Accounting Procedures Rules of Debit & Credit | Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce PDF Download
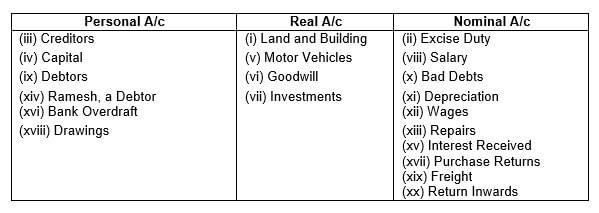
Q1: Following accounts are being maintained in the books of Shri Ashok. Classify them into Personal, Real and Nominal Accounts:
(i) Land and Building
(ii) Excise Duty
(iii) Creditors
(iv) Capital
(v) Motor Vehicles
(vi) Goodwill
(vii) Investments
(viii) Salary
(ix) Debtors
(x) Bad Debts
(xi) Depreciation
(xii) Wages
(xiii) Repairs
(xiv) Ramesh, a debtor
(xv) Interest Received
(xvi) Bank Overdraft
(xvii) Purchase Returns
(xviii) Drawings
(xix) Freight
(xx) Return Inwards.
Ans: The account classification is made as follows
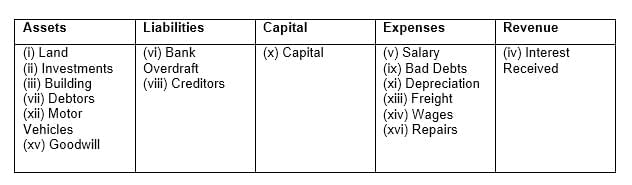
Q2: Classify the following into Assets, Liabilities, Capital, Expenses and Revenue:
(i) Land
(ii) Investments
(iii) Building
(iv) Interest Received
(v) Salary
(vi) Bank Overdraft
(vii) Debtors
(viii) Creditors
(ix) Bad Debts
(x) Capital
(xi) Depreciation
(xii) Motor Vehicles
(xiii) Freight
(xiv) Wages
(xv) Goodwill
(xvi) Repairs
Ans: The classification is made as follows
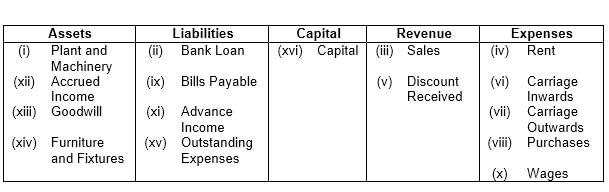
Q3: Classify the following into assets, liabilities, capital, revenue, and expenses:
(i) Plant and Machinery
(ii) Bank Loan
(iii) Sales
(iv) Rent
(v) Discount Received
(vi) Carriage Inwards
(vii) Carriage outwards
(viii) Purchases
(ix) Bills Payable
(x) Wages
(xi) Advance Income
(xii) Accrued Income
(xiii) Goodwill
(xiv) Furniture and Fixtures
(xv) Outstanding Expenses
(xvi) Capital
Ans: The classification is made as follows
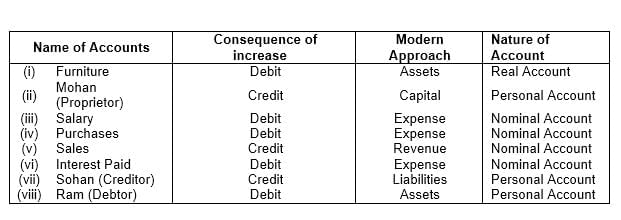
Q4: On which side will the increase in the following accounts be recorded? Also, state the nature of the account:
(i) Furniture A/c
(ii) Mohan (proprietor)
(iii) Salary A/c
(iv) Purchases A/c
(v) Sales A/c
(vi) Interest Paid A/c
(vii) Sohan (Creditor)
(viii) Ram (Debtor)
Ans: The solution for this question is as follows:
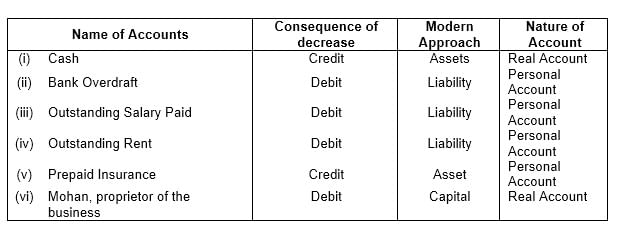
Q5: On which side will the decrease in the following accounts be recorded? Also, state the nature of the account:
(i) Cash
(ii) Bank Overdraft
(iii) Outstanding salary paid
(iv) Outstanding Rent
(v) Prepaid Insurance
(vi) Mohan, Proprietor of the business
Ans: The solution for this question is as follows:
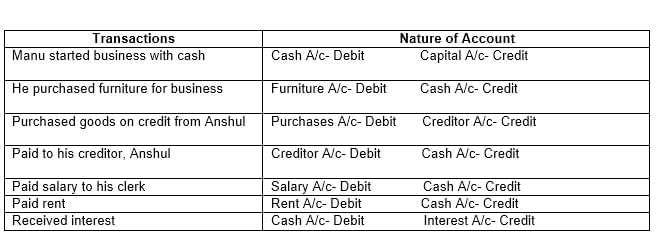
Q6: From the following Transactions, state the nature of account and state which account will be debited and which account credited:
(i) Manu started business with cash – ₹ 1,00,000
(ii) He purchased furniture for business – ₹ 20,000
(iii) Purchase goods on credit from Anshul – ₹ 6,000
(iv) Paid to his creditor, Anshul – ₹ 2,000
(v) Paid salary to his clerk – ₹ 1,000
(vi) Paid Rent – ₹ 500
(vii) Received Interest – ₹ 200
Ans: The solution for this question is as follows:
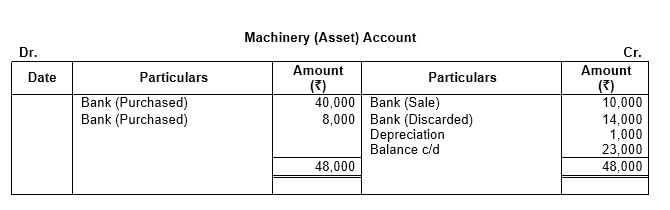
Q7: Open a ‘T’ shape account for machinery and put the following transactions on the proper side: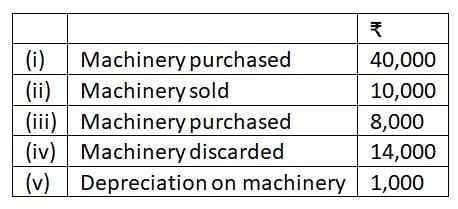
Ans: The solution for this question is as follows:
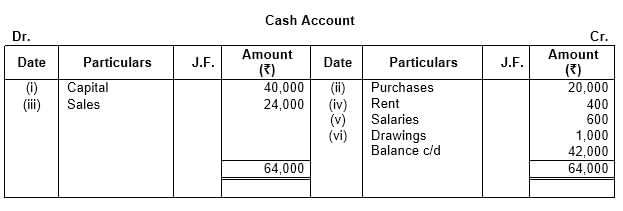
Q8: Open a ‘T’ shape Cash Account. Put the following transactions on the proper side and balance the account:
(i) Mohan started business with cash – ₹ 40,000
(ii) Purchased Goods – ₹ 20,000
(iii) Sold Goods – ₹ 24,000
(iv) Paid Rent – ₹ 400
(v) Paid salaries – ₹ 600
(vi) Drew for personal use – ₹ 1,000
Ans: This question is as follows:
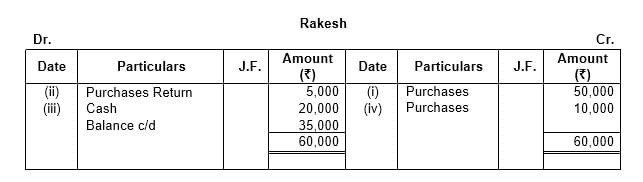
Q9: Open a ‘T’ shape account of creditor, Rakesh and write the following transactions on the proper side:
(i) Goods purchased from Rakesh on credit – ₹ 50,000
(ii) Goods returned to Rakesh for – ₹ 5,000
(iii) Paid to Rakesh – ₹ 20,000
(iv) Purchase goods from Rakesh on credit – ₹ 10,000
Ans: This question is as follows:
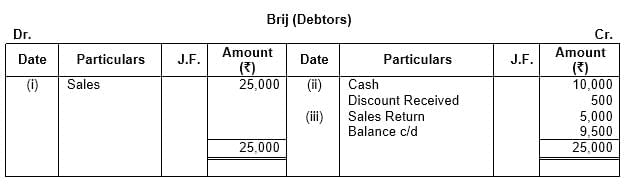
Q10: Open a ‘T’ shape account of debtor ‘Brij’ and write the following transactions on the proper side:
(i) Sold goods to Brij on credit – ₹ 25,000
(ii) Cash received from Brij – ₹ 10,000 Discount allowed to him – ₹ 500
(iii) Goods returned by Brij – ₹ 5,000
Ans: This question is as follows:
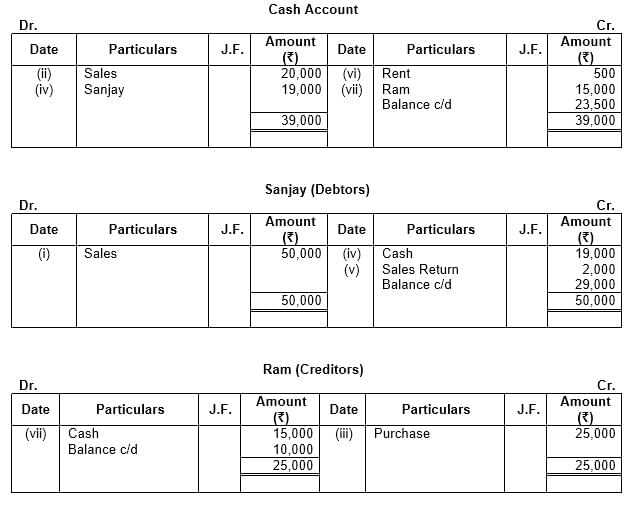
Q11: Put the following on the proper side of a Cash Account, a Debtor’s Account and a Creditor’s Account:
(i) Sold goods to Sanjay on credit – ₹ 50,000
(ii) Sold goods to Mohan for cash – ₹ 20,000
(iii) Purchased goods from Ram on credit – ₹ 25,000
(iv) Cash received from Sanjay – ₹ 19,000
(v) Goods returned by Sanjay – ₹ 2,000
(vi) Paid rent – ₹ 500
(vii) Cash paid to Ram – ₹ 15,000
Ans: This question is as follows:
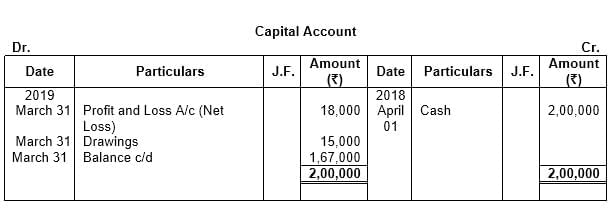
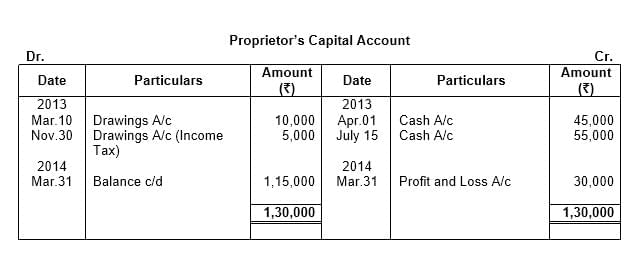
Q12: From the following particulars, prepare the proprietor’s Capital Account:
₹
1st April, 2018 − Commenced business with cash 2,00,000
31st March, 2019 − Net Loss as per Profit and Loss Account 18,000
31st March, 2019 − Drawings during the period 15,000
Balance the same and explain what the closing balance indicates.
Ans: This question is as follows:
Q13: From the following particulars, prepare the proprietor’s Capital Account: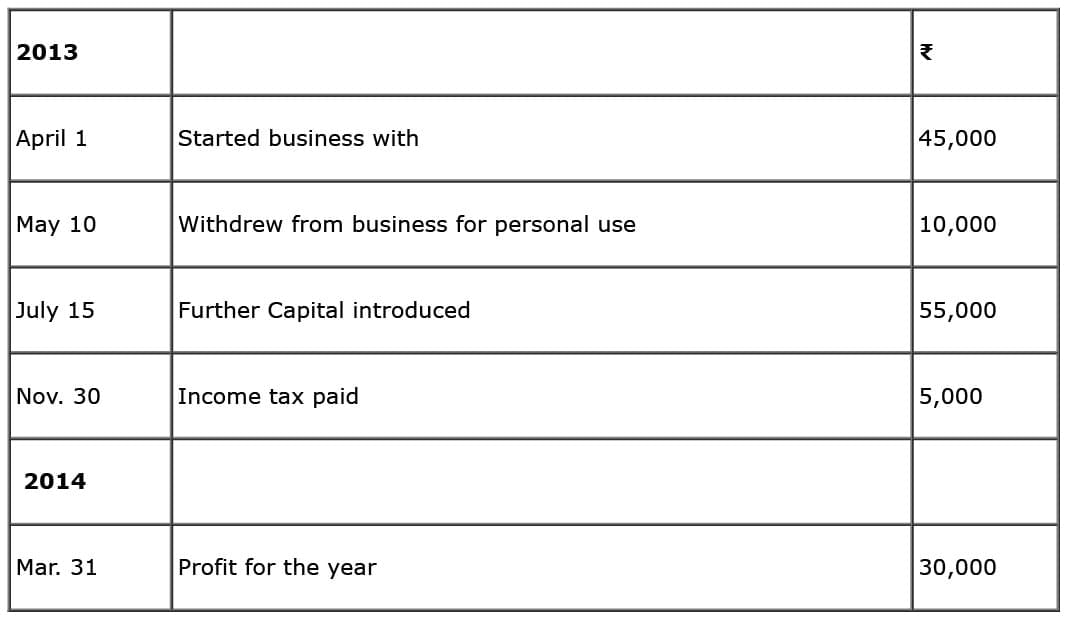
Ans: This question is as follows:
|
61 videos|154 docs|35 tests
|
FAQs on Accounting Procedures Rules of Debit & Credit - Accountancy Class 11 - Commerce
| 1. What are the basic rules of debit and credit in accounting? |  |
| 2. How do debits and credits affect financial statements? |  |
| 3. Can you explain the importance of the double-entry bookkeeping system? |  |
| 4. How do you determine which account to debit or credit in a transaction? |  |
| 5. What are some common examples of transactions and their corresponding debits and credits? |  |