Class 11 Exam > Class 11 Questions > Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethyl...
Start Learning for Free
Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethylene in presence of HCl and anhyd. AlCl3 gives:
- a)Styrene
- b)Stilbene
- c)Ethylbenzene
- d)1,1-Diphenylethylene
Correct answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
| FREE This question is part of | Download PDF Attempt this Test |
Verified Answer
Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethylene in presence of HCl an...
Benzene can be converted into ethyl benzene as follows.
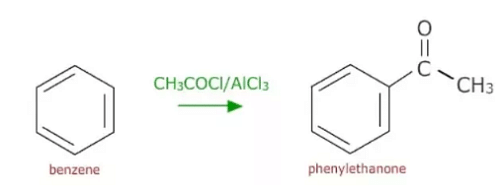
Step-1:—Conversion of benzene into
Benzene is treated with acetyl chloride in presence of anhydrous AlCl₃ to form aetophenone (phenyl ethanone).This is electrophilic substitution reaction.
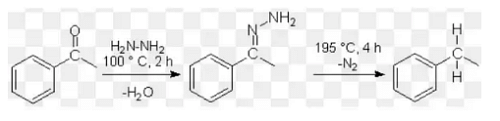
Step-2:—Reduction of acetophenone into ethyl benzene.
Acetophenone is treated with hydrazine to form acetophenone hydrazone,which on heating in presence of high boiling solvent like ethylene glycol gives ethyl benzene.This raction is known as Wolff-Kishner reduction.
Most Upvoted Answer
Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethylene in presence of HCl an...
Friedel-Crafts reaction is a type of electrophilic aromatic substitution reaction in which a hydrogen atom on an aromatic ring is replaced with an alkyl or acyl group. In this specific case, the reaction is between benzene and ethylene in the presence of HCl and anhydrous aluminum chloride (AlCl3) as a catalyst.
The reaction proceeds through the following steps:
1. Formation of the electrophile: The anhydrous aluminum chloride (AlCl3) reacts with the HCl to form a complex, AlCl3·HCl. This complex acts as a Lewis acid and accepts a chloride ion from HCl to form the electrophilic species, a carbocation (C+).
2. Activation of the benzene ring: The carbocation formed in the previous step attacks the benzene ring, displacing a hydrogen atom and forming a sigma complex. This step is facilitated by the presence of the Lewis acid catalyst, which helps in stabilizing the carbocation.
3. Rearrangement (if necessary): In some cases, the carbocation formed may undergo a rearrangement to form a more stable carbocation. However, in the case of the reaction between benzene and ethylene, rearrangement is not required.
4. Deprotonation: The sigma complex formed in step 2 is highly unstable and undergoes deprotonation to regenerate the aromaticity of the benzene ring. The deprotonation is usually carried out by a Lewis base, such as the chloride ion.
The final product of the reaction is ethylbenzene, in which the ethyl group is attached to the benzene ring. The reaction can be represented as follows:
Benzene + Ethylene → Ethylbenzene
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C', ethylbenzene.
The Friedel-Crafts reaction is an important method for the synthesis of alkylated aromatic compounds. It is widely used in organic synthesis to introduce alkyl groups onto aromatic rings. The reaction conditions, such as the choice of catalyst and reaction temperature, can be varied to achieve different substitution patterns on the aromatic ring.
The reaction proceeds through the following steps:
1. Formation of the electrophile: The anhydrous aluminum chloride (AlCl3) reacts with the HCl to form a complex, AlCl3·HCl. This complex acts as a Lewis acid and accepts a chloride ion from HCl to form the electrophilic species, a carbocation (C+).
2. Activation of the benzene ring: The carbocation formed in the previous step attacks the benzene ring, displacing a hydrogen atom and forming a sigma complex. This step is facilitated by the presence of the Lewis acid catalyst, which helps in stabilizing the carbocation.
3. Rearrangement (if necessary): In some cases, the carbocation formed may undergo a rearrangement to form a more stable carbocation. However, in the case of the reaction between benzene and ethylene, rearrangement is not required.
4. Deprotonation: The sigma complex formed in step 2 is highly unstable and undergoes deprotonation to regenerate the aromaticity of the benzene ring. The deprotonation is usually carried out by a Lewis base, such as the chloride ion.
The final product of the reaction is ethylbenzene, in which the ethyl group is attached to the benzene ring. The reaction can be represented as follows:
Benzene + Ethylene → Ethylbenzene
Therefore, the correct answer is option 'C', ethylbenzene.
The Friedel-Crafts reaction is an important method for the synthesis of alkylated aromatic compounds. It is widely used in organic synthesis to introduce alkyl groups onto aromatic rings. The reaction conditions, such as the choice of catalyst and reaction temperature, can be varied to achieve different substitution patterns on the aromatic ring.
Attention Class 11 Students!
To make sure you are not studying endlessly, EduRev has designed Class 11 study material, with Structured Courses, Videos, & Test Series. Plus get personalized analysis, doubt solving and improvement plans to achieve a great score in Class 11.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Similar Class 11 Doubts
Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethylene in presence of HCl and anhyd. AlCl3gives:a)Styreneb)Stilbenec)Ethylbenzened)1,1-DiphenylethyleneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethylene in presence of HCl and anhyd. AlCl3gives:a)Styreneb)Stilbenec)Ethylbenzened)1,1-DiphenylethyleneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethylene in presence of HCl and anhyd. AlCl3gives:a)Styreneb)Stilbenec)Ethylbenzened)1,1-DiphenylethyleneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethylene in presence of HCl and anhyd. AlCl3gives:a)Styreneb)Stilbenec)Ethylbenzened)1,1-DiphenylethyleneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethylene in presence of HCl and anhyd. AlCl3gives:a)Styreneb)Stilbenec)Ethylbenzened)1,1-DiphenylethyleneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? for Class 11 2024 is part of Class 11 preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Class 11 exam syllabus. Information about Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethylene in presence of HCl and anhyd. AlCl3gives:a)Styreneb)Stilbenec)Ethylbenzened)1,1-DiphenylethyleneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Class 11 2024 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethylene in presence of HCl and anhyd. AlCl3gives:a)Styreneb)Stilbenec)Ethylbenzened)1,1-DiphenylethyleneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethylene in presence of HCl and anhyd. AlCl3gives:a)Styreneb)Stilbenec)Ethylbenzened)1,1-DiphenylethyleneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Class 11.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Class 11 Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethylene in presence of HCl and anhyd. AlCl3gives:a)Styreneb)Stilbenec)Ethylbenzened)1,1-DiphenylethyleneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethylene in presence of HCl and anhyd. AlCl3gives:a)Styreneb)Stilbenec)Ethylbenzened)1,1-DiphenylethyleneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethylene in presence of HCl and anhyd. AlCl3gives:a)Styreneb)Stilbenec)Ethylbenzened)1,1-DiphenylethyleneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethylene in presence of HCl and anhyd. AlCl3gives:a)Styreneb)Stilbenec)Ethylbenzened)1,1-DiphenylethyleneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice Friedel Crafts reaction of benzene with ethylene in presence of HCl and anhyd. AlCl3gives:a)Styreneb)Stilbenec)Ethylbenzened)1,1-DiphenylethyleneCorrect answer is option 'C'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Class 11 tests.

|
Explore Courses for Class 11 exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.
























