, Physical Chemistry theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice What is Adsorption Hysteresis Related: Introduction to Adsorption - Adsorption, Physical Chemistry tests, examples and also practice IIT JAM tests.

|
Explore Courses for IIT JAM exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















