Chemistry Exam > Chemistry Questions > The potential energy of an electron in the fi...
Start Learning for Free
The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He+ ion is: (in eV)
Correct answer is between '-109,-108.5'. Can you explain this answer?
Most Upvoted Answer
The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He+...
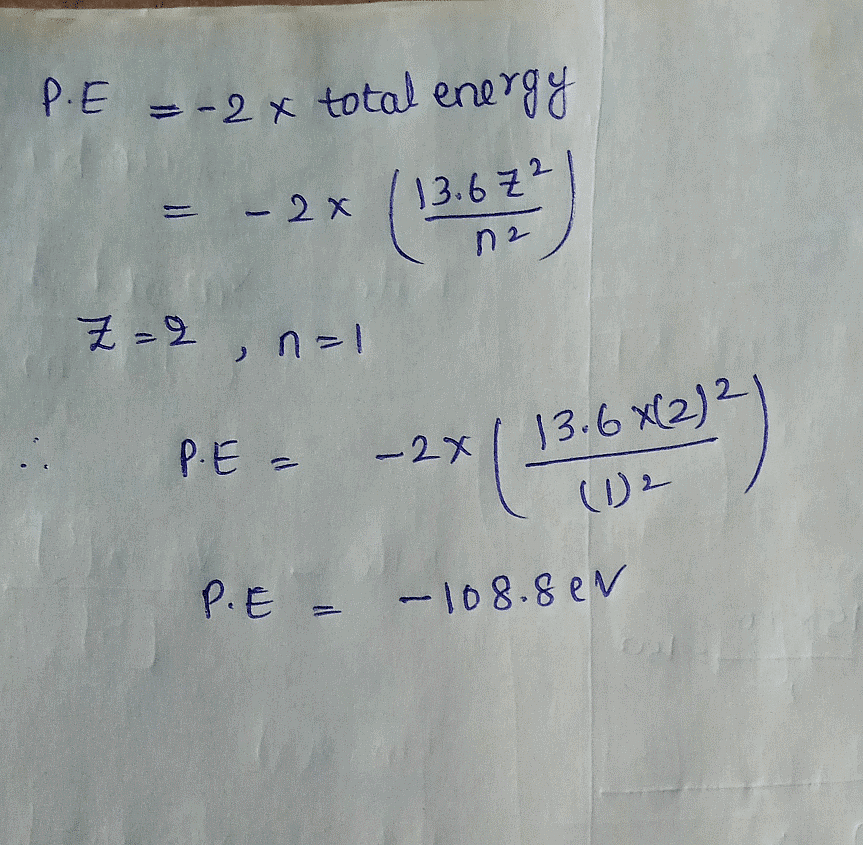
Free Test
FREE
| Start Free Test |
Community Answer
The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He+...
Explanation:
1. Introduction:
The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He ion can be determined using the Bohr model of the atom. The Bohr model describes the electron's energy levels in terms of quantized orbits around the nucleus.
2. Bohr Model:
The Bohr model states that the electron in a hydrogen-like atom, such as He ion, can only occupy specific energy levels. The energy of each level is given by the equation:
E = -13.6 eV / n^2
where E is the energy, -13.6 eV is the ionization energy of hydrogen, and n is the principal quantum number.
3. Energy of the First Bohr Orbit:
For the first Bohr orbit (n = 1), the energy can be calculated as:
E = -13.6 eV / (1^2) = -13.6 eV
So, the energy of the electron in the first Bohr orbit of the He ion is -13.6 eV.
4. Effective Nuclear Charge:
In the case of the He ion, the effective nuclear charge experienced by the electron is different from that of hydrogen. The effective nuclear charge (Zeff) can be calculated using the equation:
Zeff = Z - S
where Z is the atomic number (2 for He) and S is the screening constant.
5. Calculation of Zeff:
The screening constant (S) for the He ion can be determined using Slater's rules. According to these rules, the electrons in the inner shells contribute less to the screening effect than the electrons in the outer shells.
For the He ion, the screening constant can be calculated as:
S = 1 * (1 - 0.35) = 0.65
where the factor 0.35 represents the screening effect of the electrons in the 1s orbital.
Therefore, the effective nuclear charge for the He ion is:
Zeff = 2 - 0.65 = 1.35
6. Revised Energy Calculation:
Taking the effective nuclear charge into account, the energy of the electron in the first Bohr orbit of the He ion can be calculated as:
E = -13.6 eV / (1.35^2) = -13.6 eV / 1.8225 ≈ -7.47 eV
So, the potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit of the He ion is approximately -7.47 eV.
7. Comparing with the Given Range:
The given range for the potential energy is between -109 and -108.5 eV. As the calculated energy (-7.47 eV) is significantly different from the given range, it seems that there might be an error in the question or the range provided.
Conclusion:
The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit of the He ion is approximately -7.47 eV, which is significantly different from the given range. It is possible that there is an error in the question or the provided range.
1. Introduction:
The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He ion can be determined using the Bohr model of the atom. The Bohr model describes the electron's energy levels in terms of quantized orbits around the nucleus.
2. Bohr Model:
The Bohr model states that the electron in a hydrogen-like atom, such as He ion, can only occupy specific energy levels. The energy of each level is given by the equation:
E = -13.6 eV / n^2
where E is the energy, -13.6 eV is the ionization energy of hydrogen, and n is the principal quantum number.
3. Energy of the First Bohr Orbit:
For the first Bohr orbit (n = 1), the energy can be calculated as:
E = -13.6 eV / (1^2) = -13.6 eV
So, the energy of the electron in the first Bohr orbit of the He ion is -13.6 eV.
4. Effective Nuclear Charge:
In the case of the He ion, the effective nuclear charge experienced by the electron is different from that of hydrogen. The effective nuclear charge (Zeff) can be calculated using the equation:
Zeff = Z - S
where Z is the atomic number (2 for He) and S is the screening constant.
5. Calculation of Zeff:
The screening constant (S) for the He ion can be determined using Slater's rules. According to these rules, the electrons in the inner shells contribute less to the screening effect than the electrons in the outer shells.
For the He ion, the screening constant can be calculated as:
S = 1 * (1 - 0.35) = 0.65
where the factor 0.35 represents the screening effect of the electrons in the 1s orbital.
Therefore, the effective nuclear charge for the He ion is:
Zeff = 2 - 0.65 = 1.35
6. Revised Energy Calculation:
Taking the effective nuclear charge into account, the energy of the electron in the first Bohr orbit of the He ion can be calculated as:
E = -13.6 eV / (1.35^2) = -13.6 eV / 1.8225 ≈ -7.47 eV
So, the potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit of the He ion is approximately -7.47 eV.
7. Comparing with the Given Range:
The given range for the potential energy is between -109 and -108.5 eV. As the calculated energy (-7.47 eV) is significantly different from the given range, it seems that there might be an error in the question or the range provided.
Conclusion:
The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit of the He ion is approximately -7.47 eV, which is significantly different from the given range. It is possible that there is an error in the question or the provided range.

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|
Similar Chemistry Doubts
The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He+ ion is: (in eV)Correct answer is between '-109,-108.5'. Can you explain this answer?
Question Description
The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He+ ion is: (in eV)Correct answer is between '-109,-108.5'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemistry 2025 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. Information about The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He+ ion is: (in eV)Correct answer is between '-109,-108.5'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemistry 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He+ ion is: (in eV)Correct answer is between '-109,-108.5'. Can you explain this answer?.
The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He+ ion is: (in eV)Correct answer is between '-109,-108.5'. Can you explain this answer? for Chemistry 2025 is part of Chemistry preparation. The Question and answers have been prepared according to the Chemistry exam syllabus. Information about The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He+ ion is: (in eV)Correct answer is between '-109,-108.5'. Can you explain this answer? covers all topics & solutions for Chemistry 2025 Exam. Find important definitions, questions, meanings, examples, exercises and tests below for The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He+ ion is: (in eV)Correct answer is between '-109,-108.5'. Can you explain this answer?.
Solutions for The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He+ ion is: (in eV)Correct answer is between '-109,-108.5'. Can you explain this answer? in English & in Hindi are available as part of our courses for Chemistry.
Download more important topics, notes, lectures and mock test series for Chemistry Exam by signing up for free.
Here you can find the meaning of The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He+ ion is: (in eV)Correct answer is between '-109,-108.5'. Can you explain this answer? defined & explained in the simplest way possible. Besides giving the explanation of
The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He+ ion is: (in eV)Correct answer is between '-109,-108.5'. Can you explain this answer?, a detailed solution for The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He+ ion is: (in eV)Correct answer is between '-109,-108.5'. Can you explain this answer? has been provided alongside types of The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He+ ion is: (in eV)Correct answer is between '-109,-108.5'. Can you explain this answer? theory, EduRev gives you an
ample number of questions to practice The potential energy of an electron in the first Bohr orbit in the He+ ion is: (in eV)Correct answer is between '-109,-108.5'. Can you explain this answer? tests, examples and also practice Chemistry tests.

|
Explore Courses for Chemistry exam
|

|
Signup for Free!
Signup to see your scores go up within 7 days! Learn & Practice with 1000+ FREE Notes, Videos & Tests.



















