Class 12 Exam > Class 12 Questions > Horizontally oriented ovule in Angiosperm is ...
Start Learning for Free
Horizontally oriented ovule in Angiosperm is called -
- a)Amphitropous
- b)Hemitropous
- c)Campylotropous
- d)Circinotropous
Correct answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
Horizontally oriented ovule in Angiosperm is called -a)Amphitropousb)H...
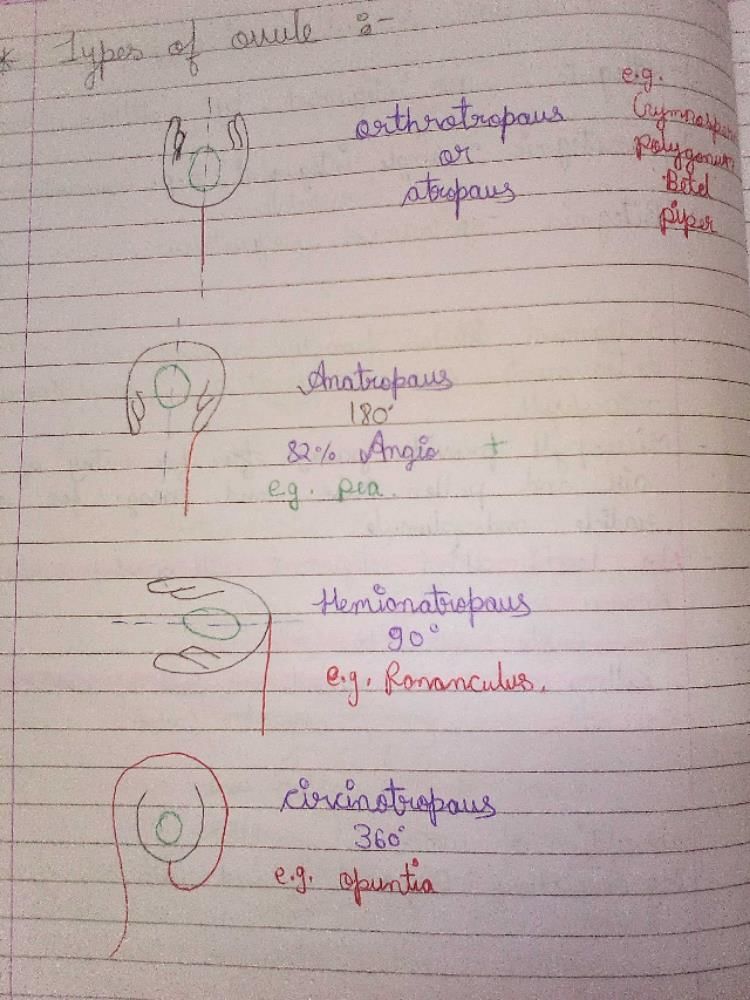
Hemitropous Ovule in Angiosperm
An ovule is the reproductive structure of a flower that develops into a seed after fertilization. The ovule contains the female gamete, which is fertilized by the male gamete to form a zygote. The orientation of the ovule in the flower is of great significance and is used to classify the ovules into different types.
Hemitropous ovule is one of the types of ovules found in angiosperms. The term "hemitropous" is derived from the Greek words "hemi" meaning half and "tropos" meaning turn. Thus, hemitropous ovules are half-turned ovules and are horizontally oriented.
Characteristics of Hemitropous Ovule
- A hemitropous ovule is curved and bent, with the micropyle (the opening through which the pollen tube enters) and the chalaza (the base of the ovule where the integuments are attached) almost parallel to each other.
- The ovule is attached to the placenta by a short stalk called the funicle.
- The integuments (outer layer) of the ovule are fused together except at the micropyle, which is open.
- The embryo sac (the female gametophyte) is located at the micropylar end of the ovule.
- The pollen tube enters the ovule through the micropyle and fertilizes the egg cell and the central cell to form the zygote and endosperm, respectively.
Significance of Hemitropous Ovule
Hemitropous ovules are significant in angiosperms due to the following reasons:
- The curved shape of the ovule allows for efficient pollination as the pollen tube can easily navigate through the ovule to reach the embryo sac.
- The micropyle is located at the top of the ovule, which prevents the entry of unwanted pollen grains and ensures the fertilization of only the desired pollen grain.
- The fusion of the integuments except at the micropyle provides protection to the developing embryo and endosperm.
Conclusion
Hemitropous ovules are horizontally oriented ovules found in angiosperms. They are curved and bent, with the micropyle and chalaza almost parallel to each other. The ovule is attached to the placenta by a short stalk called the funicle. The curved shape of the ovule allows for efficient pollination, and the micropyle is located at the top of the ovule, which prevents the entry of unwanted pollen grains. The fusion of the integuments except at the micropyle provides protection to the developing embryo and endosperm.
An ovule is the reproductive structure of a flower that develops into a seed after fertilization. The ovule contains the female gamete, which is fertilized by the male gamete to form a zygote. The orientation of the ovule in the flower is of great significance and is used to classify the ovules into different types.
Hemitropous ovule is one of the types of ovules found in angiosperms. The term "hemitropous" is derived from the Greek words "hemi" meaning half and "tropos" meaning turn. Thus, hemitropous ovules are half-turned ovules and are horizontally oriented.
Characteristics of Hemitropous Ovule
- A hemitropous ovule is curved and bent, with the micropyle (the opening through which the pollen tube enters) and the chalaza (the base of the ovule where the integuments are attached) almost parallel to each other.
- The ovule is attached to the placenta by a short stalk called the funicle.
- The integuments (outer layer) of the ovule are fused together except at the micropyle, which is open.
- The embryo sac (the female gametophyte) is located at the micropylar end of the ovule.
- The pollen tube enters the ovule through the micropyle and fertilizes the egg cell and the central cell to form the zygote and endosperm, respectively.
Significance of Hemitropous Ovule
Hemitropous ovules are significant in angiosperms due to the following reasons:
- The curved shape of the ovule allows for efficient pollination as the pollen tube can easily navigate through the ovule to reach the embryo sac.
- The micropyle is located at the top of the ovule, which prevents the entry of unwanted pollen grains and ensures the fertilization of only the desired pollen grain.
- The fusion of the integuments except at the micropyle provides protection to the developing embryo and endosperm.
Conclusion
Hemitropous ovules are horizontally oriented ovules found in angiosperms. They are curved and bent, with the micropyle and chalaza almost parallel to each other. The ovule is attached to the placenta by a short stalk called the funicle. The curved shape of the ovule allows for efficient pollination, and the micropyle is located at the top of the ovule, which prevents the entry of unwanted pollen grains. The fusion of the integuments except at the micropyle provides protection to the developing embryo and endosperm.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Horizontally oriented ovule in Angiosperm is called -a)Amphitropousb)H...

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Similar Class 12 Doubts
Horizontally oriented ovule in Angiosperm is called -a)Amphitropousb)Hemitropousc)Campylotropousd)CircinotropousCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Horizontally oriented ovule in Angiosperm is called -a)Amphitropousb)Hemitropousc)Campylotropousd)CircinotropousCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Horizontally oriented ovule in Angiosperm is called -a)Amphitropousb)Hemitropousc)Campylotropousd)CircinotropousCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Horizontally oriented ovule in Angiosperm is called -a)Amphitropousb)Hemitropousc)Campylotropousd)CircinotropousCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Horizontally oriented ovule in Angiosperm is called -a)Amphitropousb)Hemitropousc)Campylotropousd)CircinotropousCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 12 2025 is part of Class 12 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 12 exam syllabus. Information about Horizontally oriented ovule in Angiosperm is called -a)Amphitropousb)Hemitropousc)Campylotropousd)CircinotropousCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 12 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Horizontally oriented ovule in Angiosperm is called -a)Amphitropousb)Hemitropousc)Campylotropousd)CircinotropousCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Horizontally oriented ovule in Angiosperm is called -a)Amphitropousb)Hemitropousc)Campylotropousd)CircinotropousCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 12.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 12 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Horizontally oriented ovule in Angiosperm is called -a)Amphitropousb)Hemitropousc)Campylotropousd)CircinotropousCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Horizontally oriented ovule in Angiosperm is called -a)Amphitropousb)Hemitropousc)Campylotropousd)CircinotropousCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Horizontally oriented ovule in Angiosperm is called -a)Amphitropousb)Hemitropousc)Campylotropousd)CircinotropousCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Horizontally oriented ovule in Angiosperm is called -a)Amphitropousb)Hemitropousc)Campylotropousd)CircinotropousCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Horizontally oriented ovule in Angiosperm is called -a)Amphitropousb)Hemitropousc)Campylotropousd)CircinotropousCorrect answer is option 'B'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 12 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 12 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















