Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Light coming from a discharge tube filled wit...
Start Learning for Free
Light coming from a discharge tube filled with hydrogen falls on the cathode of the photoelectric cell. The work function of the surface of cathode is 4eV. Which one of the following values of the anode voltage (in Volts) with respect to the cathode will likely to make the photo current zero.
- a)–4
- b)–6
- c)–8
- d)–10
Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Light coming from a discharge tube filled with hydrogen falls on the c...
Energy of photon from H atom is gievn by the difference between the two energy level in which electron transit.for minimum wavelength, energy of the photon will be maximum.
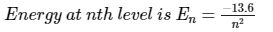
maximum energy will be

View all questions of this test
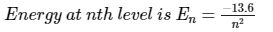
maximum energy will be

according to the einstein equation,Maximum kinetic energy if the emitted electron = energy of the incident radiation − work function
KE = 13.6 − 4 = 9.6 eV
hence potenial of the node must be greater than or equal to 9.6 volt with negatice polarity.
Hnece option (d) is correct.
Hnece option (d) is correct.
Most Upvoted Answer
Light coming from a discharge tube filled with hydrogen falls on the c...
To make the photo current zero, we need to ensure that no electrons are emitted from the cathode. This can be achieved by making the energy of the incident photons less than the work function of the cathode.
The energy of a photon is given by the equation E = hf, where E is the energy, h is Planck's constant, and f is the frequency of the light.
The work function of the cathode is 4eV. To convert this to joules, we multiply by the elementary charge, e, which is 1.6 x 10^-19 C. So, the work function in joules is 4e(1.6 x 10^-19) J.
Now, we can equate the energy of the photon to the work function:
hf = 4e(1.6 x 10^-19)
f = (4e(1.6 x 10^-19))/h
The anode voltage is the potential difference between the anode and the cathode. To make the photo current zero, we need to make this potential difference at least equal to the energy of the photons. This can be achieved by making the anode voltage equal to the energy of the photons, divided by the elementary charge:
Anode voltage = (hf)/e
Substituting the value of f from the previous equation, we have:
Anode voltage = [(4e(1.6 x 10^-19))/h]/e
Simplifying, we find:
Anode voltage = (4(1.6 x 10^-19))/h
Substituting the value of Planck's constant, h = 6.63 x 10^-34 J.s, we can calculate the anode voltage:
Anode voltage = (4(1.6 x 10^-19))/(6.63 x 10^-34)
Calculating this expression, we find:
Anode voltage ≈ 1.93 x 10^14 V
Therefore, the anode voltage that will likely make the photo current zero is approximately 1.93 x 10^14 Volts.
The energy of a photon is given by the equation E = hf, where E is the energy, h is Planck's constant, and f is the frequency of the light.
The work function of the cathode is 4eV. To convert this to joules, we multiply by the elementary charge, e, which is 1.6 x 10^-19 C. So, the work function in joules is 4e(1.6 x 10^-19) J.
Now, we can equate the energy of the photon to the work function:
hf = 4e(1.6 x 10^-19)
f = (4e(1.6 x 10^-19))/h
The anode voltage is the potential difference between the anode and the cathode. To make the photo current zero, we need to make this potential difference at least equal to the energy of the photons. This can be achieved by making the anode voltage equal to the energy of the photons, divided by the elementary charge:
Anode voltage = (hf)/e
Substituting the value of f from the previous equation, we have:
Anode voltage = [(4e(1.6 x 10^-19))/h]/e
Simplifying, we find:
Anode voltage = (4(1.6 x 10^-19))/h
Substituting the value of Planck's constant, h = 6.63 x 10^-34 J.s, we can calculate the anode voltage:
Anode voltage = (4(1.6 x 10^-19))/(6.63 x 10^-34)
Calculating this expression, we find:
Anode voltage ≈ 1.93 x 10^14 V
Therefore, the anode voltage that will likely make the photo current zero is approximately 1.93 x 10^14 Volts.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
Light coming from a discharge tube filled with hydrogen falls on the cathode of the photoelectric cell. The work function of the surface of cathode is 4eV. Which one of the following values of the anode voltage (in Volts) with respect to the cathode will likely to make the photo current zero.a)–4b)–6c)–8d)–10Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Light coming from a discharge tube filled with hydrogen falls on the cathode of the photoelectric cell. The work function of the surface of cathode is 4eV. Which one of the following values of the anode voltage (in Volts) with respect to the cathode will likely to make the photo current zero.a)–4b)–6c)–8d)–10Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Light coming from a discharge tube filled with hydrogen falls on the cathode of the photoelectric cell. The work function of the surface of cathode is 4eV. Which one of the following values of the anode voltage (in Volts) with respect to the cathode will likely to make the photo current zero.a)–4b)–6c)–8d)–10Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Light coming from a discharge tube filled with hydrogen falls on the cathode of the photoelectric cell. The work function of the surface of cathode is 4eV. Which one of the following values of the anode voltage (in Volts) with respect to the cathode will likely to make the photo current zero.a)–4b)–6c)–8d)–10Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Light coming from a discharge tube filled with hydrogen falls on the cathode of the photoelectric cell. The work function of the surface of cathode is 4eV. Which one of the following values of the anode voltage (in Volts) with respect to the cathode will likely to make the photo current zero.a)–4b)–6c)–8d)–10Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2024 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Light coming from a discharge tube filled with hydrogen falls on the cathode of the photoelectric cell. The work function of the surface of cathode is 4eV. Which one of the following values of the anode voltage (in Volts) with respect to the cathode will likely to make the photo current zero.a)–4b)–6c)–8d)–10Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Light coming from a discharge tube filled with hydrogen falls on the cathode of the photoelectric cell. The work function of the surface of cathode is 4eV. Which one of the following values of the anode voltage (in Volts) with respect to the cathode will likely to make the photo current zero.a)–4b)–6c)–8d)–10Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Light coming from a discharge tube filled with hydrogen falls on the cathode of the photoelectric cell. The work function of the surface of cathode is 4eV. Which one of the following values of the anode voltage (in Volts) with respect to the cathode will likely to make the photo current zero.a)–4b)–6c)–8d)–10Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Light coming from a discharge tube filled with hydrogen falls on the cathode of the photoelectric cell. The work function of the surface of cathode is 4eV. Which one of the following values of the anode voltage (in Volts) with respect to the cathode will likely to make the photo current zero.a)–4b)–6c)–8d)–10Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Light coming from a discharge tube filled with hydrogen falls on the cathode of the photoelectric cell. The work function of the surface of cathode is 4eV. Which one of the following values of the anode voltage (in Volts) with respect to the cathode will likely to make the photo current zero.a)–4b)–6c)–8d)–10Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Light coming from a discharge tube filled with hydrogen falls on the cathode of the photoelectric cell. The work function of the surface of cathode is 4eV. Which one of the following values of the anode voltage (in Volts) with respect to the cathode will likely to make the photo current zero.a)–4b)–6c)–8d)–10Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Light coming from a discharge tube filled with hydrogen falls on the cathode of the photoelectric cell. The work function of the surface of cathode is 4eV. Which one of the following values of the anode voltage (in Volts) with respect to the cathode will likely to make the photo current zero.a)–4b)–6c)–8d)–10Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Light coming from a discharge tube filled with hydrogen falls on the cathode of the photoelectric cell. The work function of the surface of cathode is 4eV. Which one of the following values of the anode voltage (in Volts) with respect to the cathode will likely to make the photo current zero.a)–4b)–6c)–8d)–10Correct answer is option 'D'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.


















