Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(...
Start Learning for Free
Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)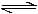 2 SO3 (g); ΔHº = -198 kJ
2 SO3 (g); ΔHº = -198 kJ
On the basis of Le Chatelier's principle, the condition favourable for the forward reaction is -
[AIEEE-2003]
- a)Lowering the temperature and increasing the pressure
- b)Any value of temperature and pressure
- c)Lowering of temperature as well as pressure
- d)Increasing temperature as well as pressure
Correct answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2 SO3 (g); ΔH&ord...
The correct answer is option A
ACCORDING TO LE CHATELIER'S PRINCIPLE
TEMPERATURE
if we increase temperature equilibrium will shift that direction which proceeds an endothermic reaction but the reaction given in question is exothermic so we have to decrease temperature to proceed forward.
PRESSURE
at equilibrium if we increase pressure equilibrium will shift that direction which has less number of moles but in given reaction products have less no. of moles than reactant that's why we increase pressure.
ACCORDING TO LE CHATELIER'S PRINCIPLE
TEMPERATURE
if we increase temperature equilibrium will shift that direction which proceeds an endothermic reaction but the reaction given in question is exothermic so we have to decrease temperature to proceed forward.
PRESSURE
at equilibrium if we increase pressure equilibrium will shift that direction which has less number of moles but in given reaction products have less no. of moles than reactant that's why we increase pressure.
Most Upvoted Answer
Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2 SO3 (g); ΔH&ord...
ACCORDING TO LE CHATELIER'S PRINCIPLE
TEMPERATURE
if we increase temperature equilibrium will shift that direction which procedes endothermic reaction but the reaction given in question is exothermic so we have to decrease temperature to proceed reaction forward.
PRESSURE
at equilibrium if we increase pressure equilibrium will shift that direction which have less number of moles but in given reaction product have less no. of moles than reactant that's why we increase pressure.
TEMPERATURE
if we increase temperature equilibrium will shift that direction which procedes endothermic reaction but the reaction given in question is exothermic so we have to decrease temperature to proceed reaction forward.
PRESSURE
at equilibrium if we increase pressure equilibrium will shift that direction which have less number of moles but in given reaction product have less no. of moles than reactant that's why we increase pressure.
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2 SO3 (g); ΔH&ord...
The reaction equilibrium you provided is missing the reactant and product coefficients. The balanced equation for the reaction is:
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g)
In this reaction, sulfur dioxide (SO2) and oxygen (O2) react to form sulfur trioxide (SO3). The reaction can proceed in both directions, with SO2 and O2 forming SO3, and SO3 decomposing back into SO2 and O2.
When the reaction reaches equilibrium, the concentrations of the reactants and products remain constant over time. The equilibrium constant (K) for this reaction is defined as the ratio of the product concentrations to the reactant concentrations, with each concentration raised to the power of its coefficient in the balanced equation.
K = [SO3]^2 / ([SO2]^2 * [O2])
The value of the equilibrium constant depends on temperature, and it indicates the relative concentrations of the reactants and products at equilibrium. A larger value of K means that the products are favored at equilibrium, while a smaller value of K means that the reactants are favored.
To calculate the value of K, you would need to know the concentrations of the reactants and products at equilibrium.
2SO2(g) + O2(g) ⇌ 2SO3(g)
In this reaction, sulfur dioxide (SO2) and oxygen (O2) react to form sulfur trioxide (SO3). The reaction can proceed in both directions, with SO2 and O2 forming SO3, and SO3 decomposing back into SO2 and O2.
When the reaction reaches equilibrium, the concentrations of the reactants and products remain constant over time. The equilibrium constant (K) for this reaction is defined as the ratio of the product concentrations to the reactant concentrations, with each concentration raised to the power of its coefficient in the balanced equation.
K = [SO3]^2 / ([SO2]^2 * [O2])
The value of the equilibrium constant depends on temperature, and it indicates the relative concentrations of the reactants and products at equilibrium. A larger value of K means that the products are favored at equilibrium, while a smaller value of K means that the reactants are favored.
To calculate the value of K, you would need to know the concentrations of the reactants and products at equilibrium.
Attention Class 11 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 11 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 11.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2 SO3 (g); ΔHº = -198 kJOn the basis of Le Chatelier's principle, the condition favourable for the forward reaction is -[AIEEE-2003]a)Lowering the temperature and increasing the pressureb)Any value of temperature and pressurec)Lowering of temperature as well as pressured)Increasing temperature as well as pressureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2 SO3 (g); ΔHº = -198 kJOn the basis of Le Chatelier's principle, the condition favourable for the forward reaction is -[AIEEE-2003]a)Lowering the temperature and increasing the pressureb)Any value of temperature and pressurec)Lowering of temperature as well as pressured)Increasing temperature as well as pressureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2 SO3 (g); ΔHº = -198 kJOn the basis of Le Chatelier's principle, the condition favourable for the forward reaction is -[AIEEE-2003]a)Lowering the temperature and increasing the pressureb)Any value of temperature and pressurec)Lowering of temperature as well as pressured)Increasing temperature as well as pressureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2 SO3 (g); ΔHº = -198 kJOn the basis of Le Chatelier's principle, the condition favourable for the forward reaction is -[AIEEE-2003]a)Lowering the temperature and increasing the pressureb)Any value of temperature and pressurec)Lowering of temperature as well as pressured)Increasing temperature as well as pressureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2 SO3 (g); ΔHº = -198 kJOn the basis of Le Chatelier's principle, the condition favourable for the forward reaction is -[AIEEE-2003]a)Lowering the temperature and increasing the pressureb)Any value of temperature and pressurec)Lowering of temperature as well as pressured)Increasing temperature as well as pressureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2 SO3 (g); ΔHº = -198 kJOn the basis of Le Chatelier's principle, the condition favourable for the forward reaction is -[AIEEE-2003]a)Lowering the temperature and increasing the pressureb)Any value of temperature and pressurec)Lowering of temperature as well as pressured)Increasing temperature as well as pressureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2 SO3 (g); ΔHº = -198 kJOn the basis of Le Chatelier's principle, the condition favourable for the forward reaction is -[AIEEE-2003]a)Lowering the temperature and increasing the pressureb)Any value of temperature and pressurec)Lowering of temperature as well as pressured)Increasing temperature as well as pressureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2 SO3 (g); ΔHº = -198 kJOn the basis of Le Chatelier's principle, the condition favourable for the forward reaction is -[AIEEE-2003]a)Lowering the temperature and increasing the pressureb)Any value of temperature and pressurec)Lowering of temperature as well as pressured)Increasing temperature as well as pressureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2 SO3 (g); ΔHº = -198 kJOn the basis of Le Chatelier's principle, the condition favourable for the forward reaction is -[AIEEE-2003]a)Lowering the temperature and increasing the pressureb)Any value of temperature and pressurec)Lowering of temperature as well as pressured)Increasing temperature as well as pressureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2 SO3 (g); ΔHº = -198 kJOn the basis of Le Chatelier's principle, the condition favourable for the forward reaction is -[AIEEE-2003]a)Lowering the temperature and increasing the pressureb)Any value of temperature and pressurec)Lowering of temperature as well as pressured)Increasing temperature as well as pressureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2 SO3 (g); ΔHº = -198 kJOn the basis of Le Chatelier's principle, the condition favourable for the forward reaction is -[AIEEE-2003]a)Lowering the temperature and increasing the pressureb)Any value of temperature and pressurec)Lowering of temperature as well as pressured)Increasing temperature as well as pressureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2 SO3 (g); ΔHº = -198 kJOn the basis of Le Chatelier's principle, the condition favourable for the forward reaction is -[AIEEE-2003]a)Lowering the temperature and increasing the pressureb)Any value of temperature and pressurec)Lowering of temperature as well as pressured)Increasing temperature as well as pressureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Consider the reaction equilibrium 2SO2(g)+O2(g)2 SO3 (g); ΔHº = -198 kJOn the basis of Le Chatelier's principle, the condition favourable for the forward reaction is -[AIEEE-2003]a)Lowering the temperature and increasing the pressureb)Any value of temperature and pressurec)Lowering of temperature as well as pressured)Increasing temperature as well as pressureCorrect answer is option 'A'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Suggested Free Tests
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.






















